PASCO TD-8550A THERMOELECTRIC CONVERTER User Manual
Page 4
012-04929A
4
scientific
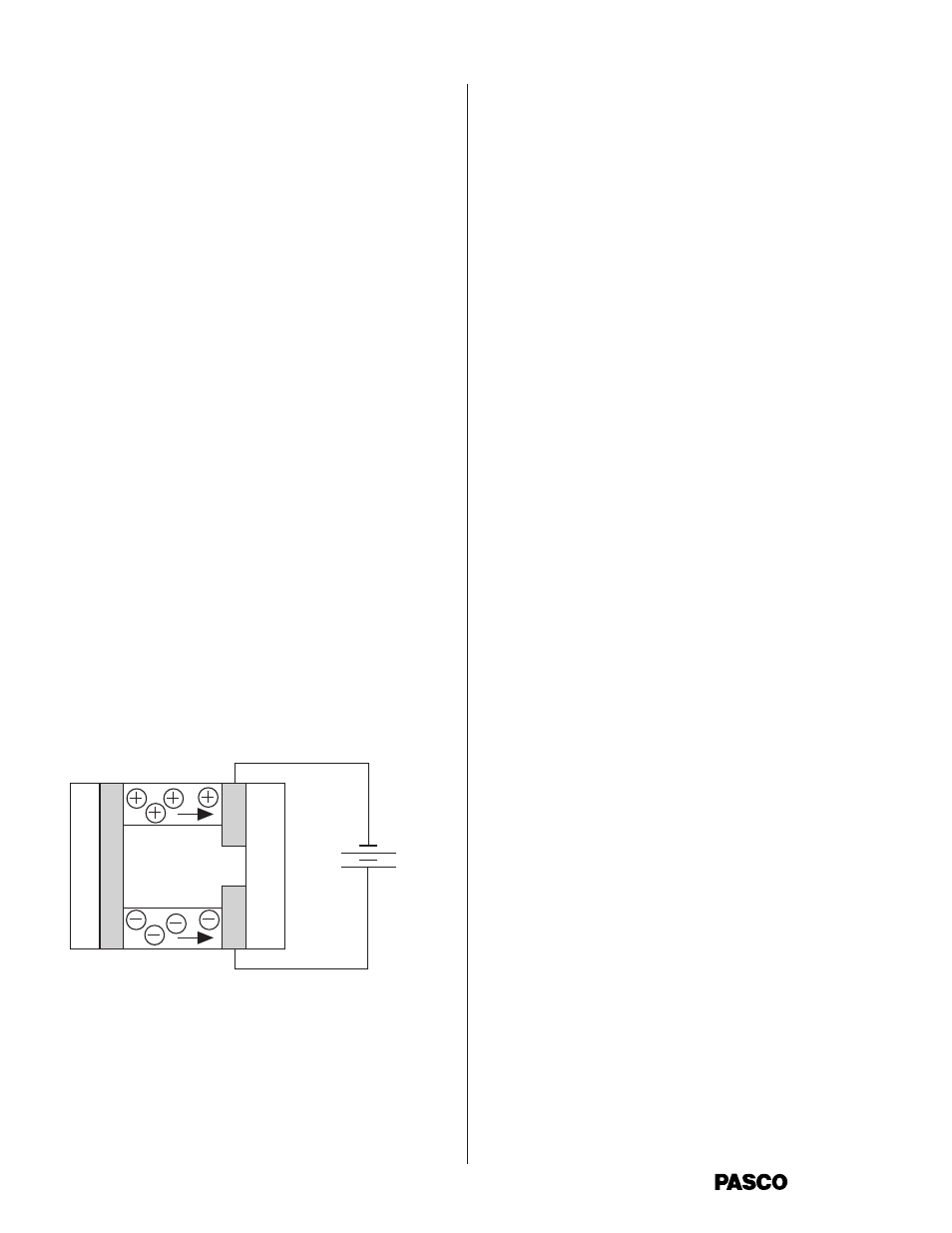
The electrons migrate, as shown, through the N-type
semiconductor material and the holes migrate through
the P-type material. (N and P type materials are merely
silicon that is “doped” with special impurities that
enhance electron and hole migration.) The electrons
flow through the external circuit and drive the fan
motor. At the other end of the circuit they reenter the
cell and encounter the holes of the P-type semiconduc-
tor. This occurs near the cold end of the cell. The
electrons can therefore drop back into holes, giving up
any excess energy they still retain as heat.
