Synchronous scan, First data transfer %i, %ai and synchronization – State Industries FANUC GFK-0827 User Manual
Page 70
4
59
GFK-0827
Chapter 4 Operation
Synchronous Scan
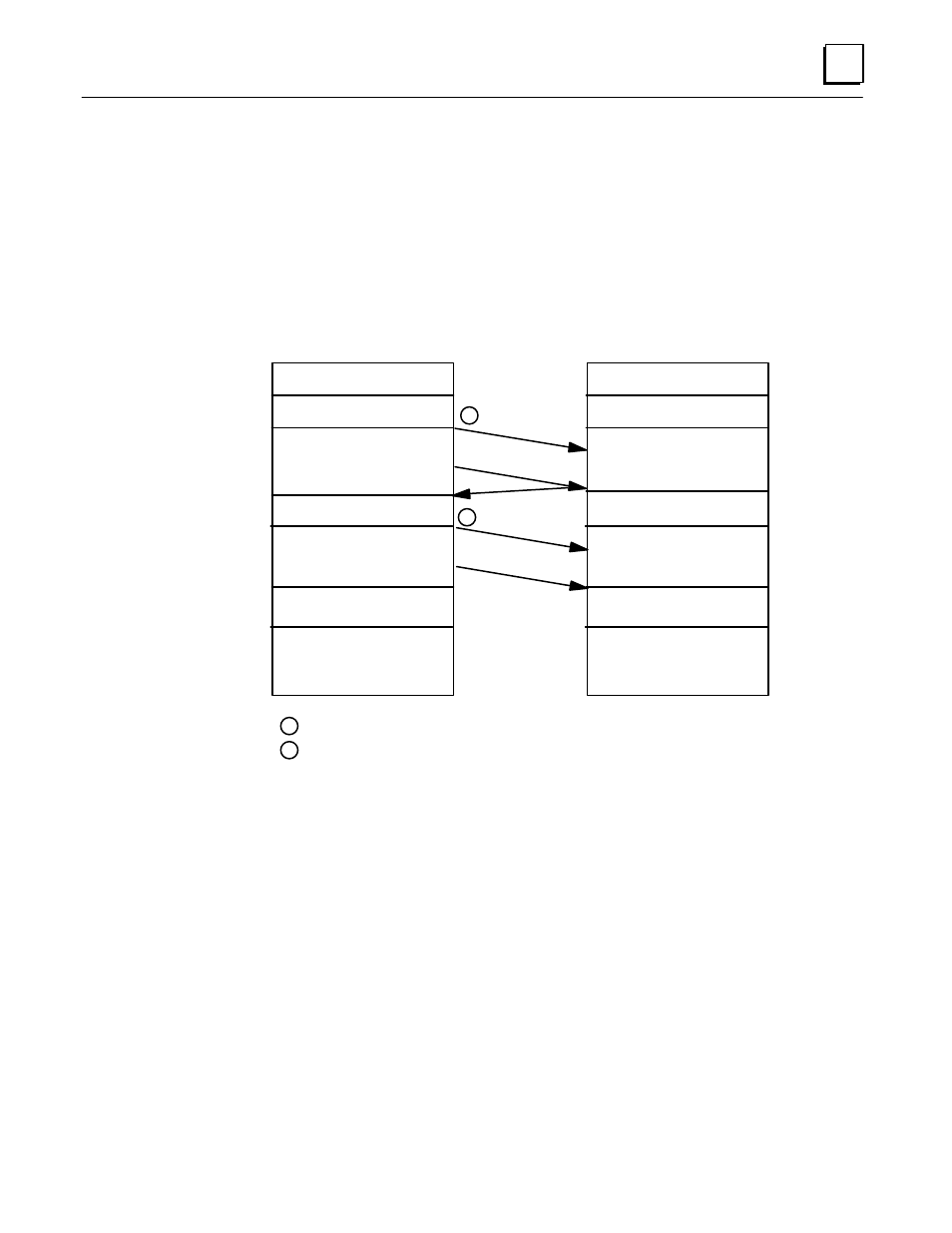
The figure below shows the sweep components for the active and the backup CPUs. It
shows the two communication points in the sweep. The first communication point is
immediately after the inputs are scanned. At this point in the sweep the newly read
inputs are sent from the active CPU to the backup CPU and synchronization information
is passed. In the second communication point, the rest of the data (outputs, internal
references, registers) is sent from the active PLC to the backup.
1
ЙЙЙЙЙЙ
ЙЙЙЙЙЙ
ЙЙЙЙЙЙ
ЙЙЙЙЙЙ
ЙЙЙЙЙЙ
ЙЙЙЙЙЙ
ACTIVE CPU
Housekeeping
Input Scan
Send Inputs
and
Synchronize
Logic Solution
Send Outputs
and
Other Data
Output Scan
Windows
and
Run-Time Diagnostics
BACKUP CPU
Housekeeping
Input Scan
Receive Inputs
and
Synchronize
Logic Solution
Receive Outputs
and
Other Data
Output Scan
Windows
and
Run-Time Diagnostics
D A T
A
D A T
A
2
1
2
First Data Transfer Occurs: %I, %AI and Synchronization
Second Data Transfer Occurs: %Q, %AQ, %R, %M
a47008
Figure 8. Active and Backup Sweeps
First Data Transfer %I, %AI and Synchronization
There are two points in the sweep where the active CPU will transfer data to the backup
unit. The first data transfer will occur immediately after the Input Scan has occurred.
The active unit will send all of the configured input data, both discrete (%I) and analog
(%AI), to the backup unit. For discrete data, the status, override, and transition
information is all transferred; if point faults are configured, point fault data is also sent.
This data will overwrite the current input data in the backup unit.
In addition to the input data transfer, a synchronizing message containing the ”Start of
Sweep Time” will be sent from the active unit to the backup unit as soon as the input
data has been transferred. The CPU’s will stay in synchronization because the active
unit will wait on the backup CPU to respond to the synchronizing message before
starting its sweep.
