PASCO TD-8561 THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY APPARATUS User Manual
Page 8
4
Thermal Conductivity Apparatus
012-03349D
h
d
1
d
2
t
a
m
wa
t
m
w
d
avg
A
R
a
R
R
0
(R
0
) (80 cal/gm) (h)
(A) (
∆
T);
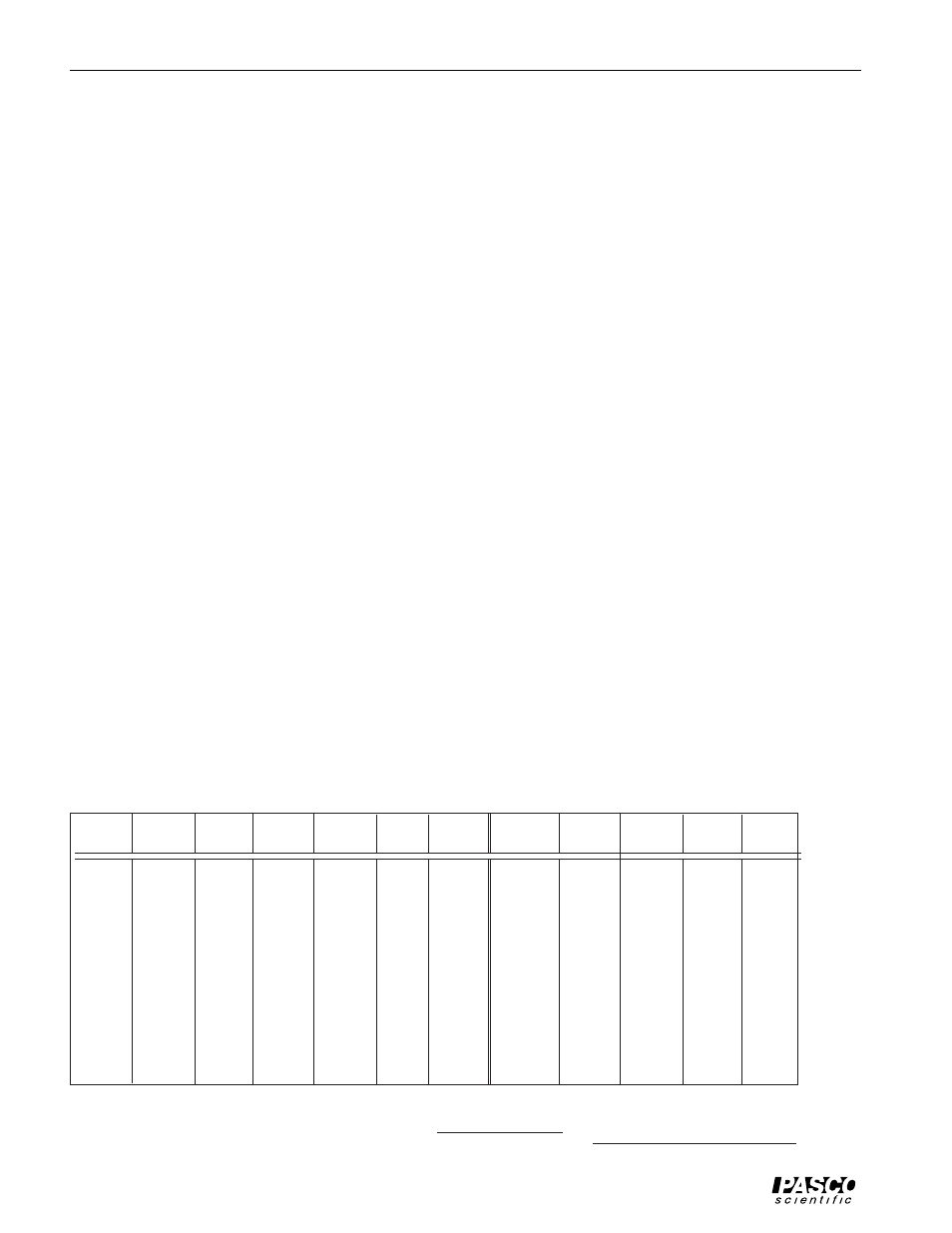
Data and Calculations Table
Let the ice sit for several minutes so it begins to melt and comes in full contact with the sample. (Don't
begin taking data before the ice begins to melt, because it may be at a lower temperature than 0
°
C.)
Obtain data for determining the ambient melting rate of the ice, as follows:
a. Determine the mass of a small container used for collecting the melted ice and record it.
b. Collect the melting ice in the container for a measured time t
a
(approximately 10 minutes).
c. Determine the mass of the container plus water and record it.
d. Subtract your first measured mass from your second to determine m
wa
, the mass of the melted ice.
➇ Run steam into the steam chamber. Let the steam run for several minutes until temperatures stablize so
that the heat flow is steady. (Place a container under the drain spout of the steam chamber to collect the
water that escapes from the chamber.)
➈ Empty the cup used for collecting the melted ice. Repeat step 7, but this time with the steam running
into the steam chamber. As before, measure and record m
w
, the mass of the melted ice, and t, the time
during which the ice melted (5-10 minutes).
➉ Remeasure the diameter of the ice block and record the value as d
2
.
DATA AND CALCULATIONS
➀ Take the average of d
1
and d
2
to determine d
avg
, the average diameter of the ice during the experiment.
➁ Use your value of d
avg
to determine A, the area over which the heat flow between the ice and the steam
chamber took place. (Assume that A is just the area of the ice in contact with the sample material.)
➂ Divide m
wa
by t
a
and m
w
by t to determine R
a
and R, the rates at which the ice melted before and after
the steam was turned on.
Subtract R
a
from R to determine R
0
, the rate at which the ice melted due to the temperature differential
only.
➄ Calculate k, the conductivity of the sample:
k (cal cm/cm
2
sec) = _________
∆
T = Boiling point of water (100
°
C at sea level) - 0
°
C.
➃
➅
➆
