Texas Instruments TMS320DM643X DMP User Manual
Page 10
Divisor
+
UART input clock frequency
Desired baud rate
16
Processor
generator
Clock
DLH:DLL
UART input clock
DSP input clock
UART
Receiver
timing and
control
Transmitter
timing and
control
Baud
generator
BCLK
Other logic
Peripheral Architecture
www.ti.com
2
Peripheral Architecture
2.1
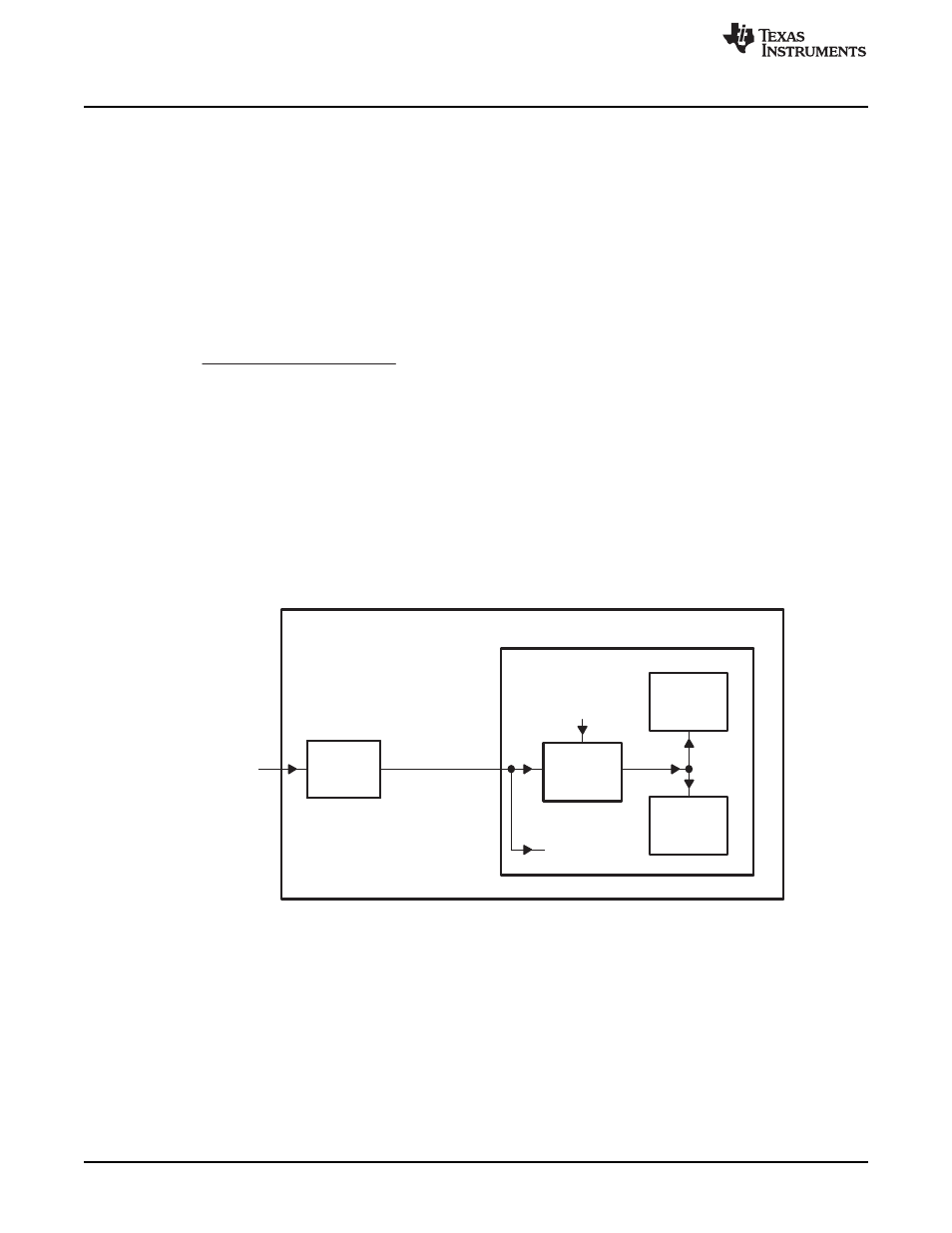
Clock Generation and Control
The UART bit clock is sourced from the PLLC1 AUXCLK. It supports up to 128 kbps maximum data rate.
is a conceptual clock generation diagram for the UART. The processor clock generator receives
a signal from an external clock source and produces a UART input clock with a programmed frequency.
The UART contains a programmable baud generator that takes an input clock and divides it by a divisor in
the range between 1 and (2
16
- 1) to produce a baud clock (BCLK). The frequency of BCLK is sixteen
times (16 ×) the baud rate; each received or transmitted bit lasts 16 BCLK cycles. When the UART is
receiving, the bit is sampled in the 8th BCLK cycle. The formula to calculate the divisor is:
(1)
Two 8-bit register fields (DLH and DLL), called divisor latches, hold this 16-bit divisor. DLH holds the most
significant bits of the divisor, and DLL holds the least significant bits of the divisor. For information about
these register fields, see
. These divisor latches must be loaded during initialization of the UART
in order to ensure desired operation of the baud generator. Writing to the divisor latches results in two wait
states being inserted during the write access while the baud generator is loaded with the new value.
summarizes the relationship between the transferred data bit, BCLK, and the UART input clock.
Example baud rates and divisor values relative to a 27-MHz UART input clock are shown in
Figure 2. UART Clock Generation Diagram
10
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
SPRU997C – December 2009
Copyright © 2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated
