Jitter & phase noise (pg 18-19), Q-tech, Class b+ products – Q-Tech CLASS B+ User Manual
Page 18: Jitter and phase noise
Q-TECH Corporation - 10150 W. Jefferson Boulevard, Culver City 90232 - Tel: 310-836-7900 - Fax: 310-836-2157 - www.q-tech.com
18 of 27
Q-TECH
CORPORATION
QPDS-0001, Rev L, June 2013 (ECO #10851)
CLASS B+ PRODUCTS
HIGH RELIABILITY HYBRID CRYSTAL CLOCK OSCILLATORS
2.5 to 5.0Vdc - 15kHz to 350MHz
Jitter And Phase Noise
As data rate increases, effect of jitter becomes critical
with its budget tighter. Jitter is the deviation of a timing
event of a signal from its ideal position. Jitter is
complex and is composed of both random jitter (RJ) and
deterministic jitter (DJ) components.
Random Jitter (RJ) is theoretically unbounded and
Gaussian in distribution, while Deterministic Jitter (DJ)
is bounded and does not follow any predictable
distribution.
Q-Tech utilizes the EZJIT Plus jitter analysis software
with Noise reduction software that supports Agilent
Infinium real-time oscilloscope. Measure at its
maximum sampling rate 40Gs/s and memory depth, we
can separate the signal’s aggregate total jitter into
Random Jitter (RJ) and Deterministic Jitter (DJ).
Since Random Jitter is unbounded and Gaussian in
style, the Total Jitter is a function of Bit Error Rate
(BER).
TJ = RJ + DJ
Where:
BER
α
10E-3
3.1
10E-6
4.75
10E-9
6
10E-12
7.0
Frequency
DJ
(p-p) ps
RJ
(rms) ps
TJ
(ps)
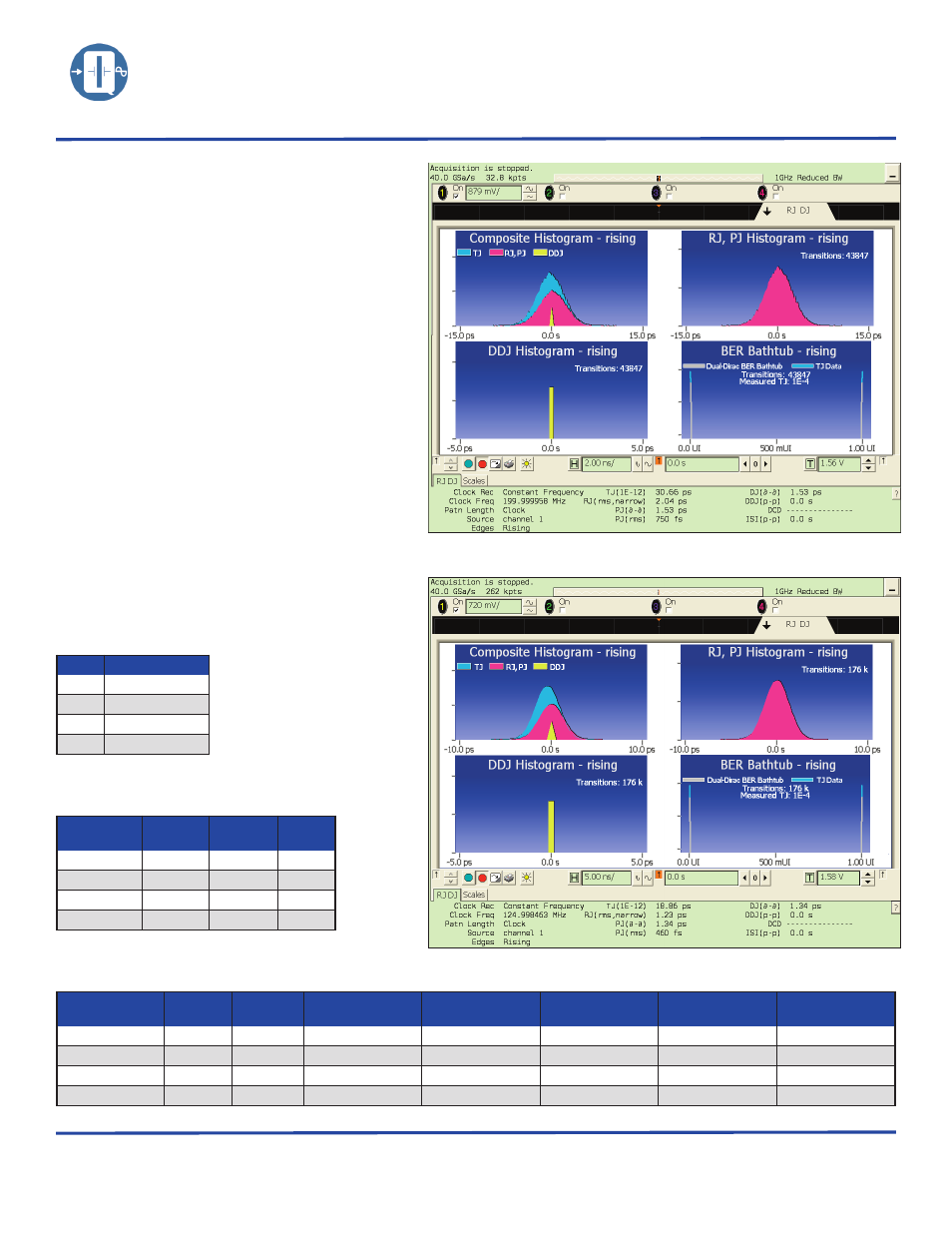
22.118MHz
31
3.36
78.9
100MHz
1.61
1.99
21.1
125MHz
1.34
1.23
18.9
200MHz
1.53
2.04
30.7
Figure 2: Jitter Analysis of a QT192LD9S-125MHz
Figure 1: Jitter Analysis of a QT128L10S-200MHz
Frequency
10Hz
100Hz
1kHz
10kHz
100kHz
1MHz
Phase Jitter
(ps) *
22.118MHz
-90
-125
-150
-157
-162
-162
0.151
100MHz
-76
-101
-128
-140
-143
-149
0.120
125MHz
-74
-101
-131
-143
-145
-150
0.118
200MHz
-73
-99
-124
-134
-145
-148
0.121
RJ = RJ(rms) x 2α + DJ(p-p)
Typical Jitter at BER=10E-12
Typical Phase Noise
(*) Integrated from 1kHz to 20MHz
