Dwyer PDWS User Manual
Page 5
Page 8
Page 9
MaiNteNaNce
Sensor Replacement.
It is very unusual for a sensor to re-
quire replacement in normal use. The primary cause of sensor
failure is overvoltage (inadvertent connection of high voltage,
for example) or incorrect polarity on hookup. The sensor is
replaced by removing the strain relief, then threading out
the sensor retainer plug. Remove the entire sensor capsule
by pulling on the cable. The new sensor capsule can then be
installed. Replace the retainer plug, and then replace and
tighten the strain relief.
Rotor Replacement.
It is unusual for a rotor to require re-
placement due to damage sustained in normal service. More
commonly, the meter is dropped while it is out of the pipe.
Another reason for rotor replacement is shaft wear after long
service. Rotors are easily field-replaced.
To install a rotor, follow these steps:
1. Unscrew the threaded bearing housings to expose
the shaft ends. If bearings are being replaced,
back them completely out.
2. Remove the rotor. Put the new rotor in its place.
3. Thread in one bearing housing part way, then the
other. Take care to start the end of the shaft into
the bearing hole before tightening further.
4. Screw in bearing housings until they bottom.
Note: Do not use excessive force.
5. Check for free spin. Blowing lightly on the rotor
should result in it spinning rapidly and coasting to a
smooth stop.
caution:
Never remove the u-clip retainer
when the pipe is under pressure. Always
remove pressure from the pipe before at-
tempting to remove the meter. Removal
under pressure may result in damage or
serious injury.
Signal troubleshooting.
The flow sensor has only one mov-
ing part, the rotor. If this is turning properly and there is no
signal, the magnetic sensor is not operating properly. To check
the signal, apply 12 Vdc power to the red (+) and black (-)
leads. Set a multimeter to voltage reading. Put the positive
multimeter lead on the red wire and the negative lead on the
white wire. Slowly turn the rotor. Voltage reading should swing
between -12 Volts and 0 Volts as the rotor turns. If it does
