Laurel Electronics LAUREATE SERIES SCALE-WEIGHT METER User Manual
Page 41
- 41 -
Reset
There are three types of Reset:
Peak Reset. Achieved by simultaneously pressing the RESET and PEAK
keys.
Latched Alarm Reset. Achieved by simultaneously pressing the RESET and
ALARMS keys.
Meter Reset. Causes the meter to reinitialize and take a tare reading when
set up for auto-tare. Achieved powering up the meter, by pressing the
RESET and MENU keys simultaneously, stepping through all top-level
menu choices, grounding a rear panel connector, or supplying an ASCII
command. rESEt is displayed briefly.
RS485 Half Duplex
Serial communications implemented with two wires, allowing data transmission
in both directions, but not simultaneously.
RS485 Full Duplex
Serial communications implemented with four wires, allowing data transmission
in two directions simultaneously.
Run Mode
The normal operating mode of the meter,
where readings are taken, as opposed to the
menu mode.
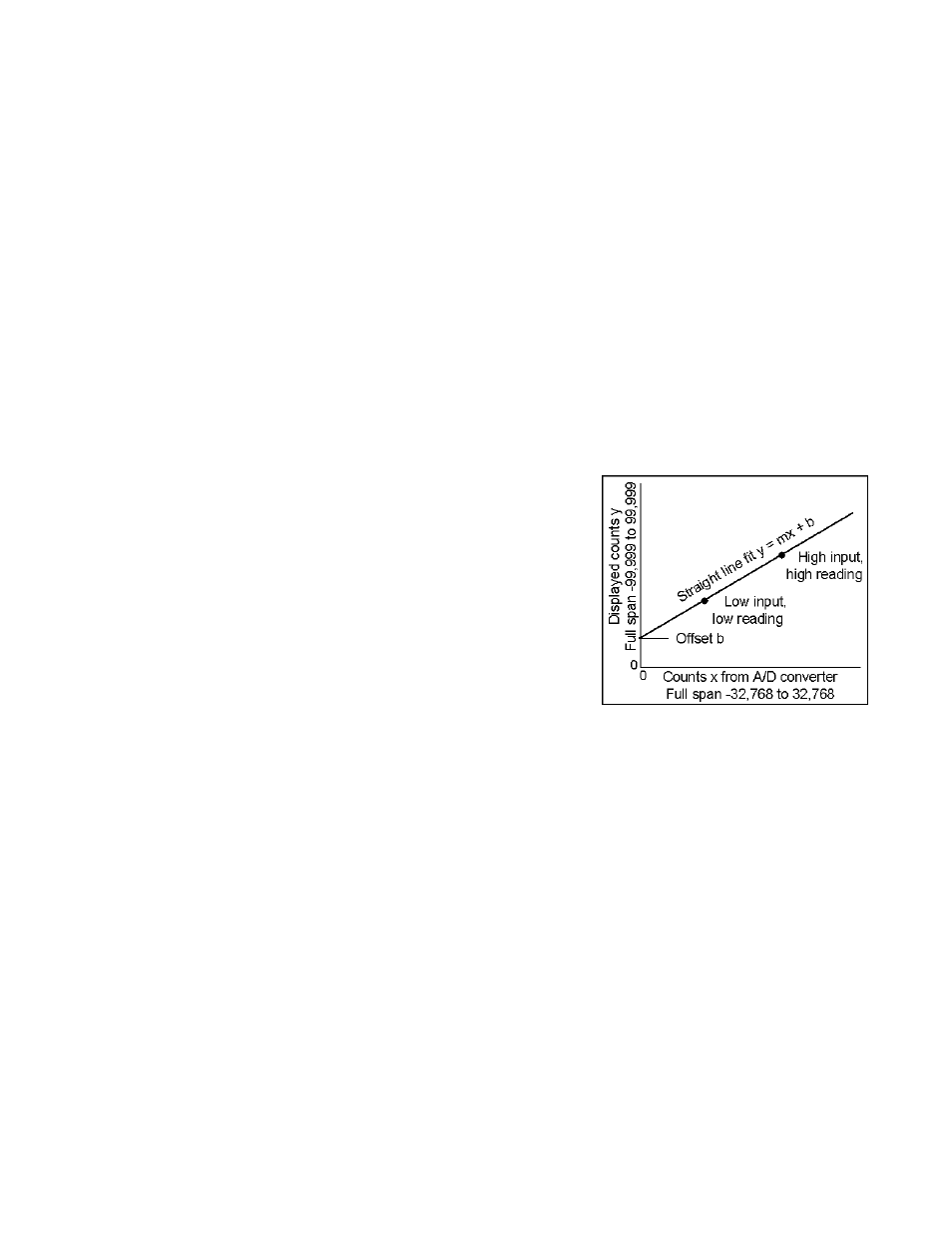
Scale
A constant multiplier used to go from A/D
converter counts to displayed counts. This is
the slope term m in the straight line formula
y = mx + b, where y is the displayed reading
in counts, m is the scale factor, x is the
measured reading in counts, and b is the
offset. For direct readout in (milli)volts or
(milli)amps, scale is 1.
Scaling
The process of setting scale and offset so that the meter reads properly in
engineering units (such as psi).
Scaling, Coordinates of 2 Points Method
A scaling method where four numbers are entered manually: low input, desired
reading at low input; high input, and desired reading at high input. The meter
then applies a straight line fit. The decimal point is set by the separate dEC.Pt
menu item.
Scaling, Scale and Offset Method
A scaling method where scale and offset are entered manually.
Scaling, Reading Coordinates of 2 Points Method
A scaling method, where the low and high input values are determined from
actual signals. A known low signal is first applied to the meter, such as the
output of a pressure transducer at zero pressure. That signal is captured as the
low input value, and the desired low reading is entered. A known high signal is
then applied, such the output of a transducer for a know weight or pressure.
That signal is captured as the high input value, and the desired high reading is
entered. The meter then applies straight line fit. This scaling method has the
advantage of calibrating the transducer and meter as a system. The actual
