Table 13. redundancy options, 87 appendix a redundancy alternatives – State Industries FANUC GFK-0827 User Manual
Page 97
A
GFK-0827
87
Appendix A Redundancy Alternatives
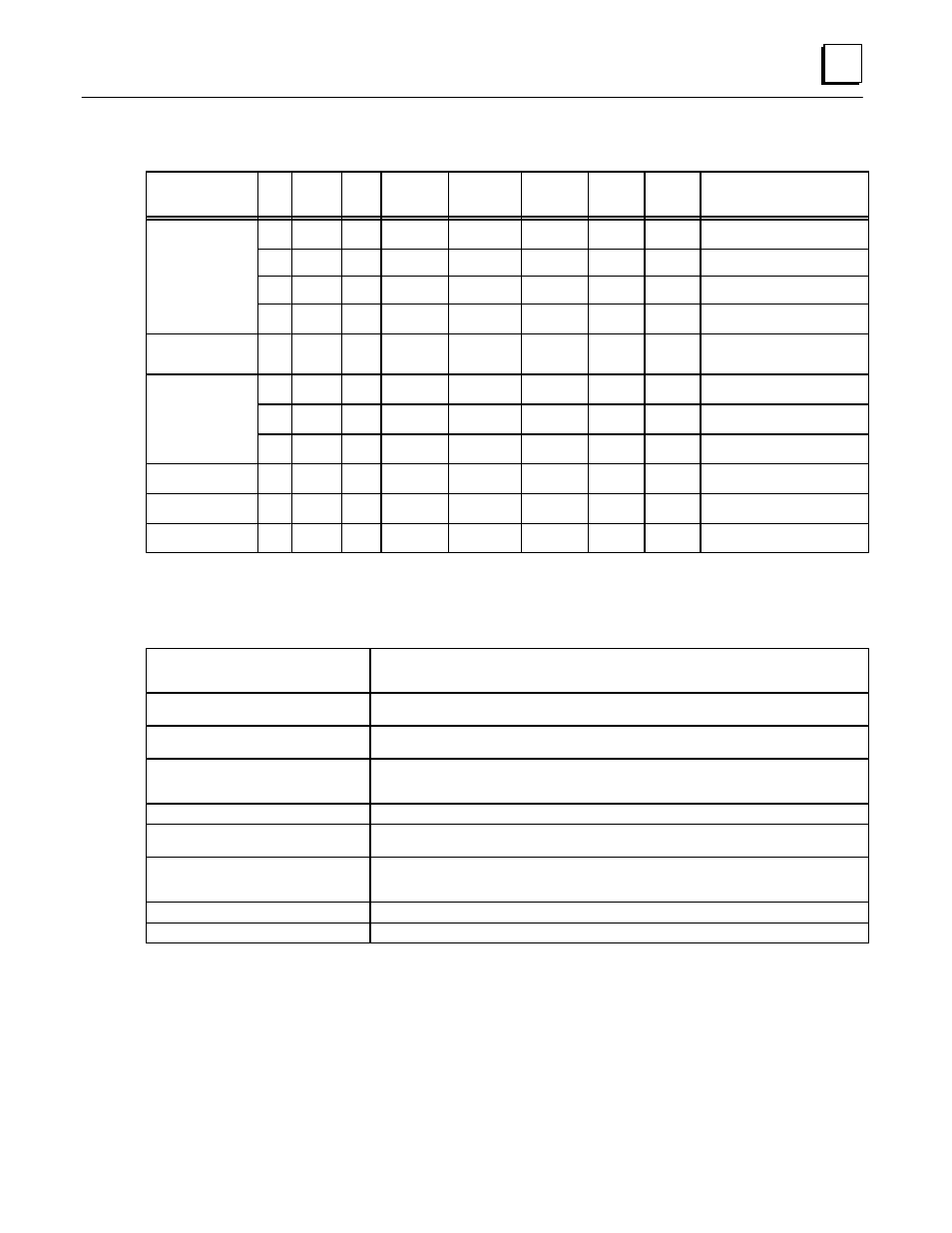
Table 13. Redundancy Options
Option
Key
PLC
Scan
Sync
Data
Sync
I/O System
Output
Selection
Method
Redund.
