Electronic signature word, Programming/erasing, Input and i/o pull-ups – Rainbow Electronics ATF16V8BQL User Manual
Page 6: Input diagram, I/o diagram, Functional logic diagram description, Compiler mode selection, Atf16v8b(ql)
ATF16V8B(QL)
6
Electronic Signature Word
There are 64 bits of programmable memory that are always
available to the user, even if the device is secured. These
bits can be used for user-specific data.
Programming/Erasing
Programming/erasing is performed using standard PLD
programmers. See CMOS PLD Programming Hardware
a n d S o f t w a r e S u p p o r t f o r i n f o r m a t i o n o n
software/programming.
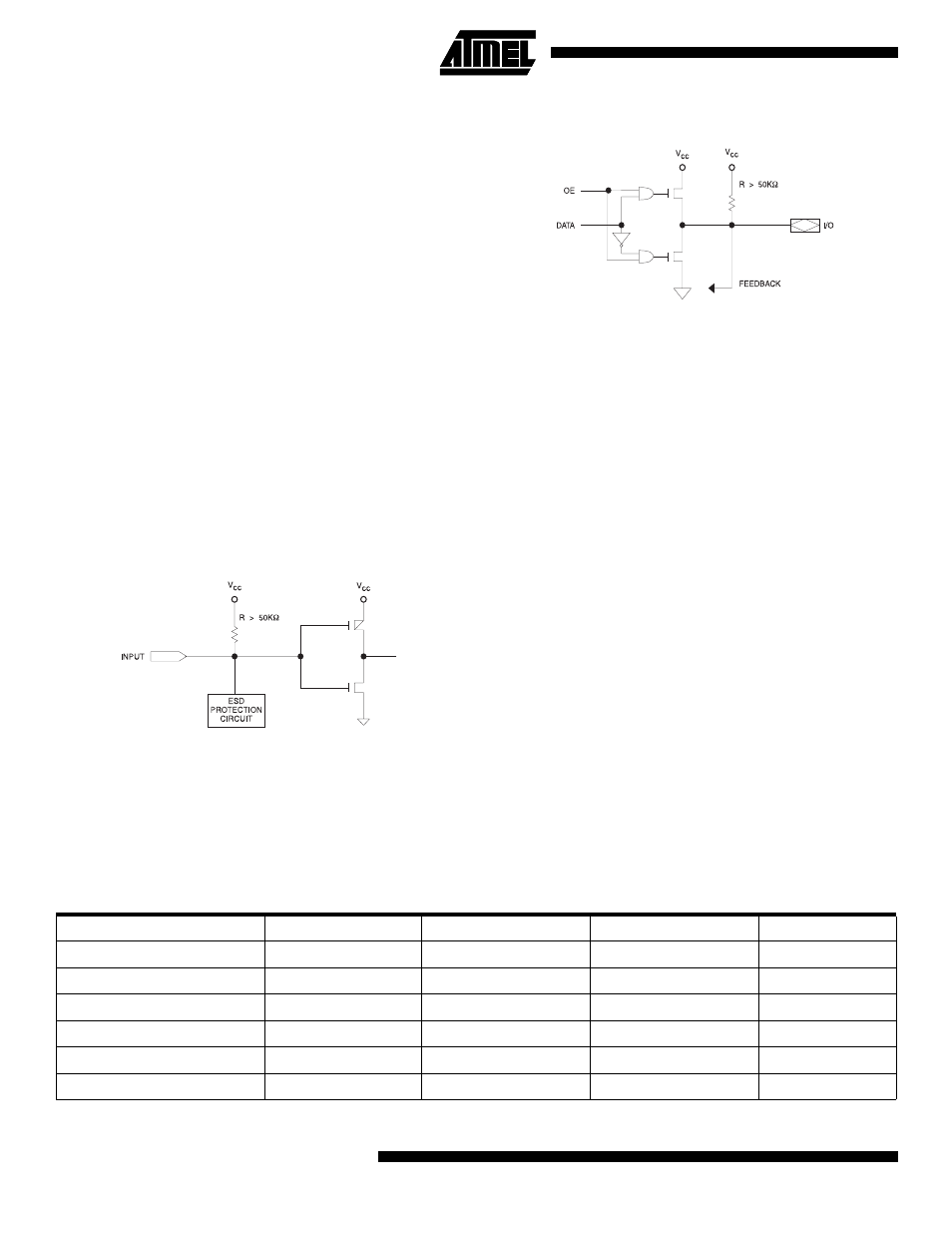
Input and I/O Pull-ups
All ATF16V8B family members have internal input and I/O
pull-up resistors. Therefore, whenever inputs or I/Os are
not being driven externally, they will float to V
CC
. This
ensures that all logic array inputs are at known states.
These are relatively weak active pull-ups that can easily be
overdriven by TTL-compatible drivers (see input and I/O
diagrams below).
Input Diagram
I/O Diagram
Functional Logic Diagram Description
The Logic Option and Functional Diagrams describe the
ATF16V8B architecture. Eight configurable macrocells can
be configured as a registered output, combinatorial I/O,
combinatorial output, or dedicated input.
The ATF16V8B can be configured in one of three different
modes. Each mode makes the ATF16V8B look like a differ-
ent device. Most PLD compilers can choose the right
mode automatically. The user can also force the selection
by supplying the compiler with a mode selection. The deter-
mining factors would be the usage of register versus
combinatorial outputs and dedicated outputs versus
outputs with output enable control.
The ATF16V8B universal architecture can be programmed
to emulate many 20-pin PAL devices. These architectural
subsets can be found in each of the configuration modes
described in the following pages. The user can download
the listed subset device JEDEC programming file to the
PLD programmer, and the ATF16V8B can be configured to
act like the chosen device. Check with your programmer
manufacturer for this capability.
Unused product terms are automatically disabled by the
compiler to decrease power consumption. A security fuse,
when programmed, protects the content of the ATF16V8B.
Eight bytes (64 fuses) of User Signature are accessible to
the user for purposes such as storing project name, part
number, revision, or date. The User Signature is accessible
regardless of the state of the security fuse.
Note:
1. Only applicable for version 3.4 or lower.
Compiler Mode Selection
Registered
Complex
Simple
Auto Select
ABEL, Atmel-ABEL
P16V8R
P16V8C
P16V8AS
P16V8
CUPL
G16V8MS
G16V8MA
G16V8AS
G16V8
LOG/iC
GAL16V8_R
GAL16V8_C7
GAL16V8_C8
GAL16V8
OrCAD-PLD
“Registered”
“Complex”
“Simple”
GAL16V8A
PLDesigner
P16V8R
P16V8C
P16V8C
P16V8A
Tango-PLD
G16V8R
G16V8C
G16V8AS
G16V8
