Application information, Ap8800a – Diodes AP8800A User Manual
Page 6
AP8800A
Document number: DS35100 Rev. 3 - 2
6 of 13
August 2012
© Diodes Incorporated
AP8800A
Application Information
(@T
A
= +25°C, V
IN
= 12V, unless otherwise specified.)
AP8800A Operation
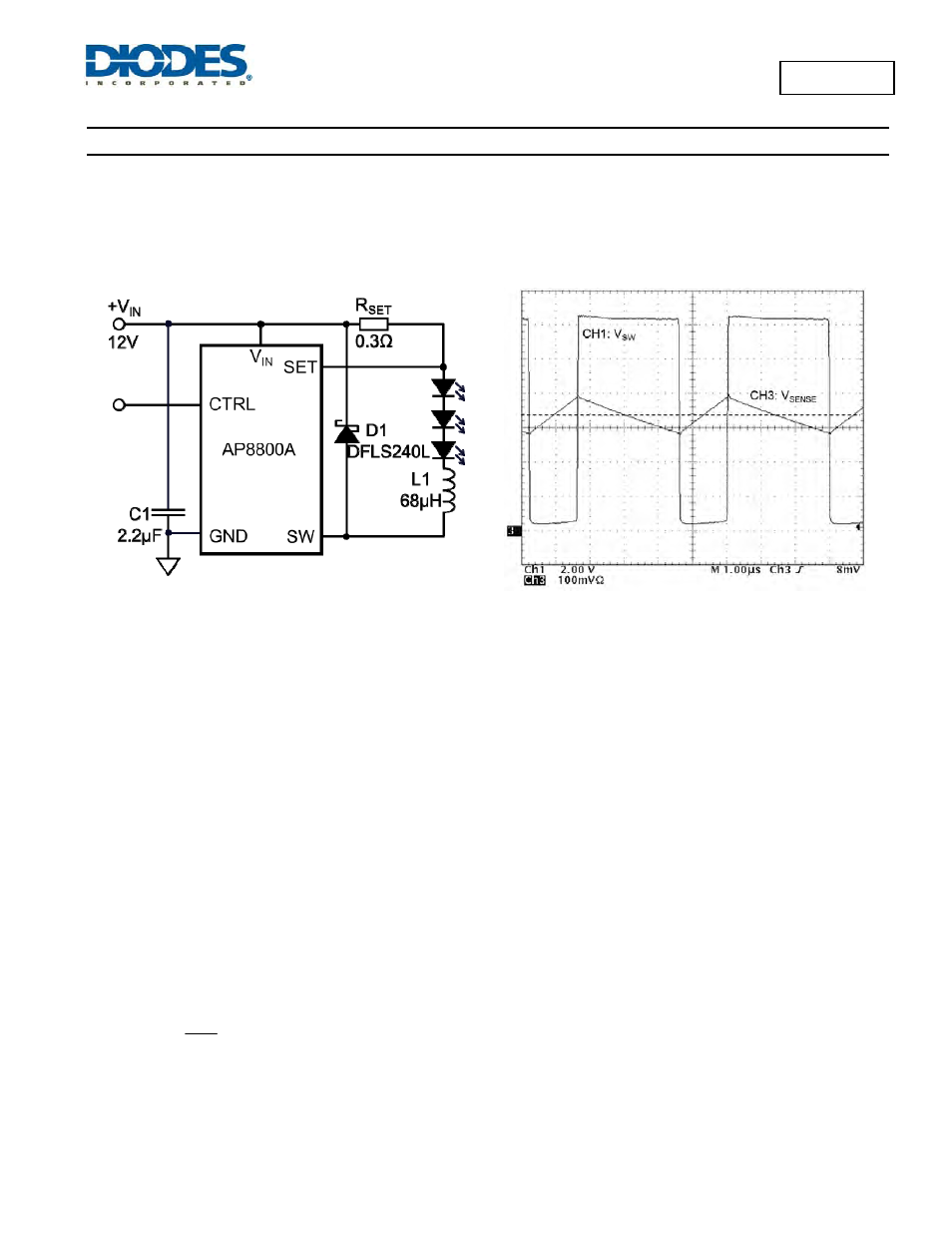
The AP8800A is a hysteretic LED current switching regulator sometimes known as an equal ripple switching regulator. In normal operation, when
voltage is applied at +V
IN
(See
Figure 1), the AP8800A internal switch is turned on. Current starts to flow through sense resistor R
1
, inductor L1,
and the LEDs. The current ramps up linearly, and the ramp rate is determined by the input voltage +V
IN
, and the inductor L1 (See Figure 2).
Figure 1 Typical Configuration
Figure 2 Typical Switching Waveform
This rising current produces a voltage ramp across R
SET
. The internal circuit of the AP8800A senses the voltage across R
SET
and applies a
proportional voltage to the input of the internal comparator.
When this voltage reaches an internally set upper threshold, the internal switch is turned off. The inductor current continues to flow through R
SET
,
L1, the LEDs and the schottky diode D1, and back to the supply rail, but it decays, with the rate of decay determined by the forward voltage drop
of the LEDs and the schottky diode.
This decaying current produces a falling voltage at R
SET
, which is sensed by the AP8800A. A voltage proportional to the sense voltage across
R
SET
is applied at the input of the internal comparator. When this voltage falls to the internally set lower threshold, the internal switch is turned on
again. This switch-on-and-off cycle continues to provide the average LED current set by the sense resistor R
SET,
with a switching current
determined by the input voltage and LED chain voltage.
In normal operation the off time is relatively constant (determined mainly by the LED chain voltage) with only the on-time varying as the input
voltage changes. At duty cycles up to around 80% the ramp of the LED/switch current is very linear; however, as the duty cycle approaches 95%
the LED current ramp starts to become more exponential. This has two effects:
1.
The overall on time starts to increase lowering the overall switching frequency.
2.
The average LED current starts to increase – which may impact accuracy.
LED Current Control
With the CTRL pin left floating and the external current sense resistor, R
SET
(greater than 0.3
Ω) is connected between V
IN
and SET, the nominal
average output current in the LEDs is:
SET
TH
LED
R
V
I
=
where V
TH
is nominally 100mV
