PASCO TD-8564 THERMAL EFFICIENCY APPARATUS User Manual
Page 19
012-05443A
Thermal Efficiency Apparatus
15
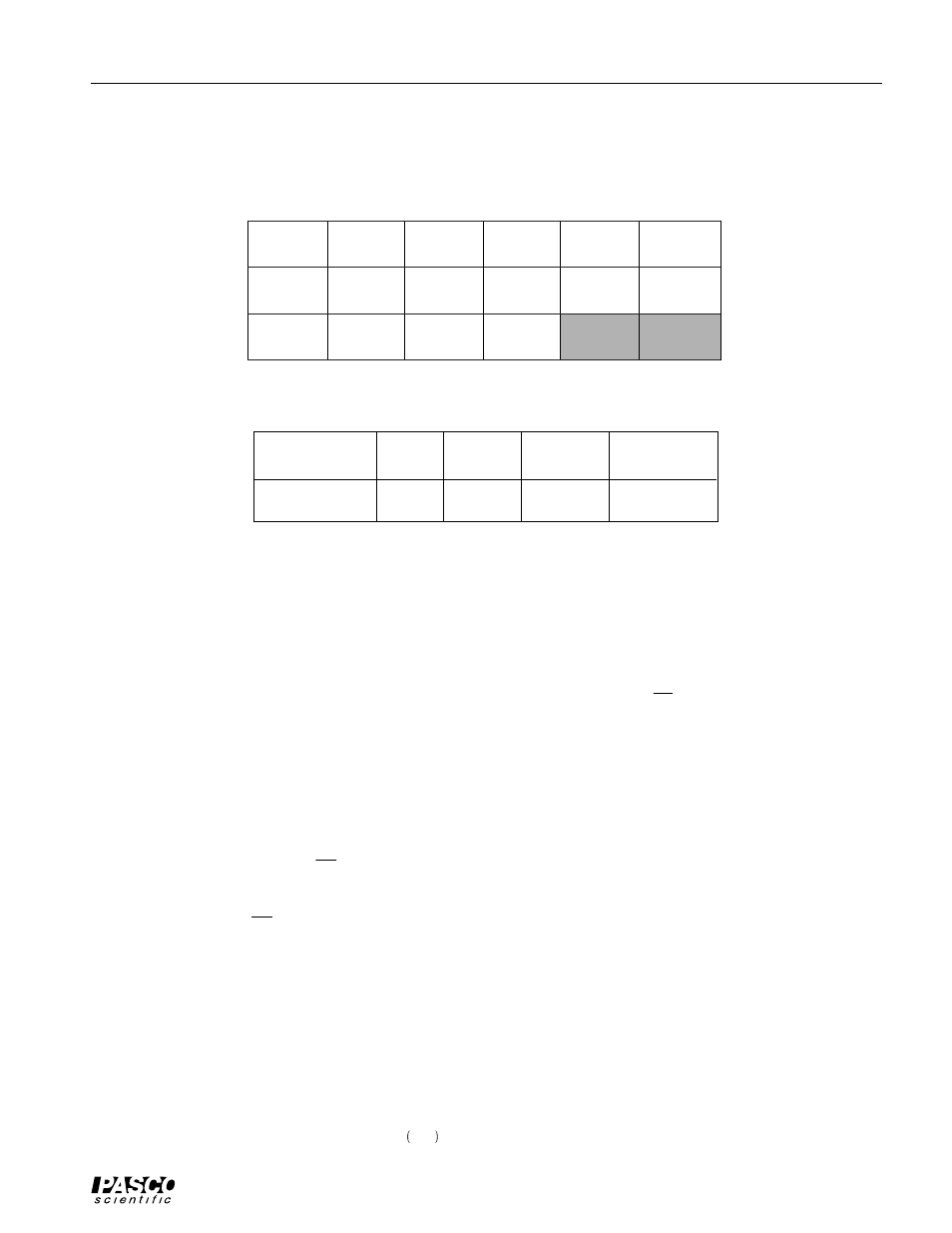
Table 2.3 Results
Maximum
(Carnot)
➁
Maximum Efficiency: Convert the temperatures to Kelvin and record in Table 2.2. Calcu-
late the Carnot efficiency using the temperatures and record in Table 2.3.
➂
Adjusted Efficiency: The purpose of the following calculations is to account for all the
energy losses and adjust the actual efficiency so that it matches the Carnot efficiency.
A. First, the work done in the actual efficiency calculation only includes
V
2
R
for the power
dissipated by the load resistor R but, to account for total work done by the device, it
should also include I
2
r for the power dissipated by the internal resistance, r, of the
device. This Joule heating of the Peltier device is not counted in the actual efficiency
because it is not useful work. Thus, in the adjusted efficiency, the total work done in
terms of power is
P
W
′
= P
W
+ I
W
2
r =
V
W
2
R
+ I
W
2
r
where
I
W
=
V
W
R
. Calculate I
W
for the 2
Ω
load and record in Table 4.
B. Second, the heat input must be adjusted. The heat that leaves the hot reservoir goes two
places. Part of it is actually available to be used by the heat engine to do work while the
other part bypasses the engine either by being radiated away from the hot reservoir or by
being conducted through the Peltier device to the cold side. The portion of the heat
which bypasses the engine by radiation and conduction would be transferred in this
same manner whether or not the device is connected to a load and the heat engine is
doing work. Therefore this heat can be considered to not be available to do work and
should not be included in the heat input in the adjusted efficiency.
P
H
′
= available heat = P
H
– P
H open
Table 2.2 Calculated Values
Internal Resistance = r = ________________
Mode
T
h
(K)
T
c
(K)
P
h
P
w
I
w
Engine
(2
Ω
load)
Open
Actual
Adjusted
% Difference
Efficiency
