Pam8124 new prod uc t, Application information – Diodes PAM8124 User Manual
Page 9
PAM8124
Document number: DS36627 Rev. 1 - 2
9 of 15
October 2013
© Diodes Incorporated
PAM8124
NEW PROD
UC
T
A Product Line of
Diodes Incorporated
Application Information
(cont.)
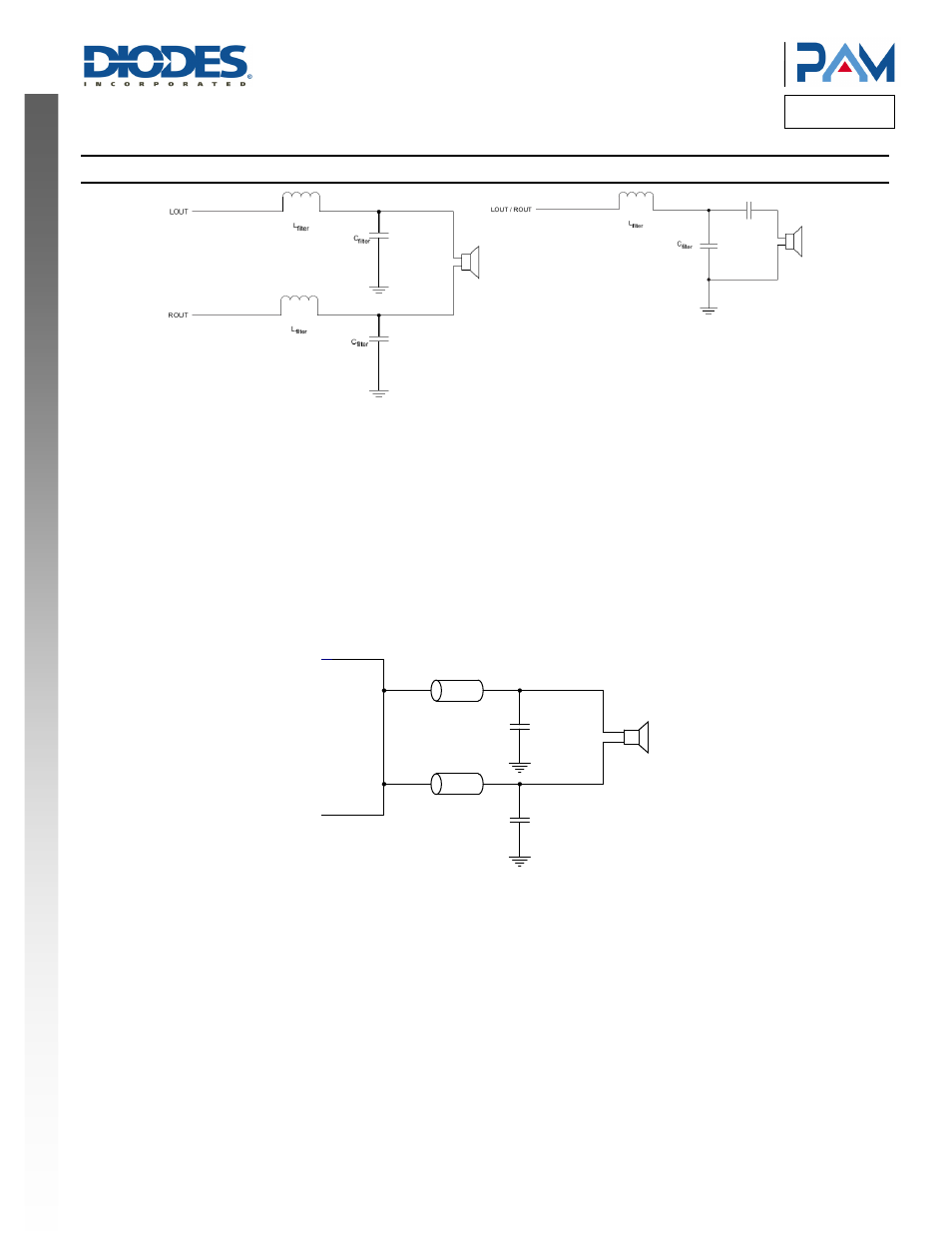
BTL Filter Configuration SE Filter Configuration
Power and Heat Dissipation
Choose speakers that are able to stand large output power from the PAM8124. Otherwise, speaker may suffer damage.
Heat dissipation is very important when the device works in full power operation. Two factors affect the heat dissipation, the efficiency of the
device that determines the dissipation power, and the thermal resistance of the package that determines the heat dissipation capability.
Generally, class-D amplifiers are high efficiency and need no heat sink. Operating at higher powers a heat sink still may not be necessary if the
PCB is carefully designed to achieve good thermal dissipation.
How to Reduce EMI
Most applications require a ferrite bead filter for EMI elimination shown at Figure 1. The ferrite filter reduces EMI around 1MHz and higher. When
selecting a ferrite bead, choose one with high impedance at high frequencies, but low impedance at low frequencies.
200pF
200pF
OUT+
OUT-
Ferrite Bead
Ferrite Bead
Figure 1. Ferrite Bead Filter to Reduce EMI
Dual-Side PCB
To achieve good heat dissipation, the PCB's copper plate should be thicker than 35um and the copper plate on both sides of the PCB should be
utilized for heat sink. The thermal pad on the bottom of the device should be soldered to the plate of the PCB, and via holes, usually 9 to 16,
should be drilled in the PCB area under the device and deposited copper on the vias should be thick enough so that the heat can be dissipated to
the other side of the plate. There should be no insulation mask on the other side of the copper plate. It is better to drill more vias on the PCB
around the device if possible.
