Overview of egd, Exchange – GE GFK-1541B User Manual
Page 151
5-2
TCP/IP Ethernet Communications for the Series 90™ PLC User's Manual
–
May 2002
GFK-1541B
5
Overview of EGD
This section describes Ethernet Global Data in general terms. It also provides key information
you need to plan and configure your Ethernet Global Data system.
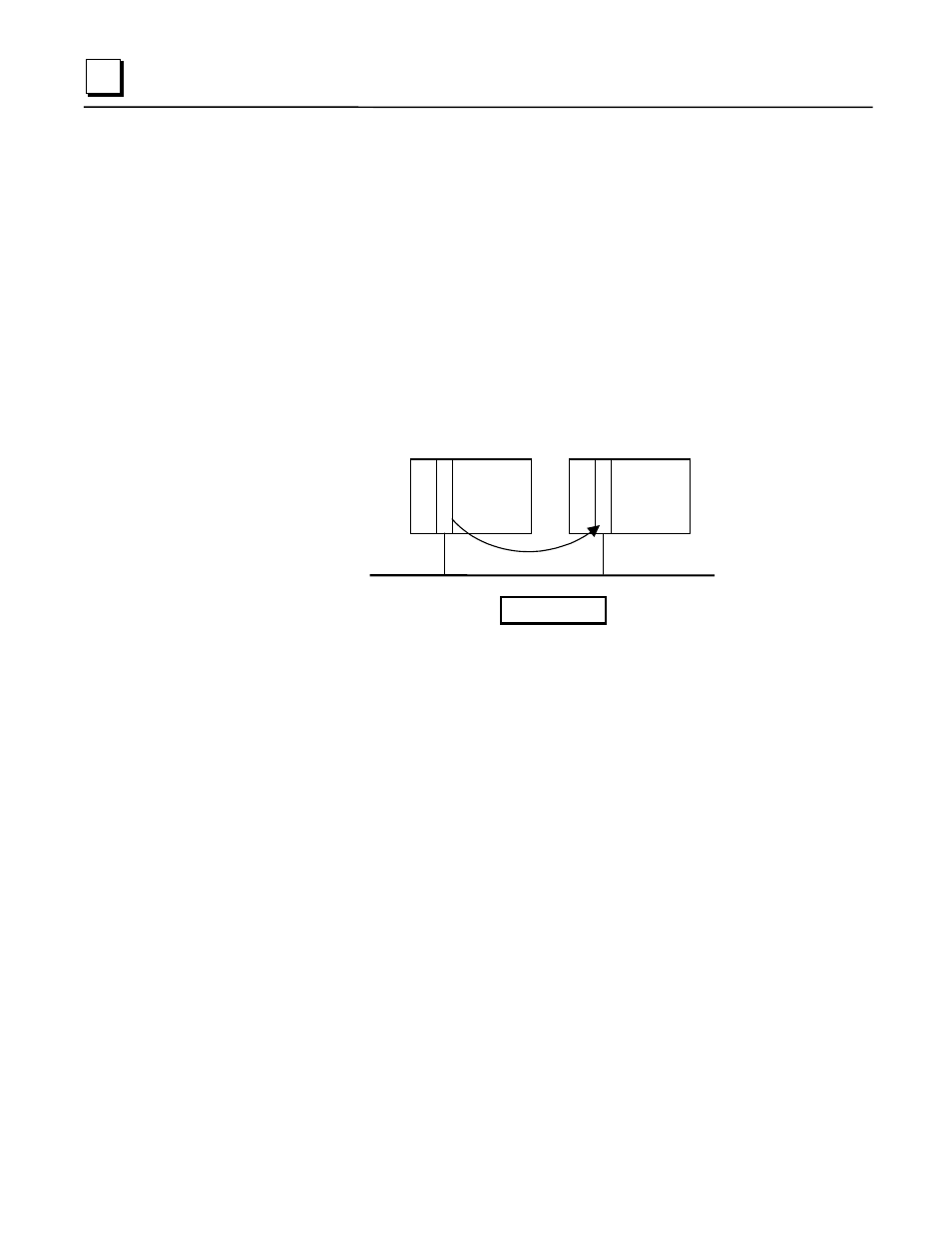
Ethernet Global Data allows one device (the producer) to share a portion of its internal memory
(the exchange) with one or more other devices (the consumers) at a regularly scheduled periodic
rate. This exchange is uniquely distinguished by a set of identifiers, the Producer ID and
Exchange ID
. The Producer ID is assigned to uniquely identify the Ethernet Global Data device
that produces the exchange on the network. The Exchange ID is a value identifying a specific
exchange
within that producing device.
Ethernet Global Data is configured using Windows-based PLC programming software (if
supported).
PLC1 - Producer
PLC2 - Consumer
P
C
Exchange
Ethernet Network
Caution
Ethernet Global Data is designed for simple, efficient communication of
sampled data between devices. It is not intended for event notification where
the possible loss of a sample of data would be significant. For event
notification, it is recommended that an Establish Read/Write Channel
command be used. See Chapter 3, “Programming SRTP Channel
Commands”, for more information.
Note
A single Ethernet Interface can be configured to both produce and consume
Ethernet Global Data at the same time, using separate exchanges.
Exchange
The exchange refers to a set of variables or memory locations that contain an internal snapshot of
memory within the PLC or other device. The Exchange ID is the value you assign to a particular
exchange that identifies it uniquely within a particular producer. You must configure an
exchange in both the producer and the consumer.
Configuring the Exchange
Exchanges are configured by filling out parameters in the Ethernet Global Data dialog box of the
PLC programming software for both the producer PLC and consumer PLC and then storing each
configuration to its associated PLC. These parameters define the content of an exchange as well
as its operational characteristics. A variable that has already been created in hardware
configuration, the program editors, or the Variable Declaration Editor window can be used in an
exchange. Or, you can create new variables in the Ethernet Global Data dialog box.
