Reference system on milling machines, Designation of the axes on milling machines, 1 f undamentals – HEIDENHAIN TNC 620 (73498x-01) ISO programming User Manual
Page 77
HEIDENHAIN TNC 620
77
3.1 F
undamentals
Reference system on milling machines
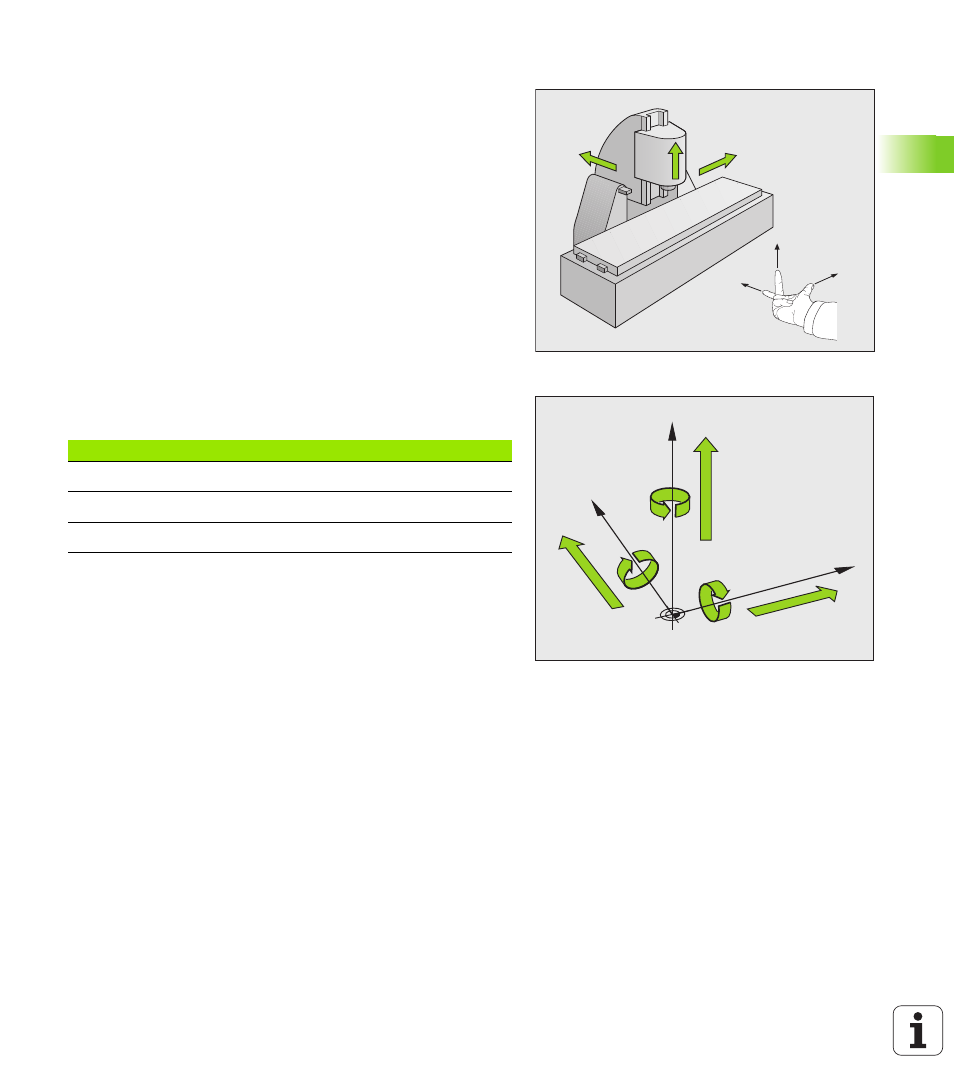
When using a milling machine, you orient tool movements to the
Cartesian coordinate system. The illustration at right shows how the
Cartesian coordinate system describes the machine axes. The figure
illustrates the right-hand rule for remembering the three axis
directions: the middle finger points in the positive direction of the tool
axis from the workpiece toward the tool (the Z axis), the thumb points
in the positive X direction, and the index finger in the positive Y
direction.
The TNC 620 can control up to 5 axes optionally. The axes U, V and W
are secondary linear axes parallel to the main axes X, Y and Z,
respectively. Rotary axes are designated as A, B and C. The illustration
at lower right shows the assignment of secondary axes and rotary
axes to the main axes.
Designation of the axes on milling machines
The X, Y and Z axes on your milling machine are also referred to as tool
axis, principal axis (1st axis) and minor axis (2nd axis). The
arrangement of the tool axis is decisive for the assignment of the
principal and minor axes.
+X
+Y
+Z
+X
+Z
+Y
W+
C+
B+
V+
A+
U+
Y
X
Z
Tool axis
Principal axis
Minor axis
X
Y
Z
Y
Z
X
Z
X
Y
