Q-tech, Class b+ products, Phase noise and phase jitter integration – Q-Tech CLASS B+ User Manual
Page 19
Q-TECH Corporation - 10150 W. Jefferson Boulevard, Culver City 90232 - Tel: 310-836-7900 - Fax: 310-836-2157 - www.q-tech.com
19 of 27
Q-TECH
CORPORATION
QPDS-0001, Rev L, June 2013 (ECO #10851)
CLASS B+ PRODUCTS
HIGH RELIABILITY HYBRID CRYSTAL CLOCK OSCILLATORS
2.5 to 5.0Vdc - 15kHz to 350MHz
Phase noise is measured in the frequency domain, and is expressed as a ratio of signal power to noise power measured in a 1Hz bandwidth
at an offset frequency from the carrier, e.g. 10Hz, 100Hz, 1kHz, 10kHz, 100kHz, etc. Phase noise measurement is made with an Agilent
E5052A Signal Source Analyzer (SSA) with built-in outstanding low-noise DC power supply source. The DC source is floated from the
ground and isolated from external noise to ensure accuracy and repeatability.
In order to determine the total noise power over a certain frequency range (bandwidth), the time domain must be analyzed in the frequency
domain, and then reconstructed in the time domain into an rms value with the unwanted frequencies excluded. This may be done by
converting L(f) back to Sφ(f) over the bandwidth of interest, integrating and performing some calculations.
The value of RMS jitter over the bandwidth of interest, e.g. 10kHz to 20MHz, 10Hz to 20MHz, represents 1 standard deviation of phase
jitter contributed by the noise in that defined bandwidth.
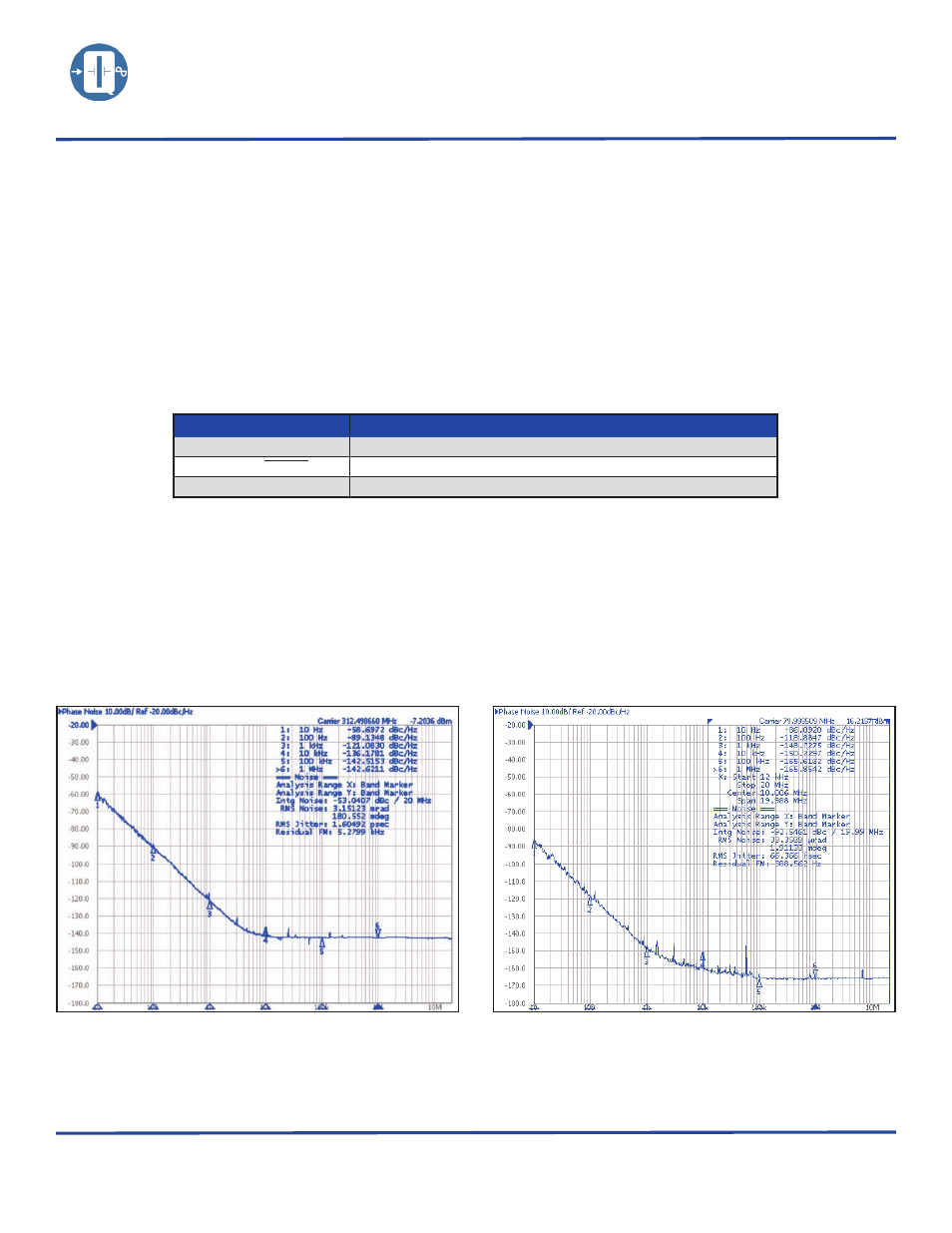
Figure below shows a typical Phase Noise/Phase jitter of a QT193NW10M, 2.5Vdc, 312MHz and QT178HC9A, 5.0Vdc, 80MHz clock
at offset frequencies 10Hz to 1MHz, and phase jitter integrated over the bandwidth of 12kHz to 1MHz.
Phase Noise and Phase Jitter Integration
Symbol
Definition
∫L(f)
Integrated single side band phase noise (dBc)
Sφ (f)=(180/Π)x
√
2 ∫L(f)df
Spectral density of phase modulation, also known as RMS phase error (in degrees)
RMS jitter = Sφ (f)/(fosc.360°)
Jitter(in seconds) due to phase noise. Note Sφ (f) in degrees.
QT178HC9A, 5.0Vdc, 80MHz
QT193NW10M, 2.5Vdc, 312MHz
