Experiment 2: dispersion, Procedure, Sin incidence – PASCO OS-8536 OPTICS TABLE User Manual
Page 9: Sin refraction, Equipment needed
5
012-06557A
Optics Table
Experiment 2: Dispersion
EQUIPMENT NEEDED
– Cylindrical Lens
– Ray Table
– Ray Table Base
– Optics Bench
– Light Source
– white paper
POWER SUPPL
Y JACK
12V @ 800mA
OS-8517
LIGHT
SOURCE
CO
LO
R
TO REPLACE BULB SEE
INSTR
UCTION MANUAL.
BULB
: 12V
10W G-4
DO NOT
TO
UCH BULB
WI
TH
FINGERS.
DISCONNECT
PO
WE
R
BEFORE CHAN
GING BULB
.
TO REMOVE LIGHT
SOURCE
GENTL
Y SPREAD BRACKET
.
5
3
1
RA
Y
SL
IT
S
BASIC OPTICS
PA
SC
O
scientific
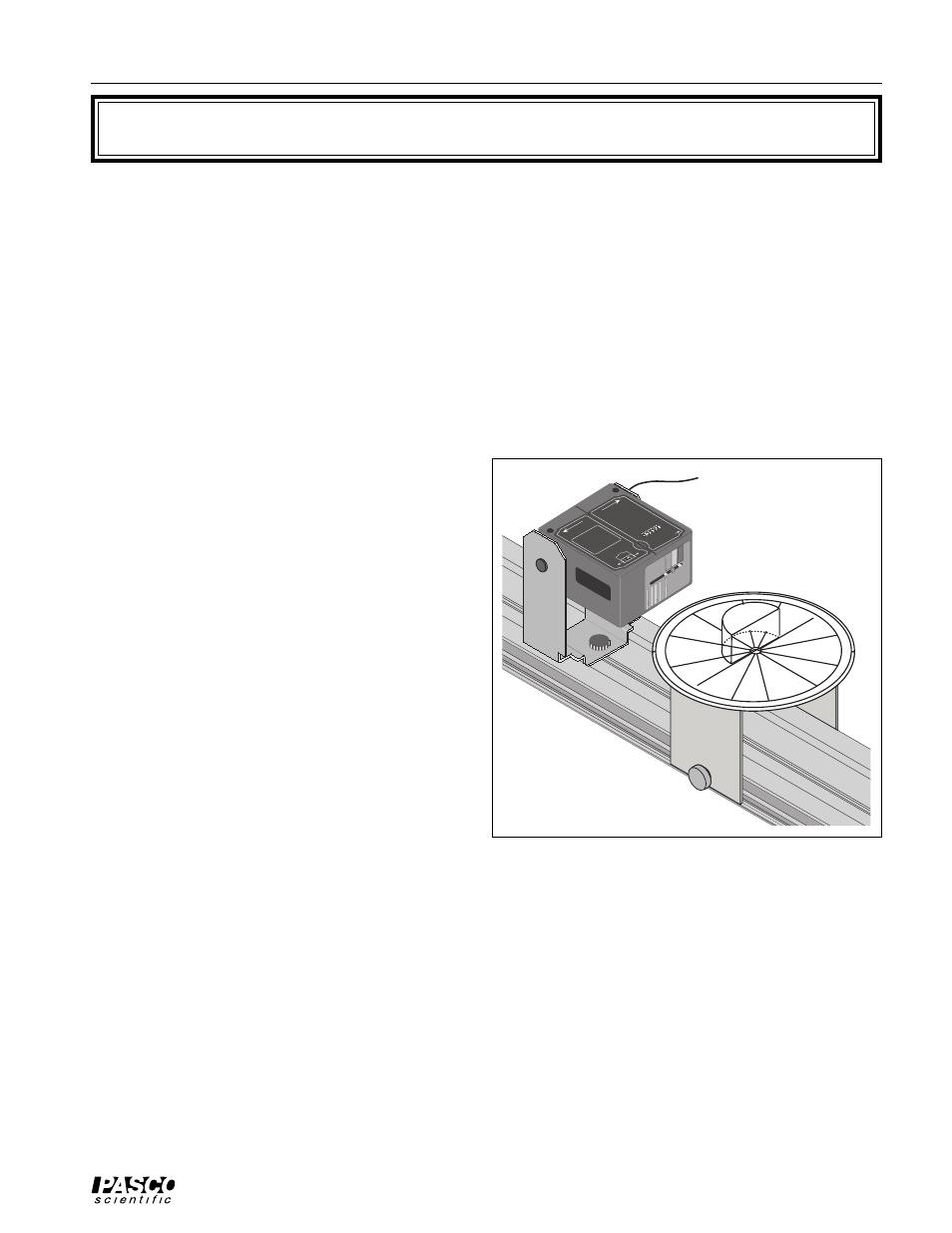
Figure 2.1
Procedure
Mount the Ray Table Base, Ray Table, Cylindrical Lens, and the Light Source on the Optics Bench.
1. Put the Ray Table on the base with the polar grid (DEGREE SCALE) facing up. Turn the Ray Table so the
0 (zero) degree line (NORMAL) points to the Light Source.
2. Set up the equipment as shown in Figure 2.1.
Adjust the slit mask on the Light Source so a
single light ray is incident on the curved sur-
face of the Cylindrical Lens.
Record data
Set the Ray Table so the angle of incidence of the
single ray striking the flat surface of the lens
(from inside the lens) is zero-degrees. Hold a
piece of white paper against the edge of the Ray
Table so the refracted ray is visible on the piece
of paper.
Slowly rotate the Ray Table to increase the angle
of incidence. As you do, watch the refracted ray
on the piece of paper.
1. At what angle of refraction do you begin to no-
tice color separation in the refracted ray?
_____________________________________________________________________________.
2. At what angle of refraction is the color separation
a maximum?
_____________________________________________________________________________..
3. What colors are present in the refracted ray? (Write them in the order of minimum to maximum angle of refrac-
tion.)
4. Measure the index of refraction of acrylic for red and blue light:
(Remember, n
air
sin Incidence
air
= n
acrylic
sin Refraction
acrylic
)
Note: The index of refraction of a given material is usually expressed as a constant. However, different colors
of light refract to slightly different angles, and therefore have slightly different indices of refraction.
n
red
=
__________________
n
blue
=
_________________
