Max9867 ultra-low power stereo audio codec, Mode configuration – Rainbow Electronics MAX9867 User Manual
Page 43
MAX9867
Ultra-Low Power Stereo Audio Codec
______________________________________________________________________________________
43
Mode Configuration
The MAX9867 includes circuitry to minimize click-and-
pop during volume changes, detect headsets, and con-
figure the headphone amplifier mode. Both volume
slewing and zero-crossing detection are included to
ensure click-and-pop free volume transitions. Table 16
is the mode configuration register.
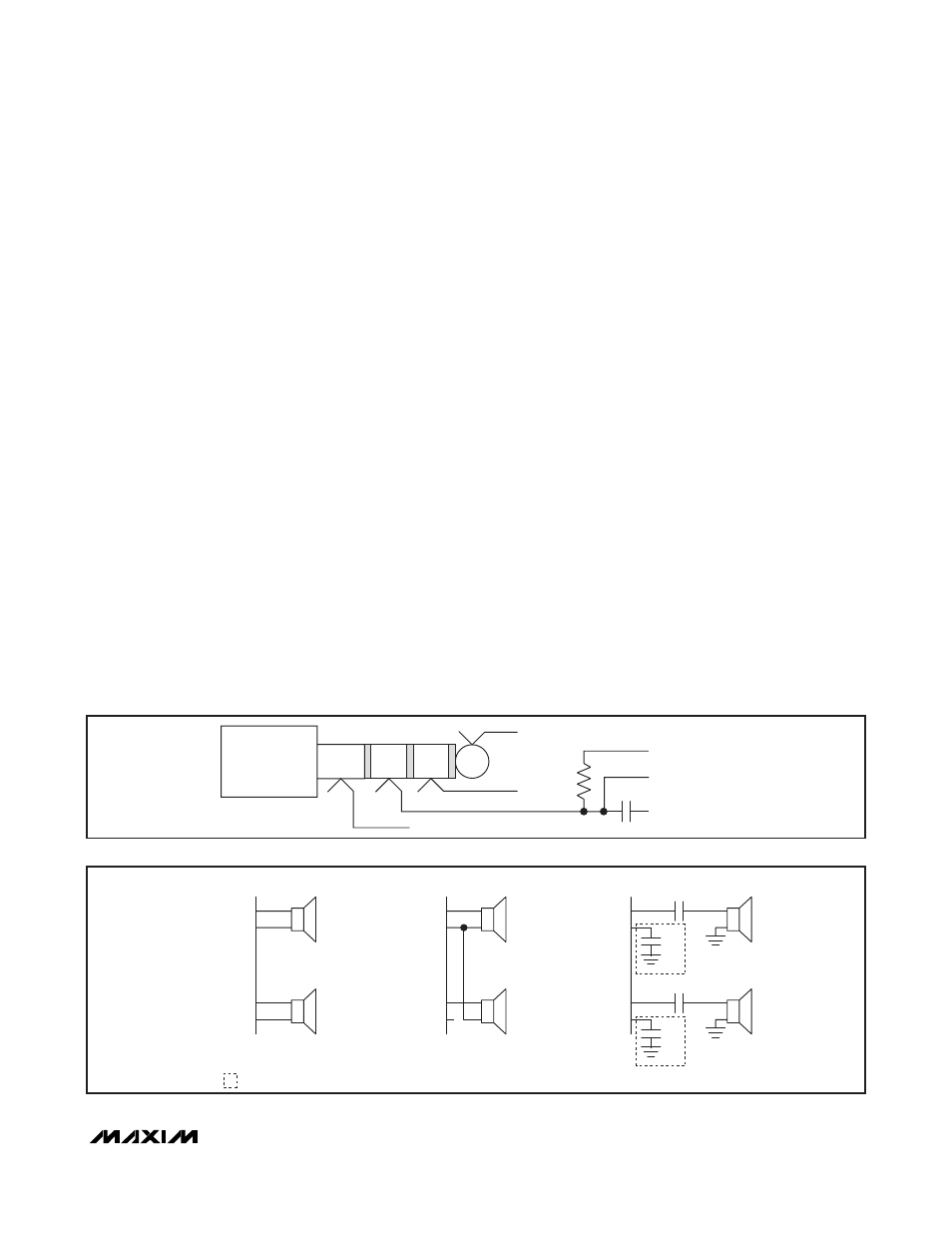
Headset Detection Overview
The MAX9867 features headset detection that can detect
the insertion and removal of a jack as well as the load
type. When a jack is detected, an interrupt on IRQ can be
triggered to alert the microcontroller of the event. Figure 7
shows the typical configuration for jack detection.
Sleep-Mode Headset Detection
When the MAX9867 is in shutdown and the power supply
is available, sleep-mode headset detection can be
enabled to detect jack insertion. Sleep mode applies a
4μA pullup current to JACKSNS/AUX and LOUTP that
forces the voltage on JACKSNS/AUX and LOUTP to
AVDD when no load is applied. When a jack is inserted,
either JACKSNS, LOUTP (assuming the headphone
amplifier is not configured in single-ended mode), or both
are loaded sufficiently to reduce the output voltage to
nearly 0V and clear the JKSNS or LSNS bits, respectively.
The change in the LSNS and JKSNS bits sets JDET and
triggers an interrupt on IRQ if IJDET is set. The interrupt
signals the microcontroller that a jack has been inserted,
allowing the microcontroller to respond as desired.
Powered-On Headset Detection
When the MAX9867 is in normal operation and the micro-
phone interface is enabled, jack insertion and removal can
be detected through the JACKSNS/AUX pin. As shown in
Figure 7, V
MIC
is pulled up by MICBIAS. When a micro-
phone is connected, V
MIC
is assumed to be between 0V
and 95% of V
MICBIAS
. If the jack is removed, V
MIC
increas-
es to V
MICBIAS
. This event causes JKMIC to be set, alert-
ing the system that the headset has been removed.
Alternatively, if the jack is inserted, V
MIC
decreases to
below 95% of V
MICBIAS
and JKMIC is cleared, alerting the
system that a jack has been inserted. The JKMIC bit can
be configured to create a hardware interrupt that alerts the
microcontroller of jack removal and insertion events.
Headphone Modes
The headphone amplifier supports differential, single-
ended, and capacitorless output modes, as shown in
Figure 8. In each mode, the amplifier can be configured
for stereo or mono operation. The differential and
capacitorless modes are inherently click and pop free.
The single-ended mode optionally includes click-and-
pop reduction to eliminate the click and pop that would
normally be caused by the output coupling capacitor.
When click-and-pop reduction is not required in the sin-
gle-ended configuration, leave LOUTN and ROUTN
unconnected.
GND
MIC
HPR
HPL
LOUTP
ROUTP
MICBIAS
JACKSNS/AUX
MICLP
LOUTN
Figure 7. Typical Configuration for Headset Detection
LOUTP
LOUTN
ROUTP
ROUTN
DIFFERENTIAL
LOUTP
LOUTN
ROUTP
ROUTN
CAPACITORLESS
1
μF
LOUTP
220
μF
LOUTN
SINGLE ENDED
1
μF
ROUTP
220
μF
ROUTN
OPTIONAL COMPONENTS REQUIRED FOR CLICK AND POP SUPPRESSION ONLY
Figure 8. Headphone Amplifier Modes
