Amer Networks SS2GD8IP User Manual
Page 162
Publication date:Dec., 2010
Revision B1
150
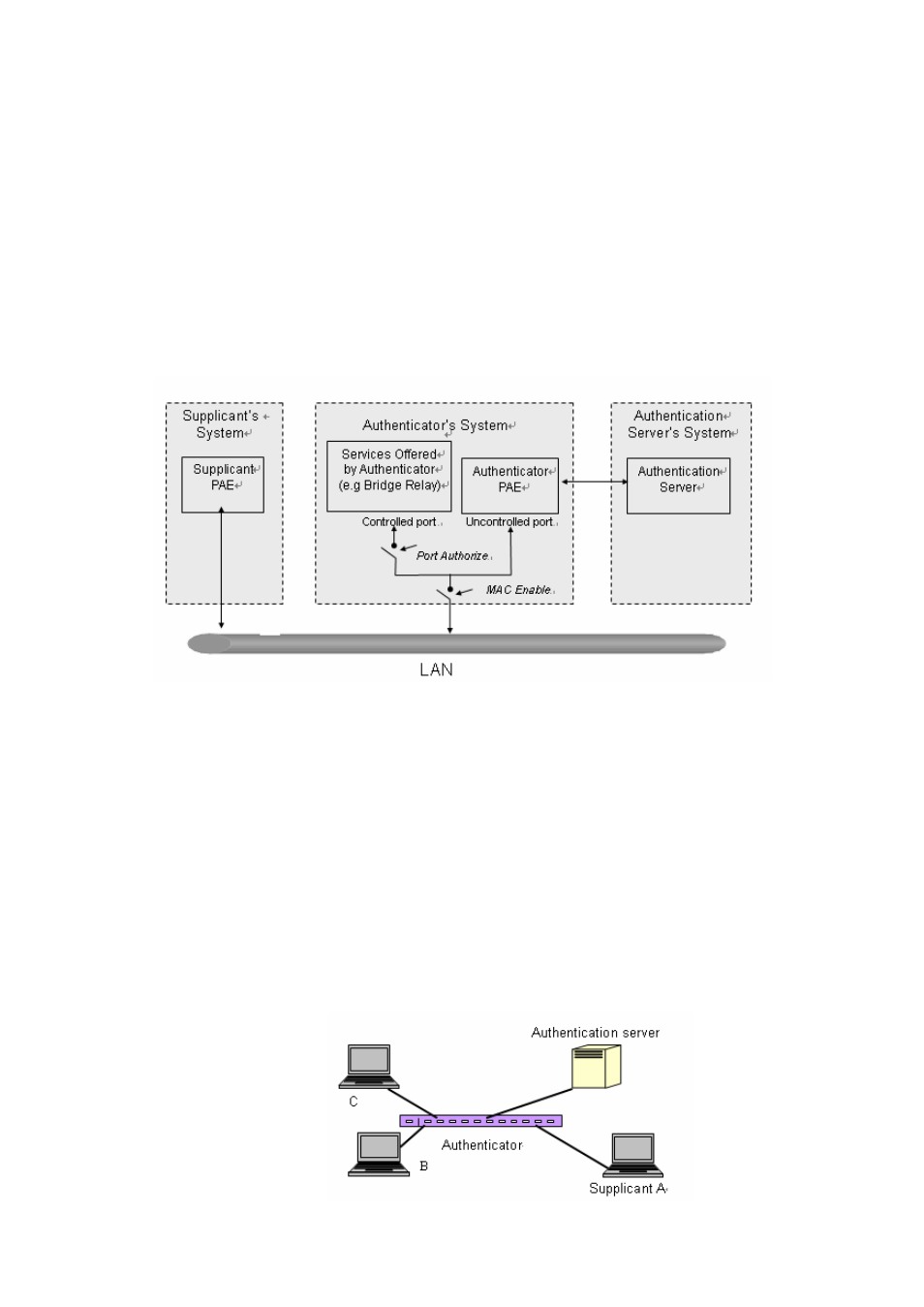
The overview of operation flow for the Fig. 3-53 is quite simple. When
Supplicant PAE issues a request to Authenticator PAE, Authenticator and
Supplicant exchanges authentication message. Then, Authenticator
passes the request to RADIUS server to verify. Finally, RADIUS server
replies if the request is granted or denied.
While in the authentication process, the message packets, encapsulated
by Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPOL), are exchanged
between an authenticator PAE and a supplicant PAE. The Authenticator
exchanges the message to authentication server using EAP
encapsulation. Before successfully authenticating, the supplicant can
only touch the authenticator to perform authentication message
exchange or access the network from the uncontrolled port.
Fig. 3-53
In the Fig. 3-54, this is the typical configuration, a single supplicant, an authenticator
and an authentication server. B and C is in the internal network, D is Authentication
server running RADIUS, switch at the central location acts Authenticator connecting
to PC A and A is a PC outside the controlled port, running Supplicant PAE. In this
case, PC A wants to access the services on device B and C, first, it must exchange
the authentication message with the authenticator on the port it connected via
EAPOL packet. The authenticator transfers the supplicant’s credentials to
Authentication server for verification. If success, the authentication server will notice
the authenticator the grant. PC A, then, is allowed to access B and C via the switch.
If there are two switches directly connected together instead of single one, for the
link connecting two switches, it may have to act two port roles at the end of the link:
authenticator and supplicant, because the traffic is bi-directional.
Fig. 3-54