not, the solid-state magnetic sensor is not working properly.
Checking for continuity is not a useful test of these sensors.
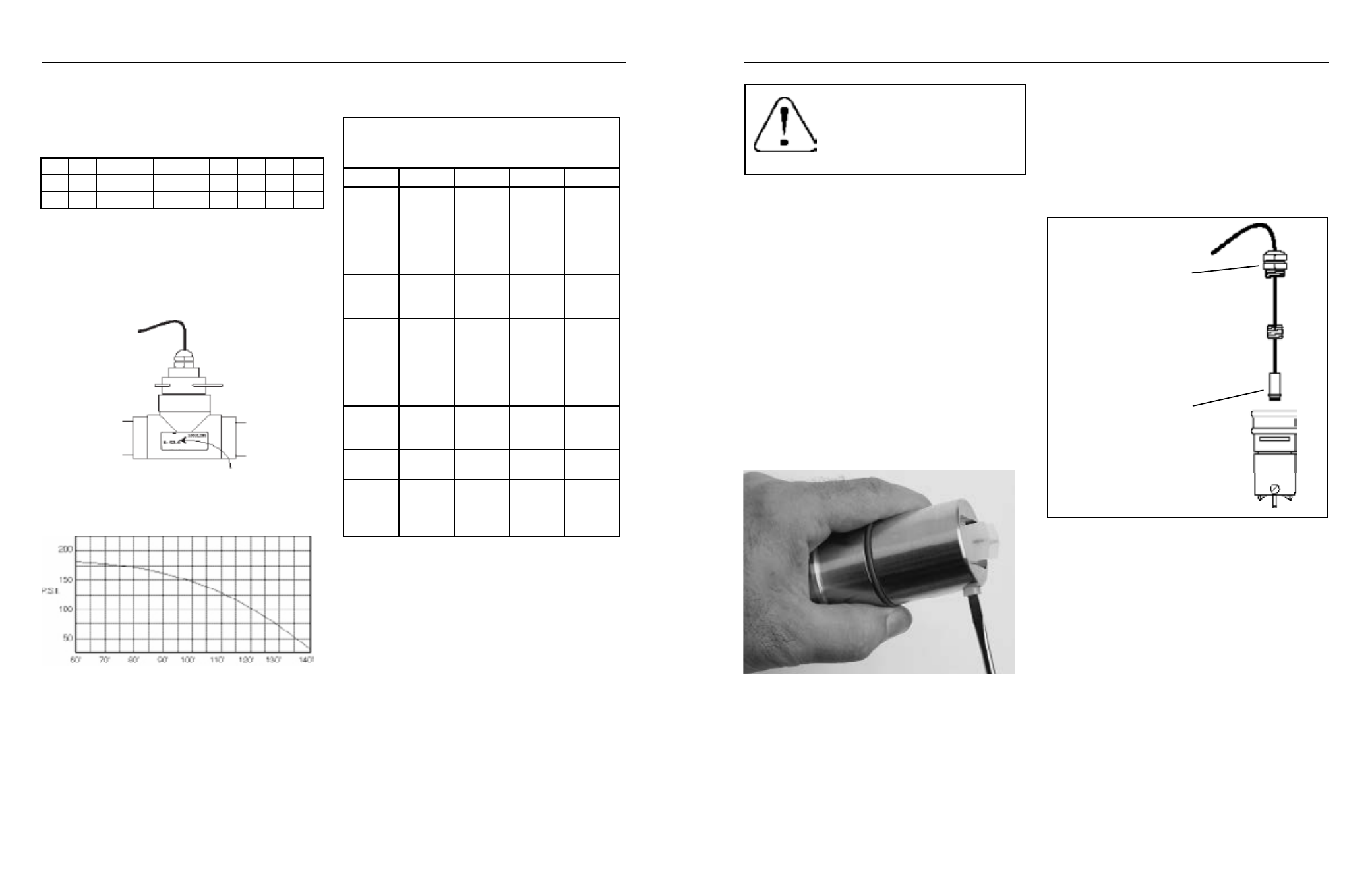
Sensor Replacement
1) Loosen and unthread
Strain Relief
2) Remove Sensor Retainer
Plug by inserting a
screwdriver blade into
one side of the slot and
turning
3) Remove the Sensor
Capsule by pulling on
the cable
4) Reverse the process
to replace
Minimum Flow.
As with any other flow sensor, there is a rate
below which the Series PDWS sensor cannot read. Check the
flow rate table below for the minimum flow rate detectable by
the sensor for a given pipe size.
calibration (“K-factor”).
The K-factor represents the number of
pulses per gallon the meter produces during a flow test. This
number must be entered into your electronic control to make
it read properly. If the PDWS Series meter is ordered with a
tee fitting
, it is factory-calibrated in the Series PWF fitting and
the K-factor is indicated on the side (see below).
Find Your K-Factor here
Field calibration.
It is possible to field-calibrate a Series
PDWS flow sensor to determine an accurate K-factor in the
actual installation. The reason for doing this would be to
compensate for an unusual condition, for instance, applica-
tions with higher viscosity fluid (PDWS meters are calibrated
for water use) or which lack adequate straight pipe ahead of
the meter.
If a saddle or weld-type fitting has been ordered, see the
table below to determine the proper K-factor.
Flow Range (GPM)
1/2" 3/4" 1" 1-1/2" 2" 3" 4" 6" 8"
Min
0.28 0.5 0.8 1.9 3.1 6.9
12
27 46.8
Max
28
50
80 190 314 691 1190 2700 4680
OPeRatiON
PReSSuRe VS. teMPeRatuRe (PVc/Polypropylene)
PDWS SeRieS K-FactORS
FOR SaDDle & WelDOlet FittiNGS
3"
4"
6"
8"
PVc/
Steel
Sch. 40
28.92
16.790
7.412
4.275
PVc/
Steel
Sch. 80
32.368
18.591
8.215
4.684
Stainless
Steel
(10S)
25.614
14.996
6.747
3.926
Stainless
Steel
(10S)
28.920
16.790
7.412
4.275
copper
tubing
(type l)
31.386
17.847
7.981
4.563
copper
tubing
(type K)
32.212
18.294
8.272
4.736
brass
Pipe
29.033
17.009
7.268
4.254
Duct.
iron
(class
52)
23.548
15.282
6.913
3.485
˚F
