Fiber overview, Wavelength-division, Multiplexing (wdm) – Grass Valley FXC-S201 User Manual
Page 10: Wavelength-division multiplexing (wdm)
6
System Overview
Fiber Overview
Fiber Overview
Fiber Optics and Fiber Optic Cable are at the heart of the CommLink FXC-S201 Fiber Optic
Intercom Link Fiber Optic Intercom Link System. The Commlink system features the ability
to multiplex and de-multiplex a variety of video, audio, and data signals so that they can be
carried over a thin strand of Fiber Optic cable for long distances.
The specific theory and operation of Fiber Optics is beyond the scope of this document, but
you need to be aware of the different types of Fiber Optic Cable and Fiber Optic Cable
Connectors. Most CommLink FXC-S201 Fiber Optic Intercom Link applications will use
Single Mode Fiber with ST Connectors.
Fig. 2-1: Single Mode Fiber Optic Cable Cross-Section
Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Fiber optic communication is enhanced by the use of Wavelength-Division Multiplexing
(WDM). With WDM, multiple optical carrier signals can be carried on a single optical fiber by
using different wavelengths of laser light for each carrier. The full theory of WDM is beyond
the scope of this manual, but it is important to understand that by using equipment with
different transmitter wavelengths on opposite ends of a fiber optic cable, signals can be
sent in both directions over that single cable.
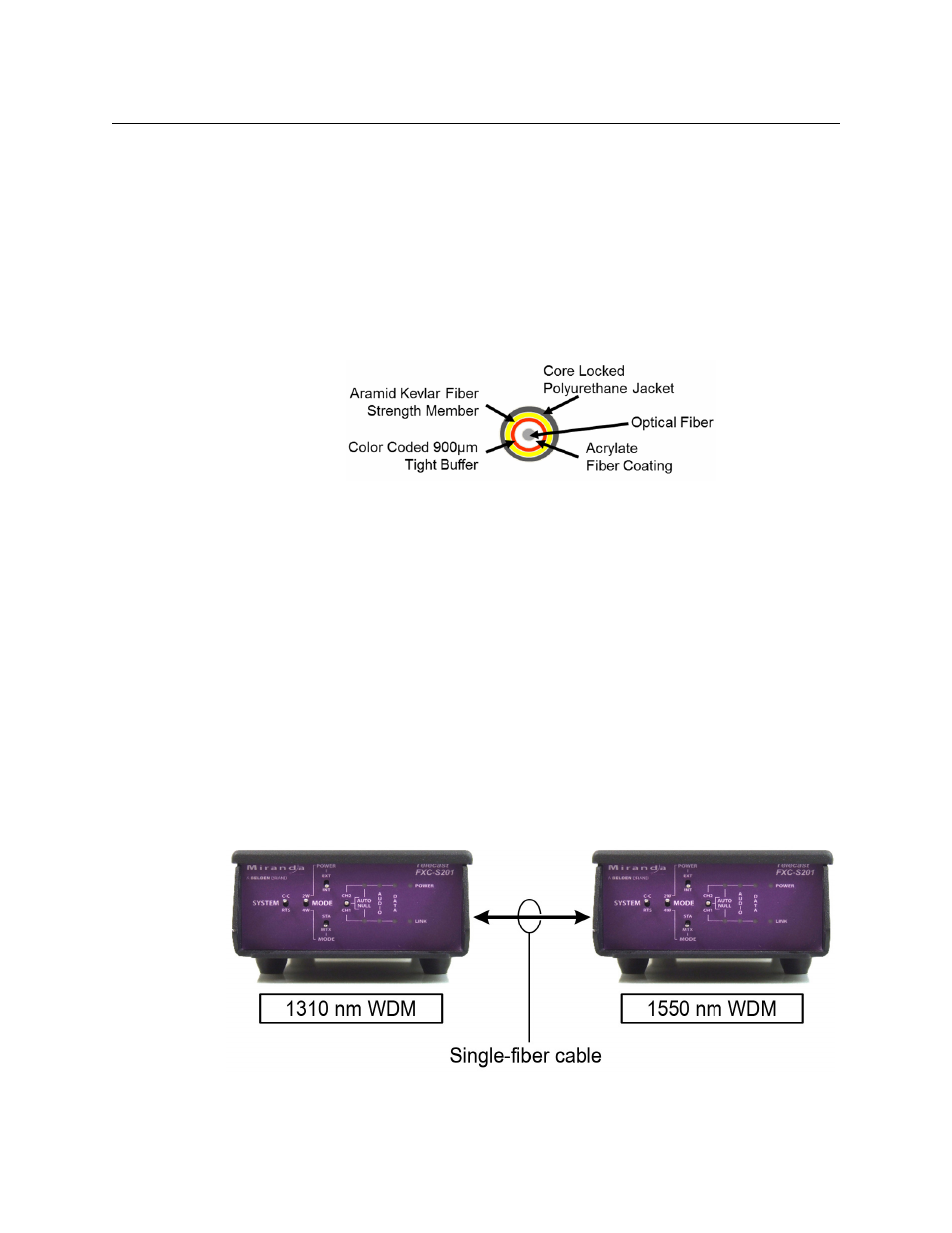
CommLink FXC-S201 units intended for WDM use are available with transmitter
wavelengths of 1310 nm and 1550 nm, and a WDM link requires one of each, as illustrated
in
.
Two units with the same transmit wavelength will not work for WDM operation over a
single-fiber cable.
Fig. 2-2: Pairing Different WDM Factor CommLink Units
