Utilities, Utilities reference, Fio-attach – HP IO Accelerator for BladeSystem c-Class User Manual
Page 22
Utilities 22
Utilities
Utilities reference
The IO Accelerator installation packages include various command line utilities, installed by default to the
/usr/bin file. These utilities provide a number of ways to access, test, and manipulate your device.
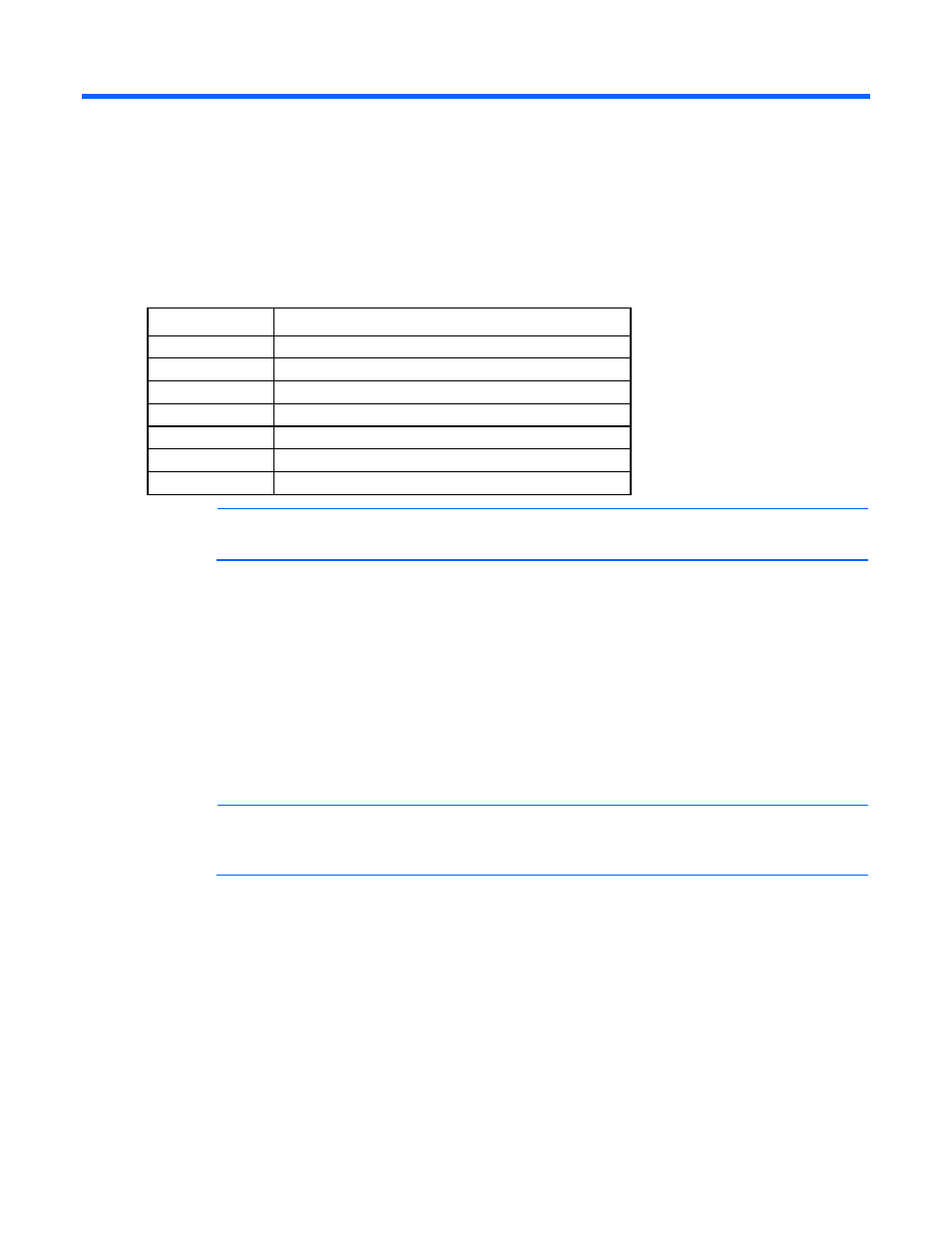
Utility
Purpose
fio-attach
Makes an IO Accelerator available to the OS
fio-beacon
Lights the IO Accelerator external LEDs
fio-bugreport
Prepares a detailed report for use in troubleshooting issues
fio-detach
Temporarily removes an IO Accelerator from OS access
fio-format
Used to perform a low-level format of an IO Accelerator
fio-status
Displays information about the device
fio-update-iodrive Updates the IO Accelerator firmware
NOTE:
All utilities have –h (Help) and –v (Version) options.
To set IO Accelerator VSL parameters, edit the iomemory-vsl.conf file:
(/usr/kernel/drv/iomemory-vsl.conf)
fio-attach
Description
Attaches the IO Accelerator device and makes it available to the operating system. This creates a block
device in /dev named fiox (where x is a, b, c, and so on). Then, you might partition or format the IO
Accelerator device, or set it up as part of a RAID array. The command displays a progress bar and
percentage as it operates.
NOTE:
In most cases, the IO Accelerator automatically attaches the device on load and does a
scan. You only have to run fio-attach if you ran fio-detach or if you set the IO Accelerator
auto_attach parameter to 0.
Syntax
fio-attach
where
2, and so on. For example, /dev/fct0 indicates the first IO Accelerator device installed on the system.
You can specify multiple IO Accelerator devices. For example, /dev/fct1 /dev/fct2 indicates the
second and third IO Accelerator devices installed on the system. You can also use a wildcard to indicate all
IO Accelerator devices on the system.
For example, /dev/fct*
