How sampling mode is organized, In sampling mode, Samples and multisamples – KORG TR Music Workstation Operation Guide 2E ii User Manual
Page 93: In sampling mode samples and multisamples, 87 basic functions, Samples, Sampling mode, Sampling frequency and bit resolution
87
Basic functions
Sampling mode
• Sample names and multisample names of up to 16
characters can be assigned. Sample names and
multisample names can also be viewed in Media
mode (
☞
PG p.143 “Translation”).
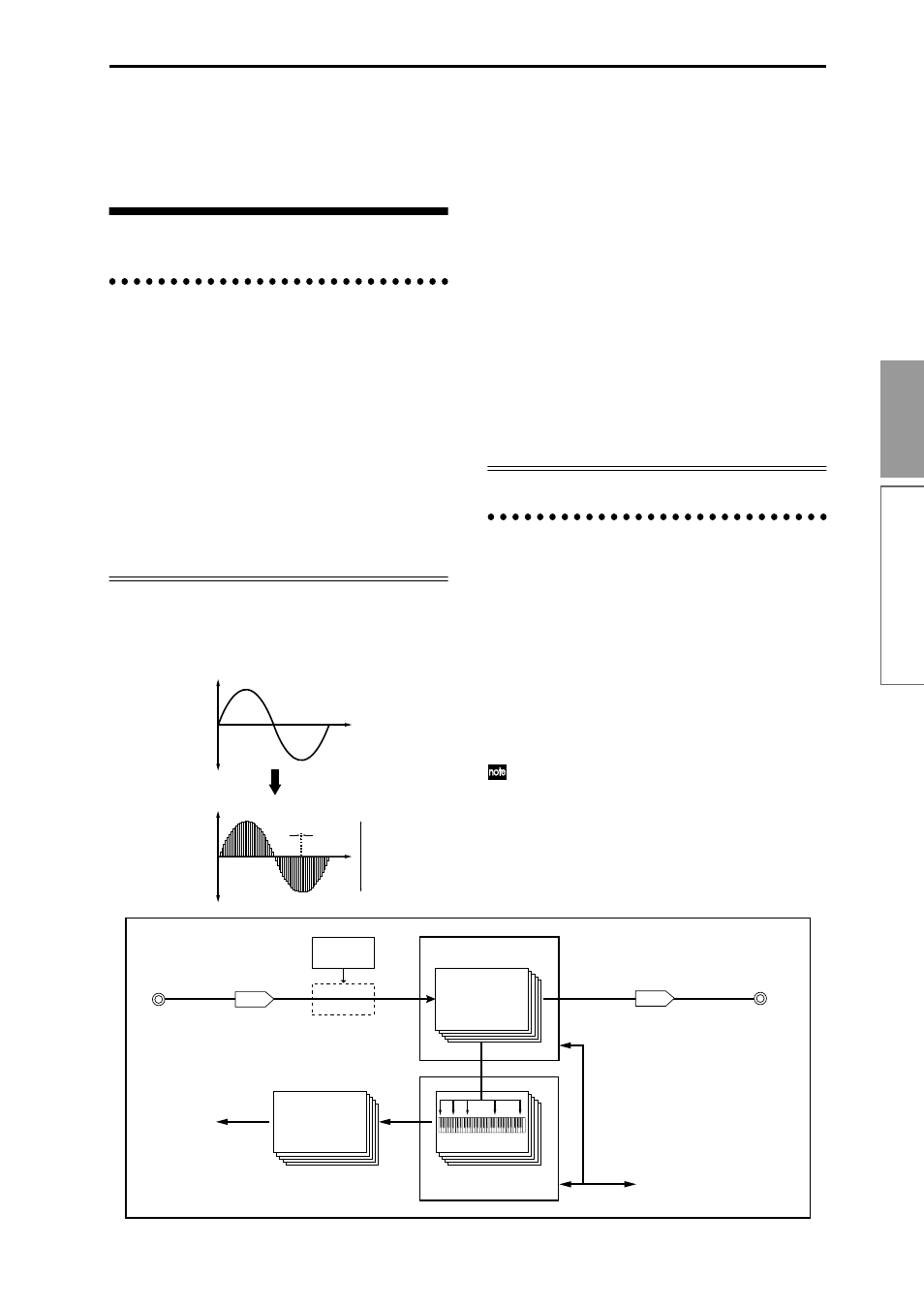
How Sampling mode is organized
In Sampling mode
• An external audio signal from an external audio
device or microphone connected to the AUDIO
INPUT 1 and 2 jacks is passed through an analog/
digital convertor, and recorded (sampled).
• You can edit the waveform and loop settings etc. of
sample data that you sampled or that you loaded
from an SD card, CD-ROM etc., in Media mode.
• You can assign samples to the keyboard to create a
multisample. These samples and multisamples can
be easily converted to a program using the Utility
menu command “Conv. To Program,” and these
programs can be used immediately in a
combination or a song.
Sampling frequency and bit resolution
As shown in the diagram, sampling reads the level of
the analog signal at fixed intervals along the time axis,
and stores the levels in memory as digital data.
The “fixed intervals” mentioned above are generally
expressed as the “sampling frequency.” 48 kHz (kilo-
hertz) means that sampling is performed 48,000 times
each second, and that the interval is 1 (second)/48,000
(times) = approximately 0.00002083 (seconds) =
approximately 0.02083 mS (millisecond).
The higher the sampling frequency is, the closer to the
original analog signal the waveform in memory will
be.
Each level is read, and converted into digital data. The
accuracy at this time is determined by the bit resolu-
tion. This process converts an analog signal with infi-
nite resolution into a digital signal with finite
resolution. With 16 bit resolution, each level is indi-
cated in 65,536 steps (the sixteenth power of two).
The greater the bit resolution is, the closer to the origi-
nal analog signal the waveform in memory will be.
48 kHz 16 bit sampling is the same quality as in audio
devices such as DAT. A CD uses 44.1 kHz 16 bit sam-
pling, which is a slightly lower sampling frequency.
Samples and Multisamples
Samples
The data that is recorded (sampled) into internal mem-
ory or loaded from a file is referred to as a sample or
sample file. Samples consist of the actual waveform
data, and parameters that specify how the data will be
played back, such as Start, Loop Start, and End
Address. Samples can be used in multisamples and
drum kits.
The TR can hold a maximum of 4,000 samples in its
internal memory.
The TR can share a single waveform among multi-
ple samples. This allows you to create multiple
samples with different playback addresses from
the same waveform without wasting internal
memory. For example, suppose that you have
waveform data that records a voice saying “One-
Two-Three.” This single piece of waveform data
could be shared by three samples, with the play-
RAM (SIMM memory):
Expandable to 64 MB
AUDIO INPUT jack Analog/digital
convertor
Digital/analog
convertor
AUDIO OUTPUT
jack
Analog signal
Digital signal
Analog signal
Digital signal
SD card, SCSI media (Media mode)
RAM (internal memory)
Used by combinations
and songs
ADC
Insert Effect
Sample 0000 ... 3999
Multisample 000 ... 999
Program
DAC
Sampled digital
waveform
Level
Time
Time
Analog waveform
16bit
= 65,536 levels
of data
48kHz
= 48,000 times every second
= 0.0208 mS cycle
Level
