2 read operations, Peripheral architecture – Texas Instruments VLYNQ Port User Manual
Page 15
www.ti.com
2.5.2
Read Operations
Address
translation
commands
Outbound
Outbound
command
FIFO
data
Return
FIFO
data
FIFO
Return
command
Inbound
FIFO
Registers
translation
Address
TxSM
8B/10B
encoding
Serializer
commands
Inbound
RxSM
Deserializer
decoding
8B/10B
Serial
TxData
Serial
RxData
System clock
Address
translation
Registers
commands
Inbound
translation
Address
commands
Outbound
8B/10B
decoding
FIFO
FIFO
command
Inbound
data
Return
FIFO
RxSM
Deserializer
RxData
Serial
encoding
8B/10B
VLYNQ Clock
command
Return
data
FIFO
Outbound
TxSM
Serializer
TxData
Serial
Slave
config bus
interface
VLYNQ Clock
System clock
Local VLYNC
Remote VLYNQ
Master
config bus
interface
Slave
config bus
interface
Master
config bus
interface
Peripheral Architecture
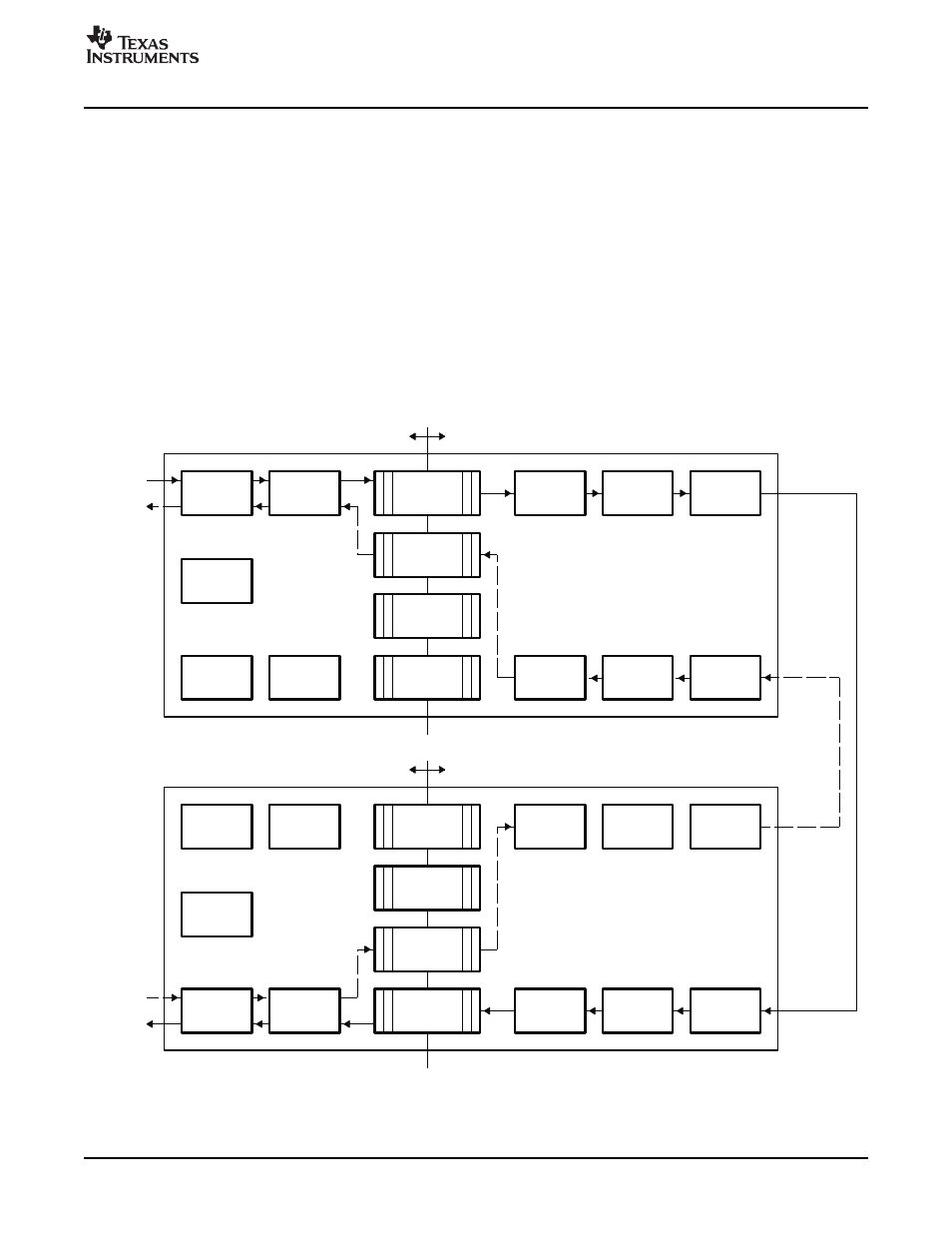
Read requests from the slave configuration bus interface are written to the outbound CMD FIFO (similar to
the write requests). Data is subsequently read from the FIFO and encapsulated into a read request
packet. The packet is encoded and serialized before it is transmitted to the remote device. Next, the
remote device deserializes, decodes the receive data, and writes the receive data to the inbound CMD
FIFO. After reading the address from the FIFO, a master configuration bus interface read operation
initiates in the remote device. When the remote master configuration bus interface receives the read data,
the data is written to the return data FIFO before it is encoded and serialized. When the receive data
reaches the local VLYNQ module, it is deserialized, decoded, and written to the return data FIFO (local
device). Finally, the read data is transferred on the local device’s slave configuration interface.
The data flow between two connected VLYNQ devices with read requests that originate from the DM644x
device is shown in
. The remote VLYNQ device returns the read data. Read data is shown with
dotted arrows.
Figure 6. Read Operations
SPRUE36A – September 2007
VLYNQ Port
15
