Basic operations, Selecting group a and group b functions, Entering values – Yamaha CBX-K2 User Manual
Page 21: Value entry — some specific examples, And anomalies, Using the shift-related functions, Example — setting the midi transmit channel to 12
21
Using the SHIFT-Related Functions
Selecting Group A and Group B Functions
● Selecting Group A Functions:
Hold down
C and press the appropriate key. (See
on pages 26 – 27 for specific Group A functions and
how to use them.)
● Selecting Group B Functions:
Hold down
C and press ç. The Group B
functions are available as long as you continue to hold
down
C. (See on pages 28 – 29 for specific Group
B functions and how to use them.)
*
1
→
0
→
0
→
3
→
K
: results in a value of
MSB = 001, LSB = 003.
*
0
→
1
→
0
→
0
→
3
→
K
: results in a
value of MSB = 001, LSB = 003.
● Entering MSB/LSB Values with J (2 digit
bytes for MSB, 2 digit bytes for LSB; 4 digits total
message). For messages beginning with zeroes, the
first zeroes can be omitted.
Examples:
*
3
→
J
: results in a value of MSB = 00, LSB = 03.
*
0
→
3
→
J
: results in a value of MSB = 00,
LSB = 03.
*
1
→
0
→
3
→
J
: results in a value of MSB
= 01, LSB = 03.
*
0
→
1
→
0
→
3
→
J
: results in a value
of MSB = 01, LSB = 03.
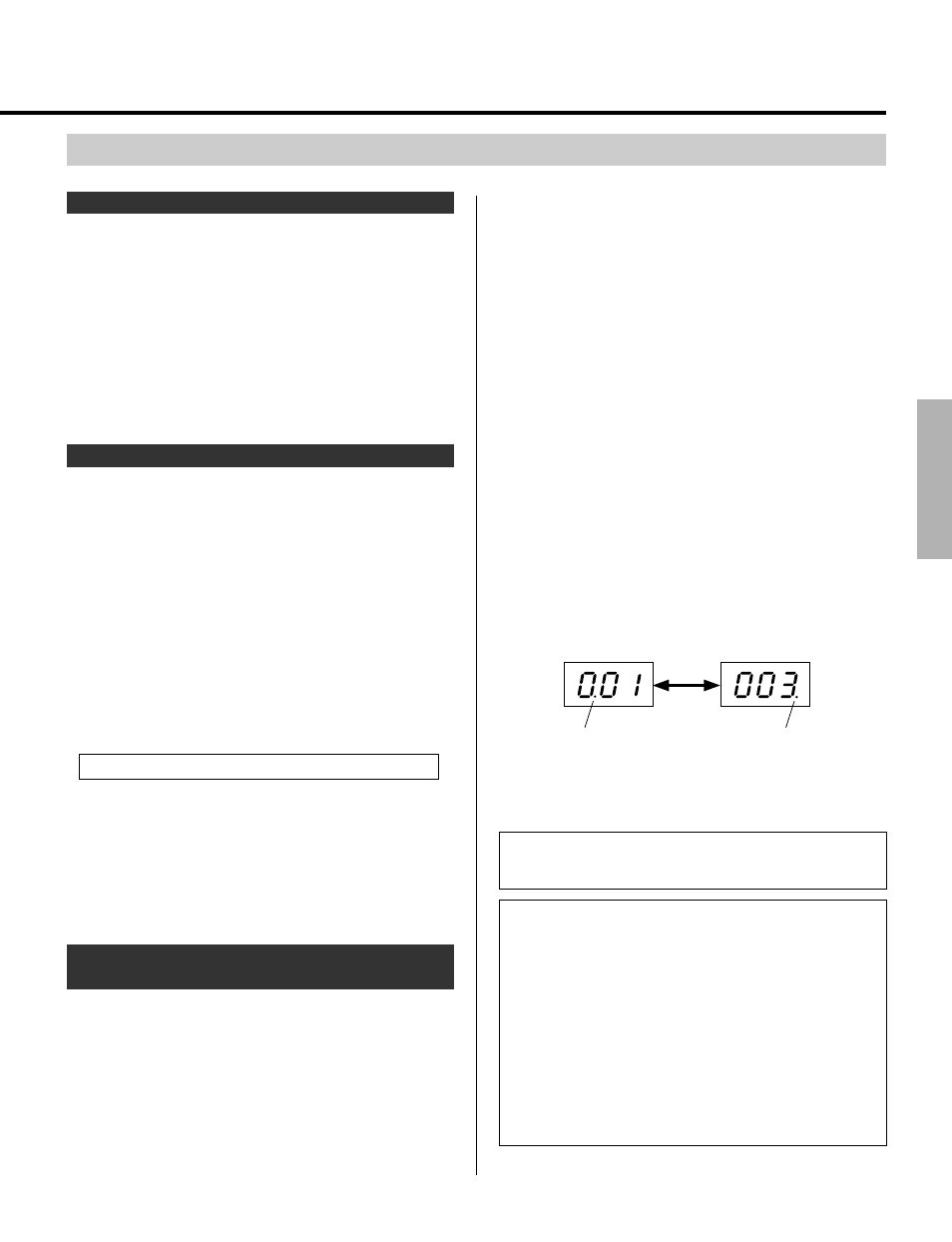
When entering MSB and LSB values, the LED display
alternately flashes the MSB and LSB values in hexadecimal
or decimal form.
Basic Operations
Value Entry — Some Specific Examples
and Anomalies
Entering Values
Value entry on the CBX-K2 can be done in two number
systems: Decimal and Hexadecimal. The keys labeled A
through F are for Hexadecimal entry.
● Entering a decimal value:
Hold down
C, press the appropriate function key,
enter the desired value in decimal format, then press
K.
● Entering a hexadecimal value:
Hold down
C, press the appropriate function key,
enter the desired value in hexadecimal format, then
press
J.
Example — Setting the MIDI Transmit Channel to 12:
Decimal:
C
+
{
→
1
→
2
→
K
Hexadecimal:
C
+
{
→
c
→
J
*
Also see the Decimal-Hexadecimal Conversion Chart
on page 33.)
● Entering MSB/LSB Values with K (3 digit bytes
for MSB, 3 digit bytes for LSB; 6 digits total message).
For messages beginning with zeroes, the first zeroes
can be omitted.
Examples:
*
3
→
K
: results in a value of MSB = 000, LSB = 003.
*
0
→
3
→
K
: results in a value of MSB = 000, LSB =
003.
NOTE
■
The order of MSB and LSB entry can be
reversed. (See MSB 1ST/LSB 1ST on page 28.)
NOTES ON THE BASIC OPERATION
■
If you inadvertently press two or more function keys
while performing a function, the last pressed key has
priority.
■
If, after entering a value, you press another function
key before pressing
L, the value will be can-
celled.
■
If you enter a value that is outside of a function’s
range, it will be ignored. Legal messages can be one
byte in length (a value from 0 – 255) exception for
Tempo value and Measure Number.
Display alternately flashes MSB and LSB
Dot in this position
indicates MSB.
Dot in this position
indicates LSB.
