Sync connector, Pll ref connector, Figure 33. sync output and duty cycle – National Instruments 5411 User Manual
Page 20: Sync connector -3 pll ref connector -3, Figure 3-3, Sync output and duty cycle -3
Chapter 3
Signal Connections
© National Instruments Corporation
3-3
DAQArb 5411 User Manual
SYNC Connector
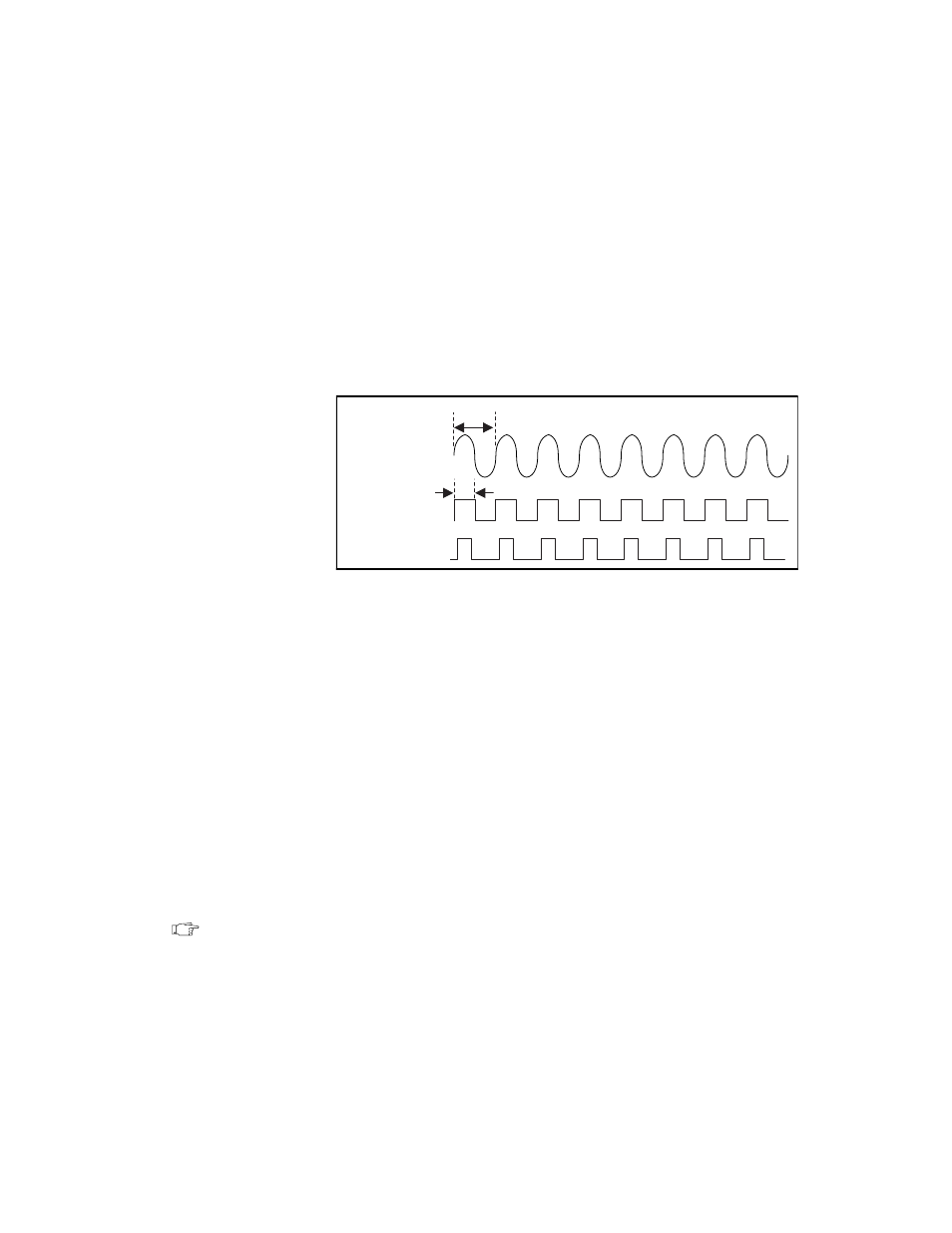
The SYNC connector is a transistor-transistor-logic (TTL) version of
the sine waveform being generated at the output. You can think of the
SYNC output as a very high frequency resolution,
software-programmable clock source for many applications. You can
also vary the duty cycle of SYNC output on the fly by software control,
as shown in Figure 3-3. t
p
is the time period of the sine wave being
generated and t
w
is the pulse width of the SYNC output. The duty cycle
is (t
w
/t
p)
x 100%.
Figure 3-3. SYNC Output and Duty Cycle
You can route the SYNC output to the RTSI lines over the RTSI bus.
The SYNC output is derived from a comparator connected to the analog
waveform and is intended to be used when the waveform is a sine
function. The SYNC output will provide a meaningful waveform only
when you are generating a sine wave on the ARB output. For more
information on SYNC output, see Chapter 4, Arb Operation.
PLL Ref Connector
The PLL Ref connector is a phase-locked loop (PLL) input connector
that can accept a reference clock from an external source and phase lock
the DAQArb internal clock to this external clock. The reference clock
should not deviate more than ±100 ppm of its nominal frequency. The
minimum amplitude levels of 1 V
pp
are required on this clock. You can
lock reference clock frequencies of 1 MHz and 5–20 MHz in 1 MHz
steps.
Note:
You can also lock the DAQArb 5411 to other National Instruments cards
over the RTSI bus using the 20 MHz RTSI clock signal.
ARB Output
t
p
SYNC Output
(50% Duty Cycle)
SYNC Output
(33% Duty Cycle)
t
w
