PASCO CI-6746 ECONOMY FORCE SENSOR User Manual
Page 4
Economy Force Sensor
012-06906B
4
®
Newton’s Second Law: Constant Force
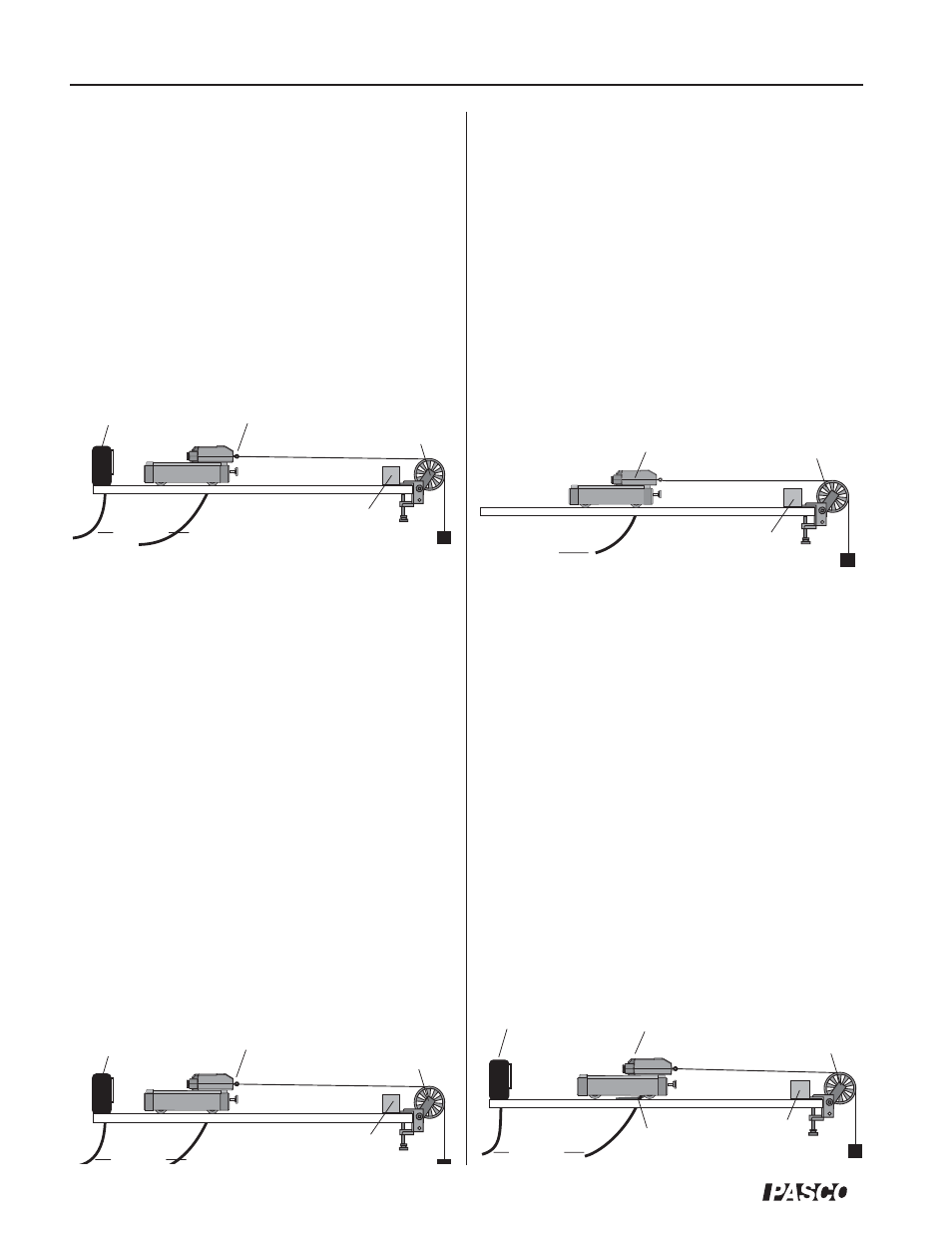
What happens if the cart is pulled by a constant force?
Arrange the Motion Sensor, Force Sensor, and cart on
the track as in the previous suggested experiment. Set
up a Super Pulley (ME-9450), string, and hanging
mass so that the cart/Force Sensor will be pulled by
the string attached to the hanging mass. Use the
Motion Sensor to measure the velocity and
acceleration of the cart as it is pulled by the string. Use
the computer program to compare the measured force
to the measured velocity and acceleration.
Change the hanging mass and repeat the experiment.
Work-Energy Theorem: W =
∆∆∆∆∆
KE
What happens to the kinetic energy of the cart as it
is pulled by a constant force? Arrange the Motion
Sensor, Force Sensor, and cart on the track as in
the previous suggested experiment. Set up a Super
Pulley (ME-9450), string, and hanging mass so
that the cart/Force Sensor will be pulled by the
string attached to the hanging mass. Use the
Motion Sensor to measure the change in position
and the velocity of the cart as it is pulled by the
string. Use the computer program to find the
integration under the curve of a force versus
distance graph. Use the program to calculate the
amount of kinetic energy gained by the cart.
Compare the calculated value of the work to the
calculated value of the final kinetic energy.
Tension
What is the tension in the string in the previous
suggested experiment? Arrange the Force Sensor
and cart on the track as in the previous suggested
experiment. Set up a Super Pulley, string, and
hanging mass so that the cart/Force Sensor will be
pulled by the string attached to the hanging mass.
First, hold the cart at rest so the tension in the string
is “mg” (the hanging mass times the acceleration
due to gravity). Then, let go of the cart so it
accelerates toward the pulley. Use the program to
measure the amount of force in the string. The
tension should be constant, but less than “mg”.
Newton’s Second Law: Friction
Make observations when a force is applied to the cart/
Force Sensor and compare its acceleration when no
friction is present to the acceleration when friction is
added. You will need to add the Friction Cart
Accessory (ME-9457) to the Dynamics Cart. Arrange
the Motion Sensor, Force Sensor, and “friction” cart
on the track as in the previous suggested experiment.
Set up a Super Pulley, string, and hanging mass so the
cart/Force Sensor will be pulled by the string attached
to the hanging mass. Adjust the friction cart accessory
so the friction pad is not in contact with the track.
Accelerate the cart with a 50 gram mass. Use the
Motion Sensor to measure the velocity and
acceleration of the cart as it is pulled by the string.
Use the computer program to compare the measured
Motion Sensor
to computer
interface
Adjustable
End Stop
Force Sensor
mass
Super
Pulley
Friction
Cart
Accessory
Super
Pulley
to computer
interface
Adjustable
End Stop
Force Sensor
mass
Super
Pulley
Motion Sensor
to computer
interface
Adjustable
End Stop
Force Sensor
mass
Super
Pulley
Motion Sensor
to computer
interface
Adjustable
End Stop
Force Sensor
mass
