System maintenance interrupt (smi) recovery stack – Rainbow Electronics DS1687 User Manual
Page 26
DS1685/DS1687
26 of 38
SYSTEM MAINTENANCE INTERRUPT (SMI) RECOVERY STACK
An SMI recovery register stack is located in the extended register bank, locations 4Eh and 4Fh. This
register stack, shown below, can be used by the BIOS to recover from an SMI occurring during an RTC
read or write.
RTC ADDRESS
RTC ADDRESS-1
4Eh
RTC ADDRESS-2
4Fh
RTC ADDRESS-3
SMI RECOVERY STACK
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
DV0
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
REGISTER BIT DEFINITION
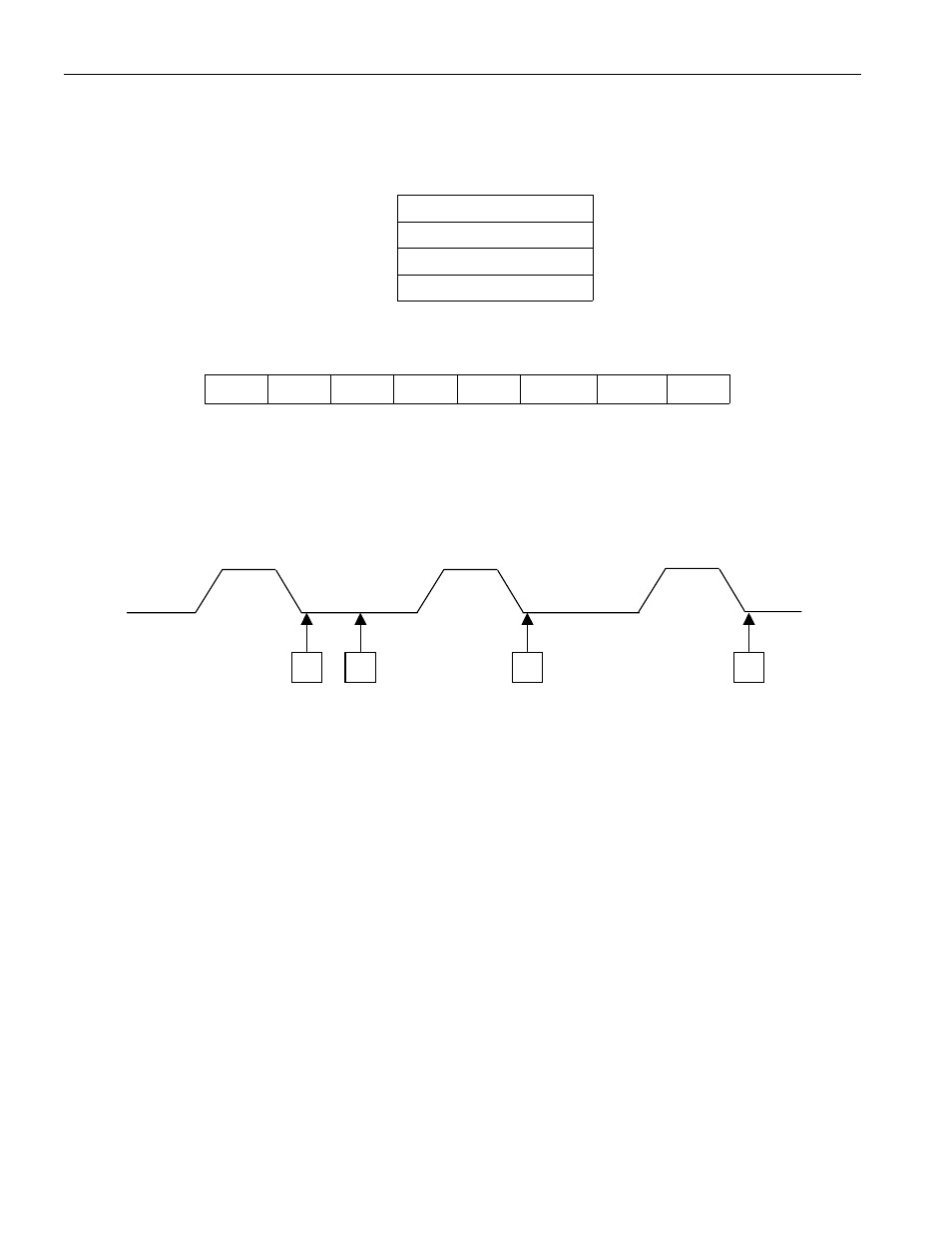
The RTC address is latched on the falling edge of the ALE signal. Each time an RTC address is latched,
the register address stack is pushed. The stack is only four registers deep, holding the three previous RTC
addresses in addition to the current RTC address being accessed. The following waveform illustrates how
the BIOS could recover the RTC address when an SMI occurs.
1) The RTC address is latched.
2) An SMI is generated before an RTC read or write occurs.
3) RTC address 0Ah is latched and the address from 1 is pushed to the RTC Address-1 stack location.
This step is necessary to change the bank select bit, DV0 = 1.
4) RTC address 4Eh is latched and the address from “1” is pushed to location “4Eh,” “RTC Address-2”
while 0Ah is pushed to the “RTC Address-1” location. The data in this register, 4Eh, is the RTC
address lost due to the SMI.
1
2
3
4
ALE
