Qos > diffserv settings, Chapter, Configuring the switch – Linksys SRW224G4P User Manual
Page 37
Chapter
Configuring the Switch
24-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Ggabt Swtch wth WebVew and Power over Ethernet
The Switch supports a common method of prioritizing
layer 3/4 traffic to meet application requirements . Traffic
priorities can be specified in the IP header of a frame
using the priority bits in the Type of Service (ToS) octet . If
priority bits are used, the ToS octet may contain six bits for
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) service . When
these services are enabled, the priorities are mapped to
a Class of Service value by the Switch and the traffic then
sent to the corresponding output queue . Because different
priority information may be contained in the traffic, the
Switch maps priority values to the output queues in the
following manner:
The precedence for priority mapping is DSCP Priority and
then Default Port Priority .
To enable DSCP priority mapping, check the DSCP Prorty
Status Enabled checkbox .
Prorty Status
Enables the DSCP priority mapping .
(Enabled is the default setting .)
DSCP to CoS
Maps Differentiated Services Code Point
values to CoS values .
Click Save Settngs to save the changes .
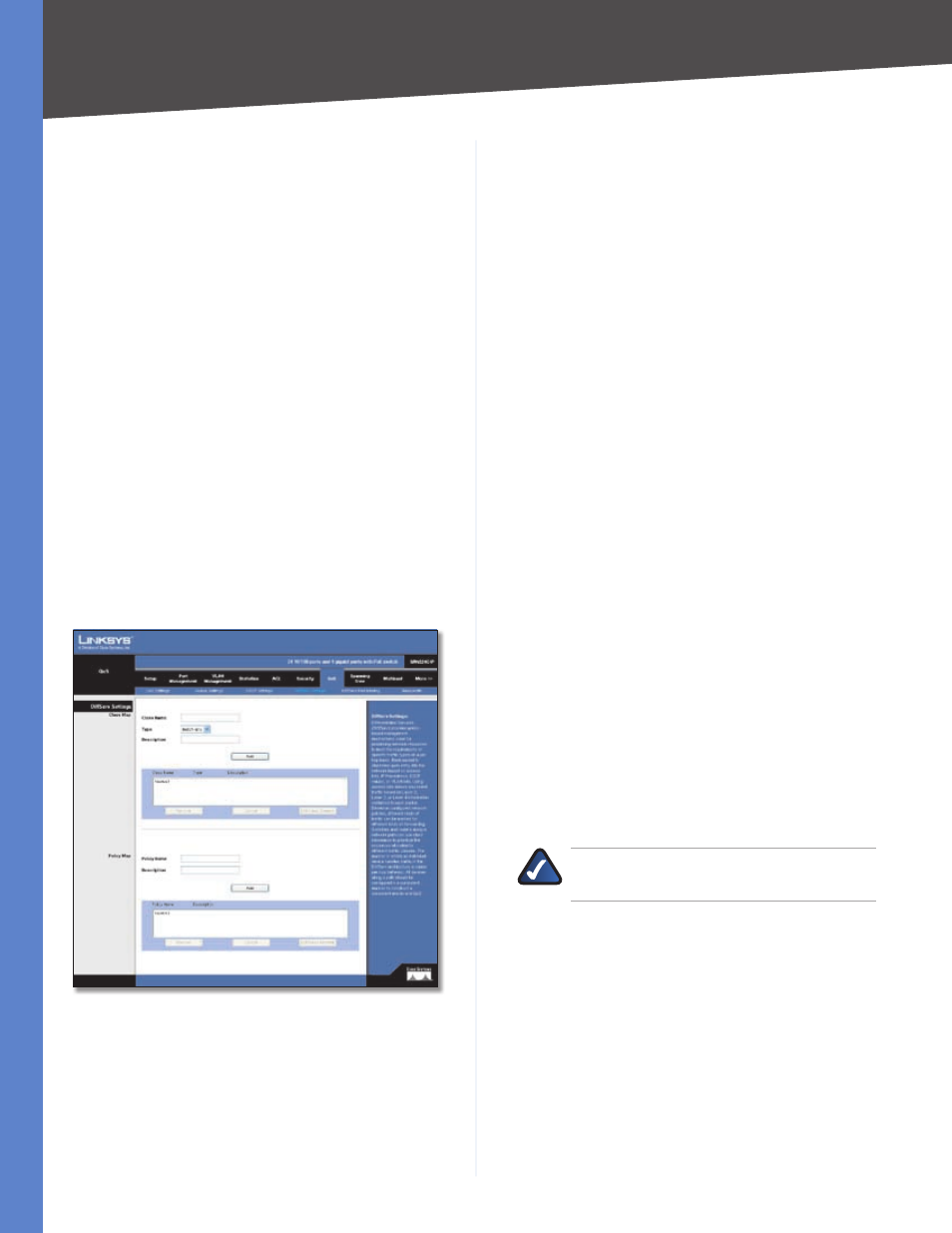
QoS > DiffServ Settings
QoS > DiffServ Settings
The commands described in this section are used to
configure Quality of Service (QoS) classification criteria
and service policies . Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
provides policy-based management mechanisms used for
prioritizing network resources to meet the requirements
of specific traffic types on a per hop basis . Each packet is
classified upon entry into the network based on access
lists, IP Precedence, DSCP values, or VLAN lists . Using
access lists allows you to select traffic based on Layer 2,
Layer 3, or Layer 4 information contained in each packet .
Based on configured network policies, different types of
traffic can be marked for different types of forwarding .
All switches or routers that access the Internet rely on class
information to provide the same forwarding treatment
to packets in the same class . Class information can be
assigned by end hosts, or switches or routers along the
path . Priority can then be assigned based on a general
policy, or a detailed examination of the packet . However,
note that detailed examination of packets should take
place close to the network edge so that core switches
and routers are not overloaded . Switches and routers
along the path can use class information to prioritize the
resources allocated to different traffic classes . The manner
in which an individual device handles traffic in the DiffServ
architecture is called per-hop behavior . All devices along
a path should be configured in a consistent manner to
construct a consistent end-to-end QoS solution .
Class Map
A class map is used for matching packets to a specified
class . The class map uses the Access Control List filtering
engine, so you must also set an ACL to enable filtering for
the criteria specified in the class map .
The class map is used with a policy map to create a
service policy for a specific interface that defines packet
classification, service tagging, and bandwidth policing .
NOTE:
One or more class maps can be assigned
to a policy map .
Class Name
Name of the class map . (Range: 1-32
characters)
Type
Only one match command is permitted per class
map, so the match-any field refers to the criteria specified
by the lone match command .
Descrpton
A brief description of a class map . (Range: 1-
256 characters)
Add
Creates a new class map using the entered class
name and description .
Remove
Removes the selected class from the list .
Edt Class Element
Modifies the class map criteria used
to classify ingress traffic .