As long as the temperature differential is maintained
between the two sides of the cell, the electrons and
holes continue to migrate, and the fan continues to turn.
However, if there is no temperature differential, the
electrons can not recombine with the holes because
there is no place to give up their excess energy.
In this
way, the thermoelectric cell is constrained by the
Second Law of Thermodynamics.
Description of Peltier effect
During the Peltier effect, the electric potential differ-
ence causes electrons and holes to migrate from one end
of the N and P type semiconductor material to the other.
The movement of the electrons in the N type semicon-
ductor results in a transfer of internal energy from that
end of the semiconductor, and it cools. The same result
occurs for the P type semiconductor during hole
migration. The heat transfer from the “cold” leg to the
“hot” leg is proportional to the carrier current passing
through the circuit and the number of thermoelectric
cells (couples) making up the thermoelectric pump.
Construction of the Thermoelectric Heat Pump:
The PASCO Thermoelectric Converter has 71 thermo-
electric cooling “couples”. These are made from two
elements of semiconductor, primarily Bismuth Tellu-
ride (a quarternary alloy of bismuth, tellurium, selenium
and antimony) heavily doped to create either an excess
(N-type) or deficiency (P-type) of electrons. The
C
O
O
L
I
N
G
W
A
R
M
I
N
G
(N-type)
(P-type)
DC
SUPPLY
Thermoelectric Converter Cell (Peltier effect)
couples, connected in series electrically and in parallel
thermally, are integrated into the thermoelectric heat
pump. The heat pump is packaged between metallized
ceramic plates.
Specifications:
When using the Thermoelectric Converter as a Peltier
device, the power required to produce a given tempera-
ture difference depends on the temperature of the hot
side. The hot side must never exceed 135 degrees C,
the melting point of the solder which bonds the Bismuth
Telluride ingots to the plates. Starting at 25 degrees C,
the hot leg temperature increases much more than the
cold leg temperature decreases (about 40 degrees versus
about 8 degrees in 2 minutes). This is because the
power dissipated by the hot side is the sum of the
supplied power and the heat transferred from the cold
side. (If the hot side is held to 25 degrees C, enough
power can be applied to create a maximum temperature
difference of about 67 degrees C.)
The resistance of the small motor is about 1 ohm.
Compatible PASCO Equipment
PASCO offers a complete line of laboratory and
demonstration equipment for thermodynamics. Experi-
ment quantitatively with the mechanical and electrical
equivalents of heat, thermal conductivity, heat capacity,
phase changes in water, and black body radiation.
Check our catalog for these and other products that can
bring PASCO quality into your classroom and labora-
tory.
Limited Warranty
PASCO scientific warrants this product to be free from
defects in materials and workmanship for a period of
one year from the date of shipment to the customer.
PASCO will repair or replace, at its option, any part of
the product which is deemed to be defective in material
or workmanship. This warranty does not cover damage
to the product caused by abuse or improper use. Deter-
mination of whether a product failure is the result of a
manufacturing defect or improper use by the customer
shall be made solely by PASCO scientific. Responsi-
bility for the return of equipment for warranty repair
belongs to the customer. Equipment must be properly
packed to prevent damage and shipped postage or
freight prepaid. (Damage caused by improper packing
of the equipment for return shipment will not be
covered by the warranty.) Shipping costs for returning
the equipment, after repair, will be paid
by PASCO
scientific.
