PASCO OS-8501 Interferometer User Manual
Page 16
scientific
Interferometer
012-02675B
12
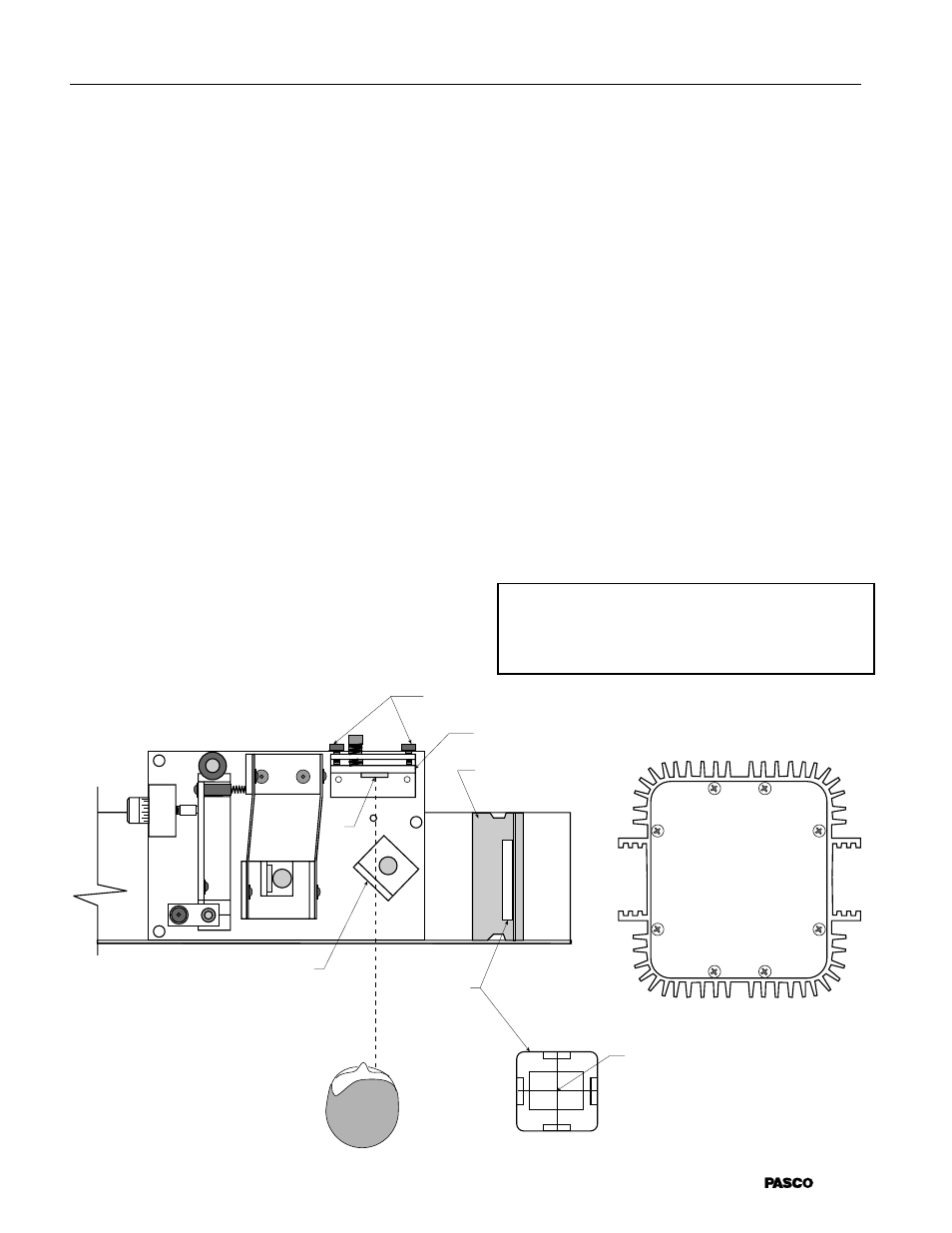
M1 ALIGNMENT SCREWS
M1 ALIGNMENT BRACKET
BEAM SPLITTER
LENS HOLDER
DIFFUSER
THIN WIRE
OR THREAD
SPECTRAL LIGHT
SOURCE
MODEL OS-9287
LOW PRESSURE SODIUM
M1
FIGURE 10 USING A SPECTRAL LIGHT SOURCE
Inteferometry with a Spectral Light Source
Although the Michelson Interferometer works best
with a laser light source, interferometry measurements
can be successfully made using any monochromatic
source of sufficient brightness. However, unless a
laser is used, it is generally not possible to project the
interference fringes onto a screen. The fringes are
viewed, instead, by looking into the beam-splitter.
A spectral light source such as the PASCO Model OS-
9287 Low Pressure Sodium Light Source works well
for this application. In addition to the spectral light
source, a diffuser is needed, such as PASCO Model
OS-9120.
To use the interferometer with a spectral or other
monochromatic light source:
➀
Tape two thin pieces of wire or thread to the sur-
face of the diffuser to form cross-hairs.
➁
Set up the equipment as shown below, and turn on
the light source. The light source should be on a
level with the interferometer mirrors.
➂
Adjust the alignment screws on the Fixed Mirror
(M
1
) until the front and back plates of the align-
ment bracket for M
1
are approximately parallel.
While looking through the beam-splitter toward
M
1
, adjust the rotation of the beam-splitter until
you see an image of the cross-hairs reflected from
M
1
.
➄
Now adjust the rotation of the Movable Mirror (M
2
)
until you see a second image of the cross-hairs.
Adjust the alignment screws on M
1
until the two
cross-hair images are superimposed. The interfer-
ence fringes should now be visible when looking
through the beam-splitter at M
1
.
➦
NOTE: If you are using a spectral light
source with spectral lines at several different
wavelengths, it may be necessary to use a filter
that blocks all but one of the spectral wave-
lengths.
➃
