PASCO PS-2163 Soil Moisture Sensor User Manual
Page 5
®
Model No.PS-2163
Setup
5
and soil conductivity because it operates at a high frequency. Therefore, its calibra-
tions should apply for all potting soil, mineral soil, and rockwool.
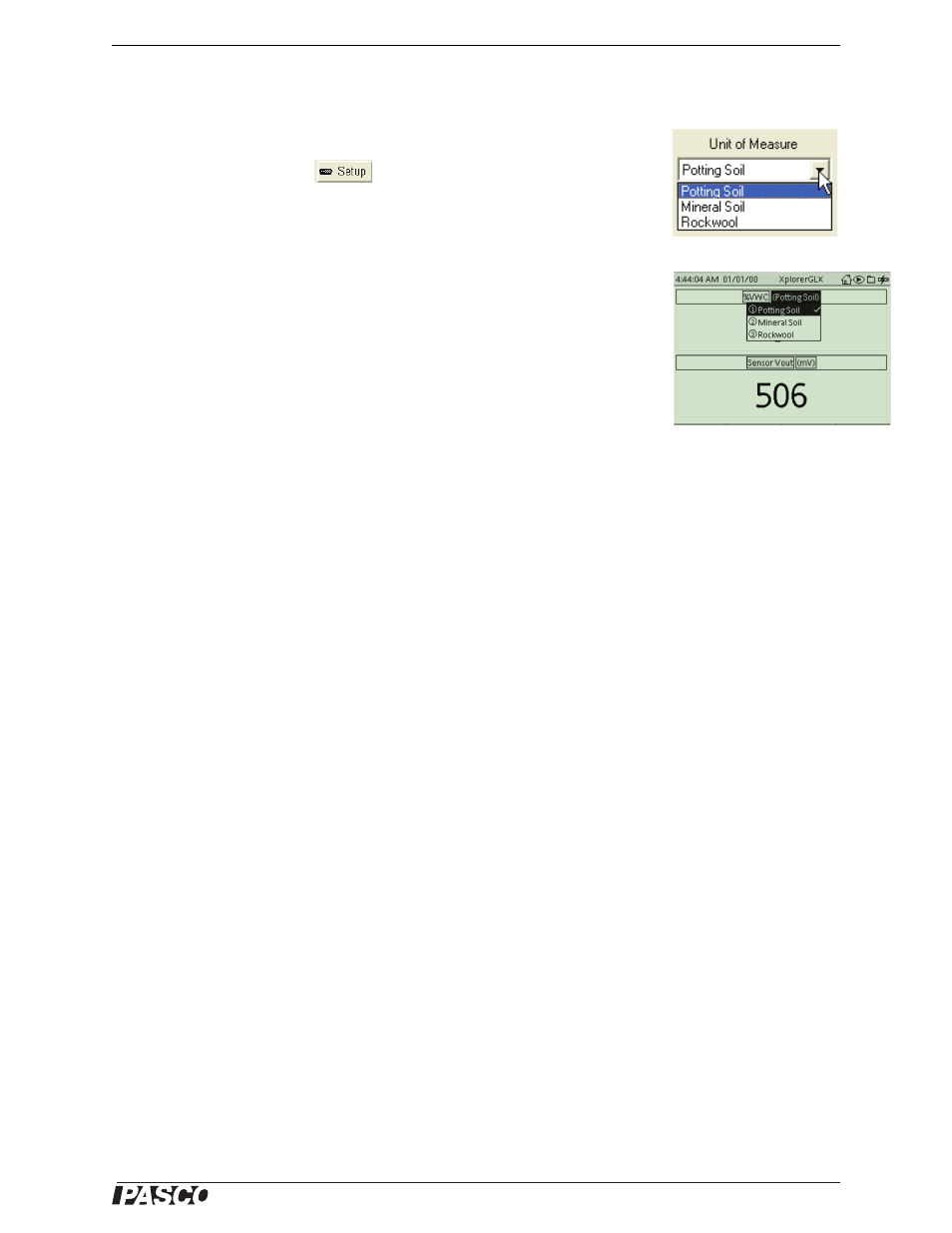
Selecting Soil Type
In DataStudio, click Setup (
) to open the Experiment Setup window. In the
Experiment Setup window, click the menu button under “Unit of Measure” and select
the soil type.
With the Xplorer, press the check button (c) to highlight the soil type, then press
the plus button (+) to toggle through the soil selection choices. Press the check but-
ton again to select your choice.
With the Xplorer GLX showing %VWC in the digits display, press the check button
(c) to open the selection menu for the display. Use the right cursor arrow key (r)
to open the soil type menu, and then use the down cursor arrow key (d) to select
the soil type. Press the check button again to select your choice.
With the SPARK SLS, connect the Soil Moisture Sensor and select the soil type from
the list of choices that will appear on the screen.
Other
If the type of soil or media that you are using does not appear in the Unit of Measure
list, you may want to make measurements to create a soil specific calibration curve
yourself, or take advantage of Decagon’s calibration service.
Information on individuual probe calibration can be found online at
www.decagon.com/appnotes/echocal.pdf
Information on Decagon’s calibration service can be found at
www.decagon.com/echo/calibration.html.
Creating a Calibration Curve
Volumetric Water Content (VWC) is the ratio of the volume of water per volume of
bulk soil. One way to create a soil specific calibration curve is to match the voltage
output from the Soil Moisture Probe to VWC values for several soil samples with dif-
ferent degrees of dryness, and then plot a graph of VWC versus probe output in milli-
volts (mV).
The basic process is to collect a measured volume of bulk soil, measure its mass, mea-
sure the probe reading in mV for the bulk soil, dry the soil to determine the amount of
water that was in the soil, and calculate the ratio of the volume of water to the volume
of bulk soil. Then, create a graph of VWC versus probe voltage and determine the
“best fit” for the graph. If the graph is linear, determine the slope and y-intercept. If
the graph is quadratic, determine the coefficients of each term. A linear calibration
curve would have a formula of y = mx + b where y is the VWC, m is the slope, x is the
probe output in mV, and b is the y-intercept. Finally, create a calculation based on the
formula for the soil specific calibration curve.
Equipment: shovel and bulk soil container, calibration container, Soil Moisture Probe and
PASCO Interface, volumetric soil sampler
1
, soil drying containers with lids (e.g., baby food jars),
scale or mass balance, drying oven.
Procedure:
1. Collect approximately 4 liters of bulk soil from the depth/location where you
want to measure with the probe.
The Soil Moisture Probe is built by
Decagon Devices, Inc.
2365 NE Hopkins Ct.
Pullman, WA 99163
See the User’s Guides for
the Xplorer GLX or the
SPARK Science Learning
System for calibration
instructions.
A quadratic calibration curve would
have a formula of y = ax
2
+ bx + c
where y is the VWC, x is the probe
output in mV, and a, b, and c are
coefficients.
1
A volumetric soil sampler could be a
3 to 5 cm section of metal conduit or
other small diameter (1.5 to 2.5 cm)
metal or thin walled plastic tubing.
Deburr both ends and sharpen one
end for easy insertion into the soil.
Measure its dimensions and calculate
the volume,
V
r
2
h
=
