Glossary – Velleman projects EDU06 Assembly instructions User Manual
Page 20
20
GLOSSARY
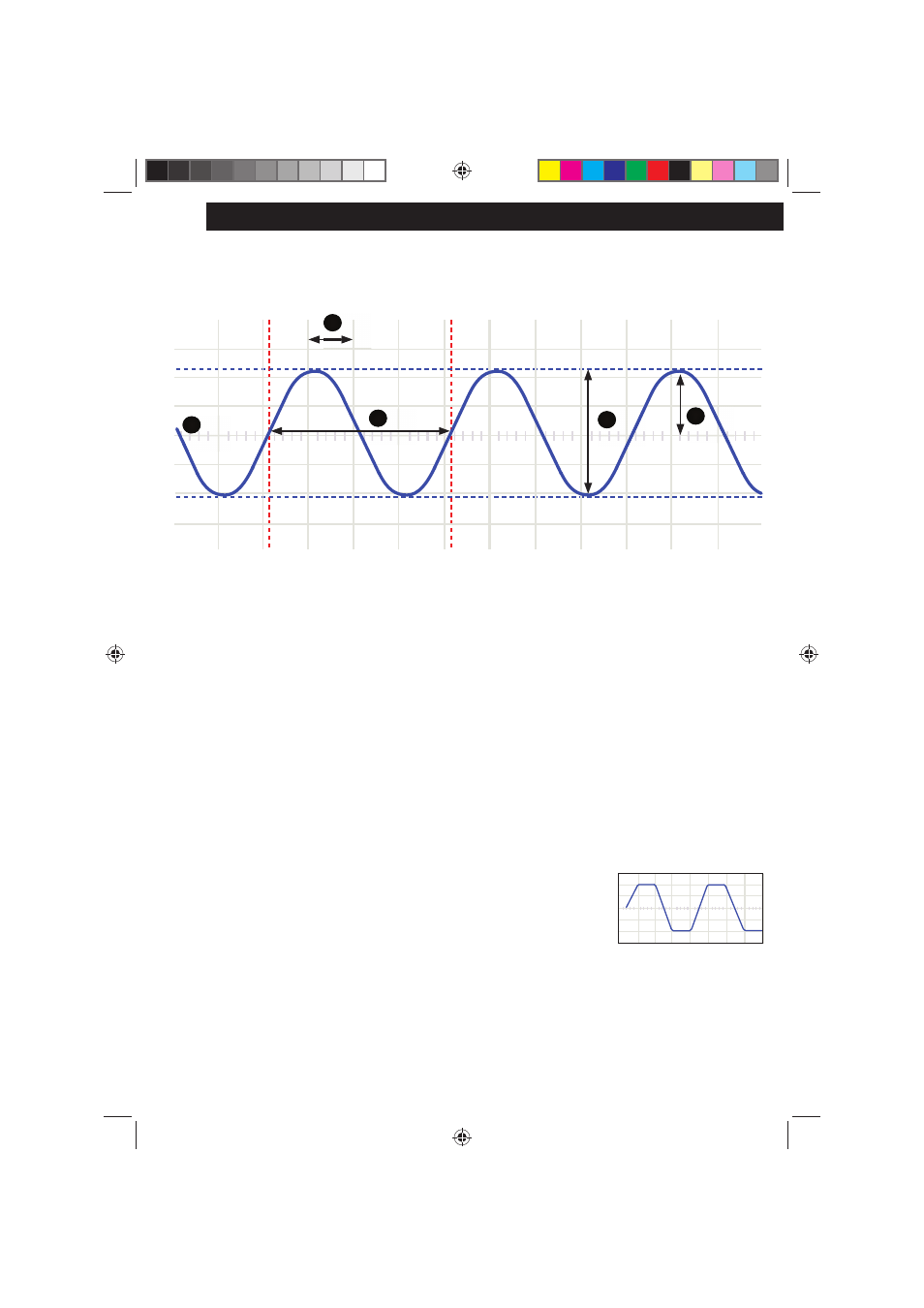
Volts/div:
1.
Determines how many volts the signal at the input must swing for the trace to move one division.
Time/div:
2.
Determines the time the trace needs to scan from the the left hand side to the right hand side of a
division.
Division:
3.
Imaginary or visible grid on the oscilloscope screen. It helps estimating signal amplitude and
period.
Period (T):
4.
Duration of one cycle of the AC waveform (= 1/f)
Frequency (f):
5.
The number cycles of the AC waveform per second
Trace:
6.
‘line’ that is drawn on the screen, which represents the signal at the input
Amplitude:
7.
How far does the signal ‘swing’in a direction. Expressed in mV or V. For repetitive signals:
Vpeak.
Peak-to-peak:
8.
Difference between most positive and most negative swing of the signal.
2xVpeak for sinusoidal signals.
AC coupling: The oscilloscope only displays the AC component of a signal, any DC level is ignored.
Analog: Analog scopes use the incoming signal to defl ect an electron beam, which scans from left to right on the
screen. The electron beam leaves an image on the screen which represents the signal you’ve applied. Analog
signals are continuously variable. See also ‘Digital’.
‘Auto-setup’ mode: The oscilloscope automatically selects a setting for Volts/div and Time/div in such a way that
one or more periods of signal are displayed correctly.
Clipping: When the ‘top’ or ‘bottom’ or both extremes of a signal are cut-off (‘clipped’),
e.g. because the signal cannot swing any further due to power supply limitations. An
undesired property of amplifi ers that are driven beyond their specs.
DC coupling: The oscilloscope displays both the AC and the DC component of a signal.
Digital: Digital scopes perform an analog to digital conversion on the incoming signal and handle all the calcula-
tions and displaying in the digital domain. Digital signals feature only two fi xed levels, usually 0V and +5V. See also
‘Analog’.
Distortion: Undesired alteration of a signal due to external causes such as overloaded circuits, badly designed
circuits, etc…
3
4
8
7
6
Glossary
