Transistor outputs npn transistor sinking outputs, Solid state relay outputs – Nematron OptiLogic Series User Manual
Page 10
Optimation, Inc.
(256)883-3050
10
OptiLogic Series
Transistor Outputs
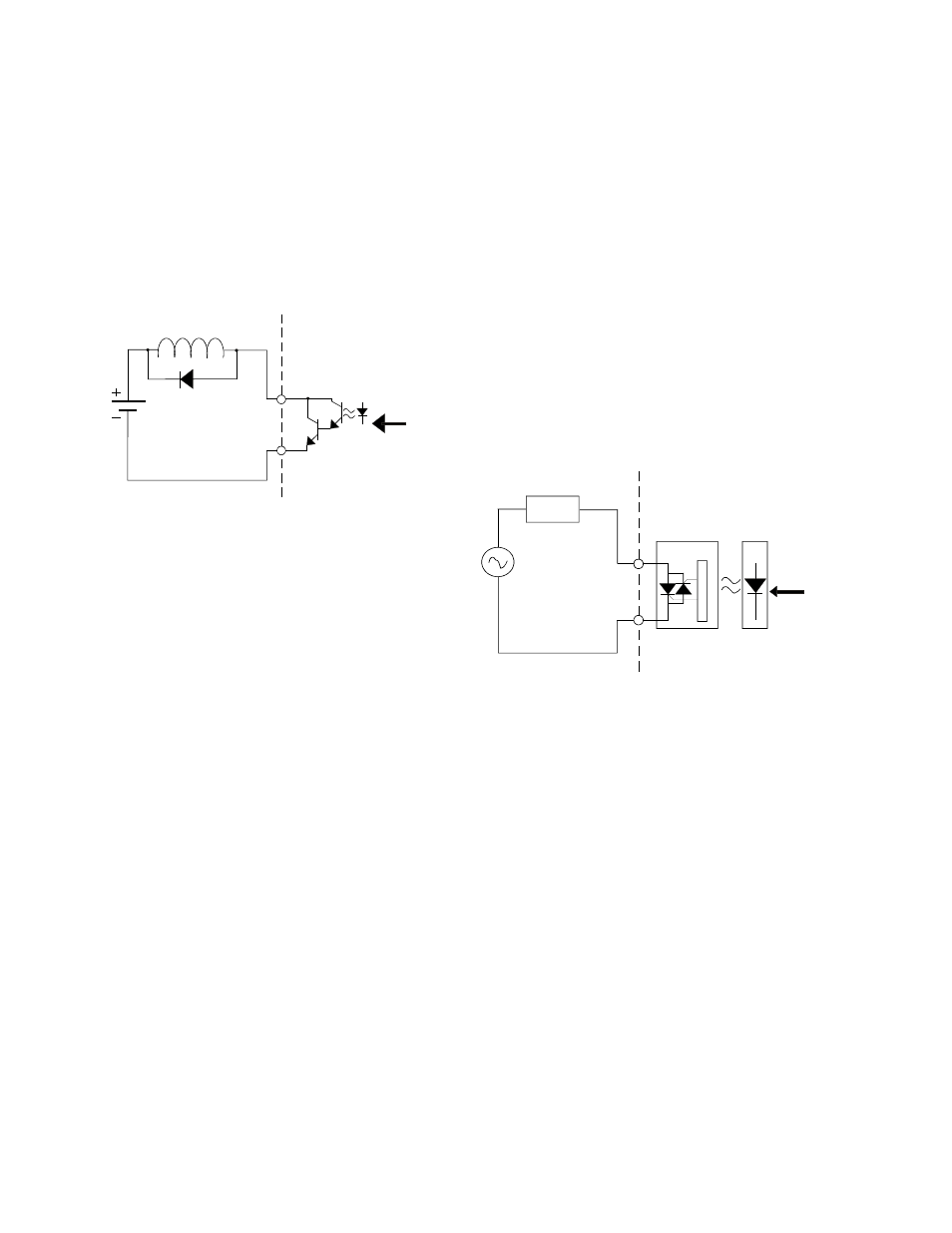
NPN Transistor Sinking Outputs
An NPN transistor sinking output
provides a path to ground. A typical circuit is
shown below.
There is a small voltage drop across the
transistor in such a circuit. The voltage drop will
generate heat in the transistor. Therefore NPN
transistor outputs are generally limited to lower
current applications.
Transistor outputs can be operated at
high frequency. There is no effective wear on a
transistor output from switching, as there is in a
mechanical relay.
Diode protection applied to inductive
loads is recommended in cases where the load
current approaches the rated current limit of the
output. In most cases OptiLogic outputs are
designed to withstand voltages of at least twice
the rated output voltage. However, diode
protection like that shown above will ensure that
turn off voltage spikes will never get to that
level.
Solid State Relay Outputs
Solid state relays are semiconductor
switches that operate very much like mechanical
relays. They have an advantage over mechanical
relays by virtue of the fact that they are
semiconductors. Solid state relays can be
switched at relatively high frequencies and they
do not wear out. However they are more
expensive and there is a small voltage drop
across the contact.
The figure below illustrates a typical
solid state relay output. OptiLogic Solid state
relays are designed for AC load operation.
Output module
isolation
optical
From
OptiLogic
processor
Inductive load
Diode protection
Output module
optical
isolation
load
From
OptiLogic
processor
