Figure 29 – linear torque mode, Figure 30 – non-linear torque mode – KB Electronics KBRC-240D User Manual
Page 18
C. The hi-pot test voltage should be set in accordance to the testing agency standards and
the leakage current should be set as low as possible without causing nuisance trips.
D. To eliminate motor speed control damage due to auxiliary equipment hi-pot failure, it is
also recommended that all signal inputs be wired together and connected to the AC input
lines as shown.
VI. OPERATION
After the KBRC-240D has been properly setup (jumpers set to desired positions and wiring
completed), the startup procedure can begin. If AC power has been properly brought to the
control, the ON and STOP LEDs will be illuminated. Before starting, be sure that the Main
Speed Potentiometer is set to the zero speed position. To start the control, momentarily set
the Start/Stop Switch to the “START” position. The STOP LED should no longer illuminate.
The motor should begin to run as the Main Speed Potentiometer is rotated.
Note: If the motor runs in the incorrect direction, it will be necessary to disconnect the AC
line, reverse the motor leads and repeat the startup procedure.
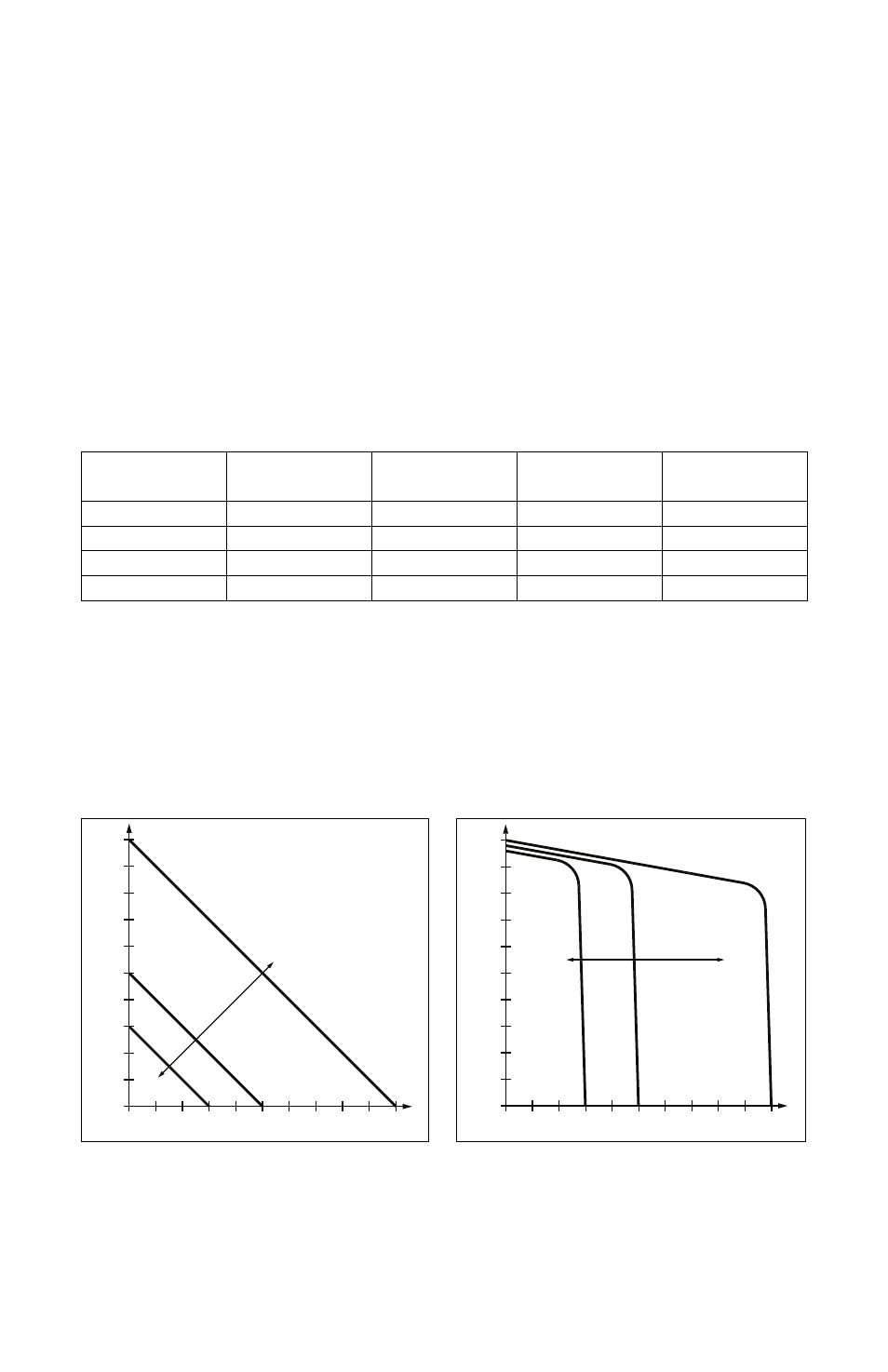
Linear Torque Mode:
In Linear Torque mode (Jumper J7 set to the “S/L” position), speed and torque vary linearly
as a function of Main Speed Potentiometer rotation or input signal. See Figure 29.
Non-Linear Torque Mode:
In Non-Linear Torque mode (Jumper J7 set to the “NL” position), the torque is varied by the
Main Speed Potentiometer or input signal, and remains constant throughout the motor’s
entire speed range. See Figure 30.
VII. AC LINE FUSING
The KBRC-240D does not contain AC line fuses. Most electrical codes require that each
ungrounded conductor contain circuit protection. It is recommended to install a 20 Amp fuse
(Littelfuse 326, BUSS ABC or equivalent) or a circuit breaker in series with each unground-
ed conductor. Check all electrical codes that apply to the application.
18
TABLE 7 – CONTROL OPERATION
HIGHER
LOWER
TORQUE
SETTING
SETTING
100
90
80
TORQUE
70
60
50
40
20
30
P
E
R
C
E
N
T
O
F
B
A
S
E
S
P
E
E
D
100
90
80
70
50
60
PERCENT OF TORQUE
40
30
20
10
10
0
0
FIGURE 29 – LINEAR TORQUE MODE
SETTING
TORQUE
LOWER
SETTING
TORQUE
HIGHER
PERCENT OF TORQUE
100
90
80
70
50
60
40
30
20
10
P
E
R
C
E
N
T
O
F
B
A
S
E
S
P
E
E
D
100
80
70
90
40
60
50
10
20
30
0
0
FIGURE 30 – NON-LINEAR TORQUE MODE
Quadrant
Type of Operation
Motor Rotation
Direction
Motor Torque
Direction
Load Torque
Direction
I
Motoring
CW
CW
CCW
II
Regeneration
CCW
CW
CCW
III
Motoring
CCW
CCW
CW
IV
Regeneration
CW
CCW
CW
