PASCO PK-9023 EQUIPOTENTIAL AND FIELD MAPPER User Manual
Page 7
scientific
3
012-04346B
4.
Connect the electrodes to a battery, DC power supply,
or any other potential source in the 5 to 20 VDC range
using the supplied connecting wires. (see Figure 4) The
potential source should be capable of supplying 25 mA.
(If possible, the potential should be equal to the full
scale reading of the electronic voltmeter used in the
experiment.)
5.
To check the electrodes for proper conductivity connect
one voltmeter lead near the push pin on an electrode.
Touch the voltmeter’s second lead to other points on the
same electrode. If the electrode has been properly
drawn, the maximum potential between any two points
on the same electrode will not exceed 1% of the
potential applied between the two electrodes.
NOTE: This test can only be made if the potential
source is connected across the two electrodes.
If the voltage across the same electrode is greater than
1% of the voltage applied between the two electrodes,
then remove the paper from the corkboard and draw
over the electrodes a second time with the conductive
ink.
6.
Equipotentials are plotted by connecting one lead of the
voltmeter (the ground) to one of the electrode push pins.
This electrode now becomes the reference. The other
voltmeter lead (the probe) is used to measure the
potential at any point on the paper simply by touching
the probe to the paper at that point.
To map an equipotential, move the probe until the
desired potential is indicated on the voltmeter. Mark the
paper at this point with a soft lead or light-colored lead
pencil. Continue to move the probe, but only in a
direction which maintains the voltmeter at the same
reading. Continue to mark these points. Connecting the
points produces an equipotential line.
7.
To plot field gradients (field lines), neither lead of the
voltmeter is connected to an electrode. Instead, the two
leads of the voltmeter will be placed on the conductive
paper side-by-side at a set distance of separation (one
centimeter is a useful separation to use). It is best to tape
the two leads of the voltmeter together for this proce-
dure (see Figure 7). The technique is to use the voltme-
ter leads to find the direction from an electrode that
follows the path of greatest potential difference from
point-to-point.
NOTE: Do Not attempt to make measurements by
placing the leads on the grid marks on the conduc-
tive paper. Touch the voltmeter leads only on the
solid black areas of the paper. It may be necessary
to use a higher voltmeter sensitivity for this
measurement than was used in measuring
equipotentials.
To plot the field lines on the conductive paper, place the
voltmeter lead connected to ground near one of the
dipoles. Place the other voltmeter lead on the paper and
note the voltmeter reading. Now pivot the lead to
several new positions while keeping the ground lead
stationary (see Figure 7). Note the voltmeter readings as
you touch the lead at each new spot on the paper. When
the potential is the highest, draw an arrow on the paper
from the ground lead to the other lead (see Figure 8).
Then move the ground lead to the tip (head) of the
M
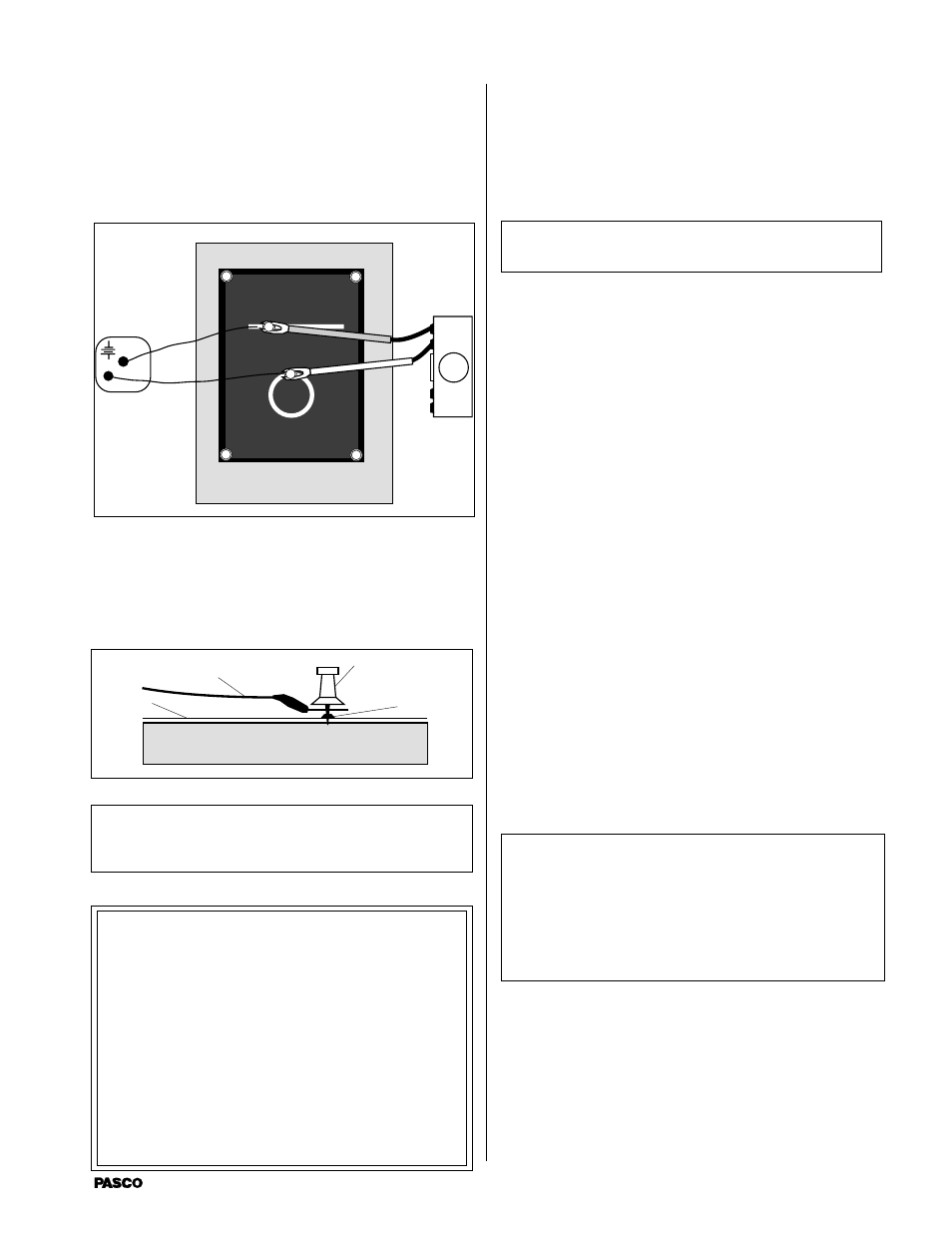
Figure 4
Meter
DC Power
supply
a. Place the terminal of a connecting wire over the
electrode, then stick a metal push pin through its
terminal and the electrode into the corkboard.
Make certain that the pin holds the terminal firmly
to the electrode. (see Figure 5).
Push pin
Connecting
wire
Paper
Electrode
Figure 5
NOTE: Check that the surface of the terminal
which touches the electrode is clean. A dirty path
may result in a bad contact.
Connect the other end of the wire to the battery.
THE ELECTRONIC VOLTMETER
Two specifications which a voltmeter must meet in
order to be used with the PASCO scientific Field
Mapper are
• first, an input impedance of 10 M
Ω
or higher
• second, a full scale range which is equal to or higher
than the potential used across the electrodes.
Any commercial electronic voltmeter, either digital
or analog, that meets these specifications is ad-
equate. The PASCO ES-9054B Electrometer or the
SE-9589 Handheld Digital Multimeter are recom-
mended.
