Waveform capture, Waveform analysis, Waveform search and display – Atec Yokogawa-DL9000 Series User Manual
Page 3: Filter functions, Advanced trigger functions, Serial bus analysis i, C/spi/can
4
5
Enhanced functions for all signal handling tasks ----- capture, display, search and analysis
To be able to observe signals after filtering out unnecessary components is extremely useful during circuit design. The DL9000 series is equipped
with two types of filters, the input stage filters and filters based on high-speed computation. You can filter out unnecessary signal components during
signal capture or apply high-speed filtering afterwards.
Filters in the input stage
:
Analog filters: 200 MHz/20 MHz
Real-time digital filters: 8 MHz/4 MHz/2 MHz/1 MHz/500 kHz/200 kHz/125 kHz/62.5 kHz/32 kHz/16 kHz/8 kHz
Filters based on computation :
Select low pass or high pass filters with variable cutoff frequencies
Display filtered waveforms in real time at up to 60 frames/sec.
Simultaneously display both pre-filtered and post-filtered waveforms.
Desired filter setting: The lowpass/highpass filter frequencies and cutoff frequency can be set to
values from 0.01 Hz to 1.0 GHz.
The DL9000 can perform I
2
C, SPI and CAN bus analysis with the different available options (/F5, /F7 and /F8). Triggers for these bus types are
standard features. These functions make it easy to discriminate between partial software failures and physical-layer waveform problems when
troubleshooting systems by observing the physical-layer characteristics of signals.
The DL9000 series allows the zooming magnification and position to be set
separately for two different areas of a waveform. Thus you can change the
timebase scale and view the two windows simultaneously.
The waveform on the right shows a measurement example of the time taken from
the point of power-on to the point of gate array oscillation. The DL9000 measures
the time length from the rising edge occurring immediately after power-on (cursor
1 of Zoom 1), to the start of oscillation (cursor 2 of Zoom 2).
Real-time bus analysis-up to 15 updates/sec
The DL9000 displays protocol analysis results while concurrently capturing bus signals.
Simultaneous analysis of different buses
With the Dual-window Zoom function, the DL9000 can simultaneously analyze and display the waveform of buses running at different speeds.
Serial data bus trigger functions
A variety of trigger conditions can be set, including triggers based on ID-Data combinations and combinations of a serial bus trigger and a regular edge trigger.
The DL9000 series can be triggered using two or more channels in addition to an edge trigger or TV trigger. You can capture only the desired signals
by combining various trigger types and thereby predetermining trigger conditions. Effective filtering helps to shorten the time needed to evaluate and
troubleshoot a design.
DL9000 Series’ Trigger Functions
Examples of Trigger Application
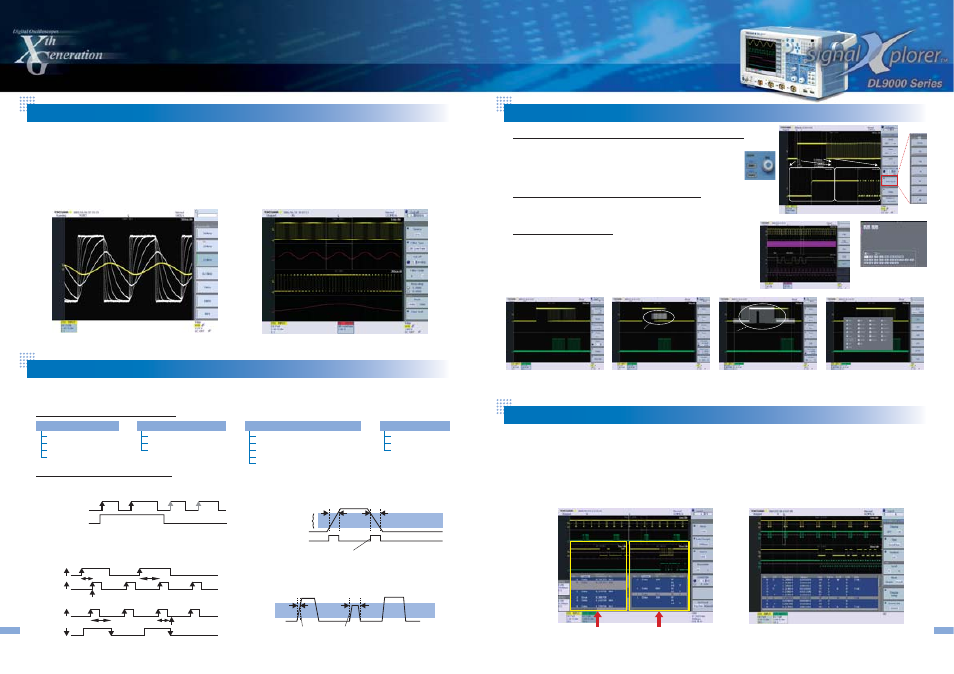
Example of input stage filtering
Example of computation filtering: PWM waveform analysis
Auto Scroll
Menu
Zoom1/Zoom2
keys
Zoom1
Selected z
Selected zone
one
Create a windo
Create a window
w
around a selected
around a selected
wavef
efor
orm
Zoom2
Example: Search
for serial pattern
A5 (1010 0101)
Example of I
2
C Bus Analysis Display
Example of High-speed/Low-speed
CAN Bus Analysis Display
CAN 500kbps
CAN 125kbps
Yellow: PWM waveform
Red: Filtering-based trend display of pulse widths
Edge/state triggers
Edge
Edge (Qualified: conditional)
Edge OR
State