Bus
Redund.
I/O
Selection Guide
1A
2 90-70s
no
Application
Logic
[
90-70
(I/O Scanner)
Hot
Standby
yes - 2
no
Higher Density Analog Inputs
Hot Standby
1B
2 90-70s
no
Application
Logic
[
90-30
(GCM+)
Hot
Standby
yes - 2
no
More competitive I/O
Application
1C
2 90-70s
no
Application
Logic
[
Genius I/O
Hot
Standby
yes - 2
no
Highly distributable with diagnos-
tics. Thermocouple. RTD
1D
2 90-70s
no
Application
Logic
[
90-30
(GCM+)
Hot
Standby
yes - 2
no
Least expensive. Limited to
512 Inputs, 512 Outputs
Hot Standby
Product plus
Application Logic
2
2 90-70s
yes
Operating
System
Function
90-30
(GCM+)
Hot
Standby
yes - 2
no
Redundant Bus Applications.
More competitive I/O.
3A
2 90-70s
yes
Operating
System
90-70
(I/O Scanner)
Hot
Standby
no
no
Higher Density Analog Inputs
Hot Standby Product
3B
2 90-70s
yes
Operating
System
90-30
(GCM+)
Hot
Standby
no
no
More competitive I/O.
3C
2 90-70s
yes
Operating
System
Genius I/O
Hot
Standby
no
no
Highly Distributable with diagnos-
tics. Thermocouple. RTD.
ESD Duplex
Application Logic
4
2 90-70s
no
no
Genius I/O
Duplex
yes - 2
yes
For Fail-Safe ESD applications.
ESD Duplex
GMR Product
5A
2 90-70s
no
no
Genius I/O
GMR
yes - 2
or 3
yes
For Fail–Safe or fault tolerant ESD
applications.
ESD Triplex
GMR Product
5B
3 90-70s
no
no
Genius I/O
GMR
yes - 3
yes
For fault tolerant ESD applications.
[ See list of restrictions below.
Explanation of terms used in the above Table of Redundancy Options.
Hot Standby Redundancy
Two CPUs are connected to one or more I/O. One CPU is active; the other is in standby. If the active
unit fails, the standby unit takes control of the process (Hot Standby Redundancy is sometimes
known as Hot Backup Redundancy).
Scan Synchronization
Scan mechanisms may be synchronized to keep active and standby units in lockstep to minimize
”bumps” or upsets to the process when switching from active to standby unit.
Data Synchronization
Keeps standby unit refreshed with the current state of the active unit to minimize ”bumps” or upsets
to the process when switching from active to standby unit.
Emergency Shutdown System (ESD)
Two or three unsynchronized CPUs solve logic asynchronously based on common inputs. Output
state is voted on by the output devices. The inputs and outputs are normally energized and do not
change state. DUPLEX ESD is Failsafe while TRIPLEX ESD is fault tolerant.
Application Logic-Based Solutions
Has many restrictions (see the list of restrictions on page 13).
Product Solutions
Has functions built into the operating system that make the system easier to engineer and more
robust. Product solutions are preferable to application solutions from a support perspective.
Output Selection Method
Refers to the algorithm in the I/O device, such as Hot Standby, Duplex, or No Redundancy Modes.
These modes may refer to existing Genius I/O terminology. GMR (Genius Modular Redundancy)
mode is a voting algorithm available in Genius I/O DC blocks.
Fail Safe
An ESD system will fail such that the process under supervision will be shutdown.
Fault Tolerant
In an ESD system any single failure will not disrupt the process under supervision.
