Eess, Ending edge shift sigma, Description – Teledyne LeCroy AORM - Advanced Optical Recording Measurements User Manual
Page 44
42
ISSUED:
June 2013
923133 Rev A
EESS
ENDING EDGE SHIFT SIGMA
Description
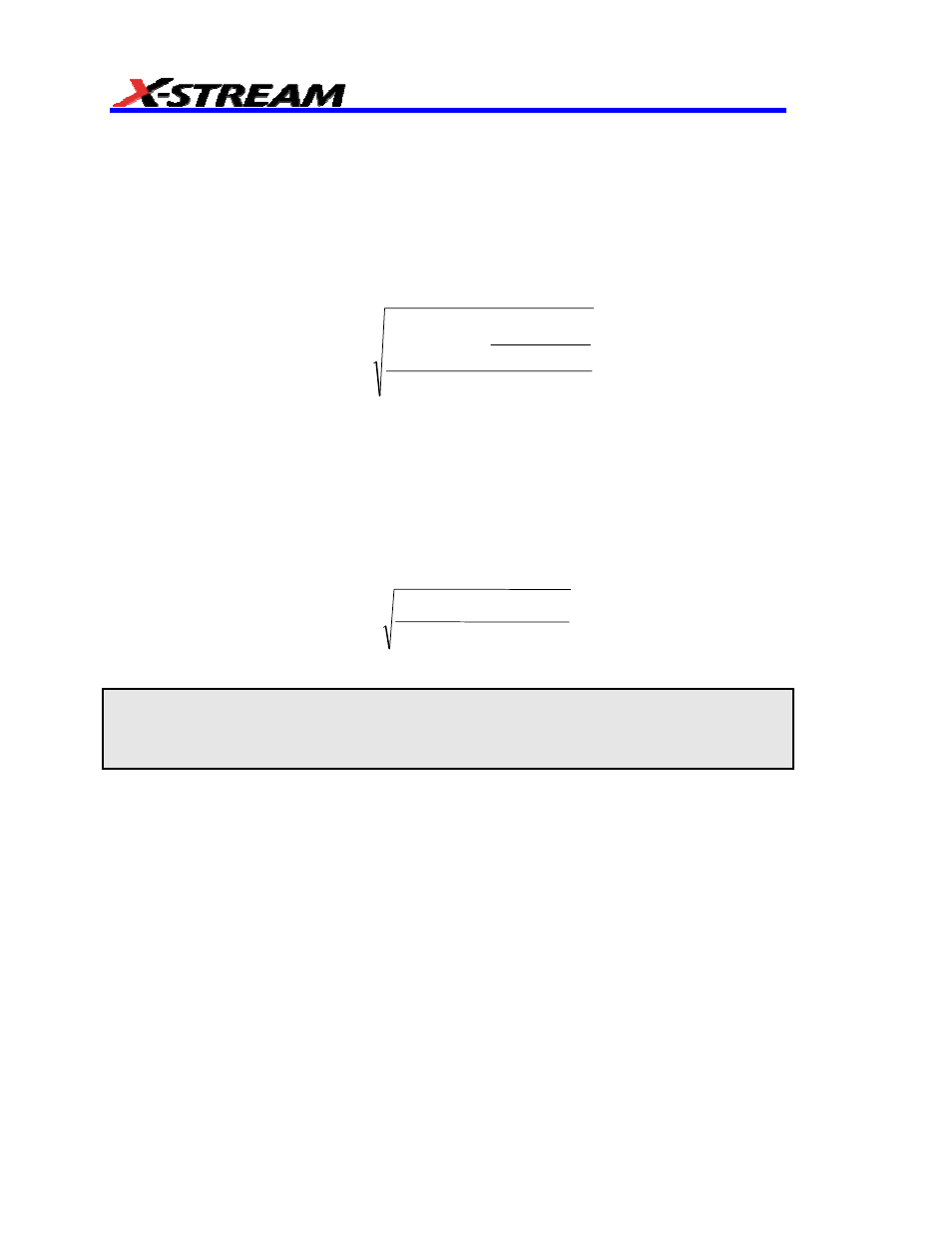
EESS
provides a measurement of the mean, normalized standard deviation of the Ending Edge
Shift measurements (see EES). When a single n is specified, or when you are in ‘nT Table’ Show
mode, the value calculated for the n
th
index is calculated using the following equation for standard
deviation:
Ending Edge Shift Sigma cannot be calculated for a given index n unless there are at least two
Ending Edge Shift values calculated for that n index.
When Ending Edge Shift is configured as a custom parameter with a range of n, the value
calculated is the standard deviation of the distribution that results by normalizing each
independent distribution categorized by the space (pit) nT following the subject pit (space).
Distributions are normalized by subtracting the mean of the distribution from all of the elements in
the distribution. This results in the following equation for overall Ending Edge Shift Sigma
resulting from the individually categorized Ending Edge Shift Sigma values:
Note: The value calculated by EESS will generally not be the same as the sigma of EES measurement when a range of
n
is used and statistics are on. This is because the two measurements are not the same. The EESS measurement
normalizes the results for each n by subtracting the mean EES from each EES in the n
th
distribution. This results in a
superposition of mean-centered distributions, not a superposition of 0-centered distributions contributing to EES
measurements. EESS will always be less than or equal to the standard deviation of EES measurements.
(
)
(
)
EESS
EESS
EES
EES
N
N
n
n
n
n
n
n
1
2
2
=
=
−
−
∑
∑
σ
EES
n
(
)
(
)
EESS
EESS
N
N
overall
n
n
n
1
1
2
=
⋅
−
−
∑
∑
