Bits of resolution, Resolution, Accuracy – Nematron OptiLogic Series User Manual
Page 12: Range, Multiplexing
Optimation, Inc.
(256)883-3050
12
OptiLogic Series
Resolution
Resolution is the number of significant
bits of information the A/D converter uses to
express the value of the measured input. A
12-bit A/D converter uses 12 bits of information,
meaning the entire range is covered by a number
between 0 and (2
(12)
-1) or 0 to 4095. A 14-bit
A/D expresses the same range as a number
between 0 and 16,383. In other words, the more
bits used, the finer the increment. In general
terms, the higher the resolution, the better.
Accuracy
Accuracy is expressed as the worst case
deviation from the
“ideal value” across the entire
input range. For example, for a 0 to 5V input
range and a 12-bit A/D module, a 2.0 volt input
should yield a value equal to 1638 (0.4 x 4096).
If it returns a value of 1636, and this is the worst
case error across the entire range of 0 to 5V, the
accuracy is 12 bits +/- 2 counts.
Range
The analog input range is the minimum
and maximum voltage, or current level,
measured by the A/C converter. Typical ranges
are 0 to 5 volts, 0 to 10 volts, +/- 5 volts, +/- 10
volts, and 4 to 20 mA.
You should try to match the input range
to the range of the signal that you are measuring.
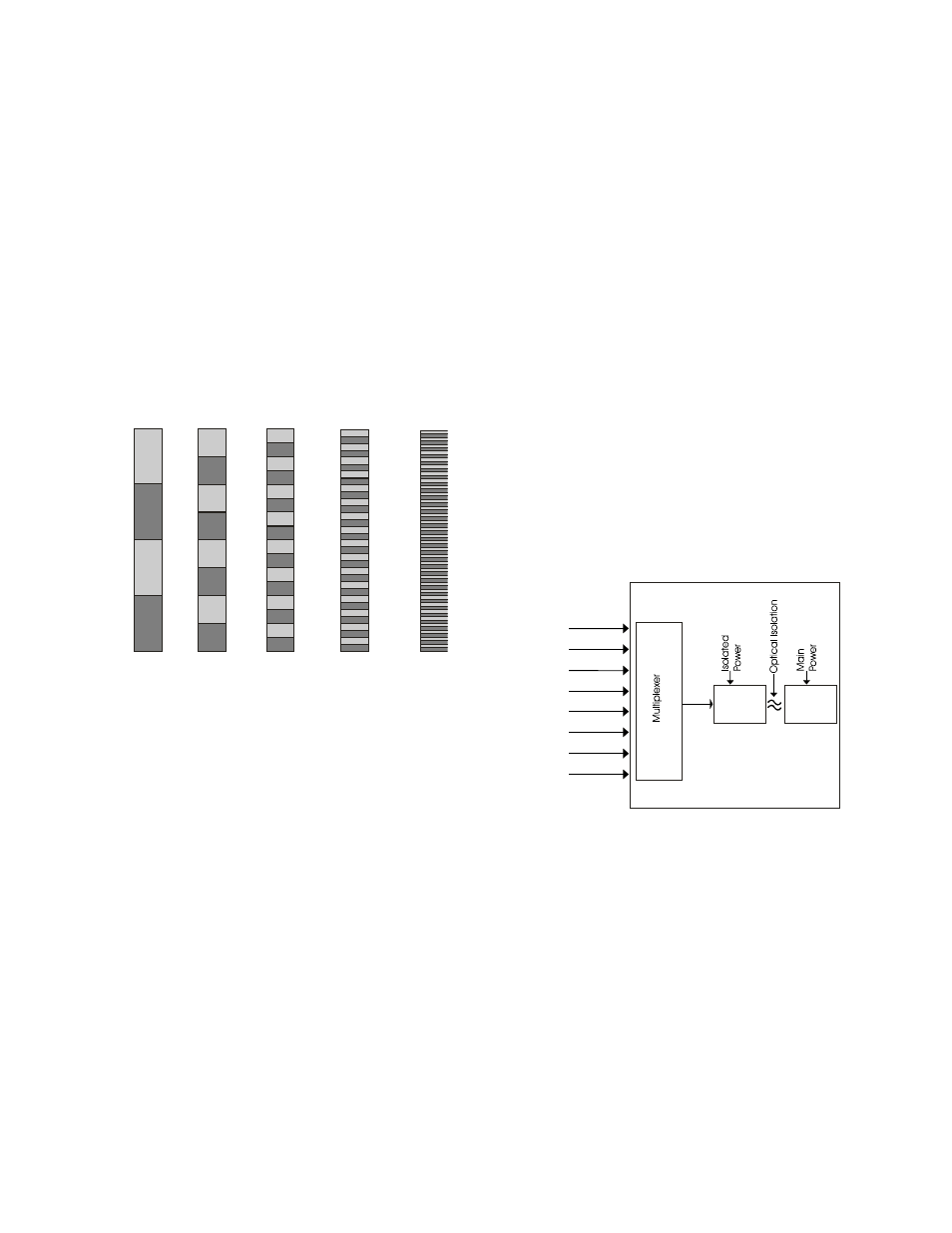
Multiplexing
Analog to digital converter devices are
typically quite expensive. In order to keep the
cost per channel of analog inputs down, a
multiplexer is commonly used.
A multiplexer switches one analog input
at a time into the A/D converter. Each input is
converted in sequence. The trade off is reduced
sampling rate for a particular channel versus
reduced cost per channel measured. In most
industrial applications, the conversion rate is so
fast in relation to the rate of change in the
measured value, that sampling rate is not a
factor.
2
3
4
5
6
Bits of Resolution
Analog
inputs
Converter Module
A/D
Converter
Bus
Interface