Pulse width triggers
Pulse width
Pulse width (Qualified)
Pulse state
(Triggered using the length of period
during which the conditions are true)
Enhanced triggers
TV (NTSC/PAL (SECAM)/HDTV)
I
2
C
SPI
CAN
Serial pattern (define patterns up to 128 bits long)
Event interval triggers
Event cycle
Event delay
Event sequence
Trigger-based gating – Edge (Qualified): conditional trigger –
The valid/invalid state of an edge trigger or pulse width trigger can be controlled according
to the conditions of any other channel’s state (high/low).
Setup and hold time triggers
To derive setup time/hold time conditions, event delay/event sequence triggers are set as
shown in the following figure.
Slew rate trigger – Window comparator and pulse state –
The time taken to pass through the voltage level range specified for the window comparator
is used to detect the pulse rise/fall time. With pulse state triggers, it is possible to derive
trigger conditions, such as “More Than,” “Less Than” and “Between,” by specifying the
ranges of rise time/fall time.
Runt pulse trigger
Runt pulses (pulses with levels lower than those of normal pulses) can also be captured in
the same way as explained above. A runt pulse stays too long within the range set by the
window comparator, as shown in the following figure. It is therefore possible to capture the
runt pulse by setting the trigger conditions to a rise time longer than those of normal
pulses.
Display of up to 2,000 Overlaid
Waveforms using History Memory
Zone search
Define 1 to 4 zones and search for waveforms
that fall inside or outside the zone (s).
Waveform window search
Select a waveform in History Memory and create
a window around the waveform by moving
up/down/left/right from the waveform. Search for
waveforms that fall inside or outside the window.
Waveform parameter search
Select a waveform parameter and define a range
for the parameter. Search for waveforms with
parameter values inside or outside the set range.
Dual-window Zoom function simultaneously zooms in on two areas
Use the auto scroll function to automatically move the zoom windows through a
long acquisition. Selecting the area to be zoomed-in on can be done easily by
scrolling forward, backward, fast forwarding or pausing.
Auto Scroll function for observing the entire waveform
The DL9000 series has a variety of waveform search functions, enabling you to
detect abnormal signals or find specific serial or parallel data patterns.
Data search types include:
• State search (based on high/low states of one or more channels)
• Serial pattern search (I
2
C/SPI/CAN/general-purpose pattern)
• Zone search
• Waveform window search
• Waveform parameter search (measured parameters, FFT, etc.)
A variety of search functions
Ch. 1 edge trigger
Valid
Valid
Invalid
Invalid
Preset window
comparator level
True
Short stay in
trigger window
Long stay in
trigger window
True
The pulse state trigger is activated according to the length
of the period during which the conditions are true.
Ch. 2 state input
(Example: Valid at “High”)
bSetup time
Event1
Event2
Trigger
(condition "Less Than": Triggered if the setup time is shorter than the preset time)
Setup time
bHold time
Event1
Event2
Setup time
Trigger
(condition "Less Than": Triggered if the
setup time is shorter than the preset time)
Waveform Capture
– Filter functions –
Waveform Capture
– Advanced trigger functions –
Waveform Analysis
– Serial bus analysis I
2
C/SPI/CAN –
Waveform Search and Display
– Searching for and displaying selected waveforms from the large-capacity memory –
