Iii. getting started, 10 steps to get the nrc online – SP Controls PX2-NRC-1142 User Manual
Page 4
III. Getting Started
Configuring the NRC to Operate Without Network Control
Some users will wish to take advantage of the NRC control capabilities without using its network inter-
face. If this is what you wish to do, follow the first four steps of the configuration process described in
this section in order to connect your PC to the NRC for configuration. Then Proceed to Chapter IV.
Basic Configuration and configure the unit directly from your PC.
Important: If you do not plan to put your NRC online, you will need to download the NRC and Puck
drivers you need from our website before configuring the NRC:
http://www.spcontrols.com/downloads_index.php
The first time you connect for configuration, the NRC will automatically create the appropriate driver
directories on your hard drive. You can also add the new directory locations yourself :
NRC projector/monitor drivers: C:\~\My Documents\SP Controls\smartpanel\drivers
Puck RS-232 or IR drivers: C:\~\My Documents\SP Controls\nrc\drivers
10 steps to get the NRC online
Step 1: Get answers to these questions from your network administrator
•
Will the NRC use a static IP address or DHCP?
•
If the NRC will be using a static IP address, what will the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, pri-
mary DNS, and secondary DNS will be assigned to this NRC?
•
If the NRC will be using DHCP, what IP address will be assigned by the DHCP server? You’ll need
to provide your network administrator with the MAC address from this NRC so he or she can assign a
unique IP address to it. The MAC address can be found under the ‘Network’ tab in the Configuration
section. (See Figure 3)
Step 2: Disable virus protection software and connect the NRC directly to
your computer
While configuring your NRC, all virus protection applications should be temporarily disabled. Virus
protection applications frequently manage your PC’s port settings in ways that can interfere with con-
figuration, though the exact nature of trouble can vary dramatically. Your browser may periodically dis-
connect from the NRC, you may be unable to upload settings, or configuration options may not work.
Most virus protection software can be disabled by right-clicking the software icon in the system tray of
your Windows
TM
Task Bar and selecting the appropriate option.
Power the NRC and connect its Ethernet port directly to your computer’s network port using a stan-
dard straight CAT5, CAT5e, or CAT6 cable with RJ-45 connectors.
Step 3: Change your computer’s network settings
(For Windows
TM
XP) Open the Control Panel on your computer, select “Network Connections,” then
“Local Area Connection.” Click on “Change settings of this connection”, and then “Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP)”, then “Properties.”
Be sure to write down your computer’s original network settings so you can revert them once
you’re finished with these first few steps.
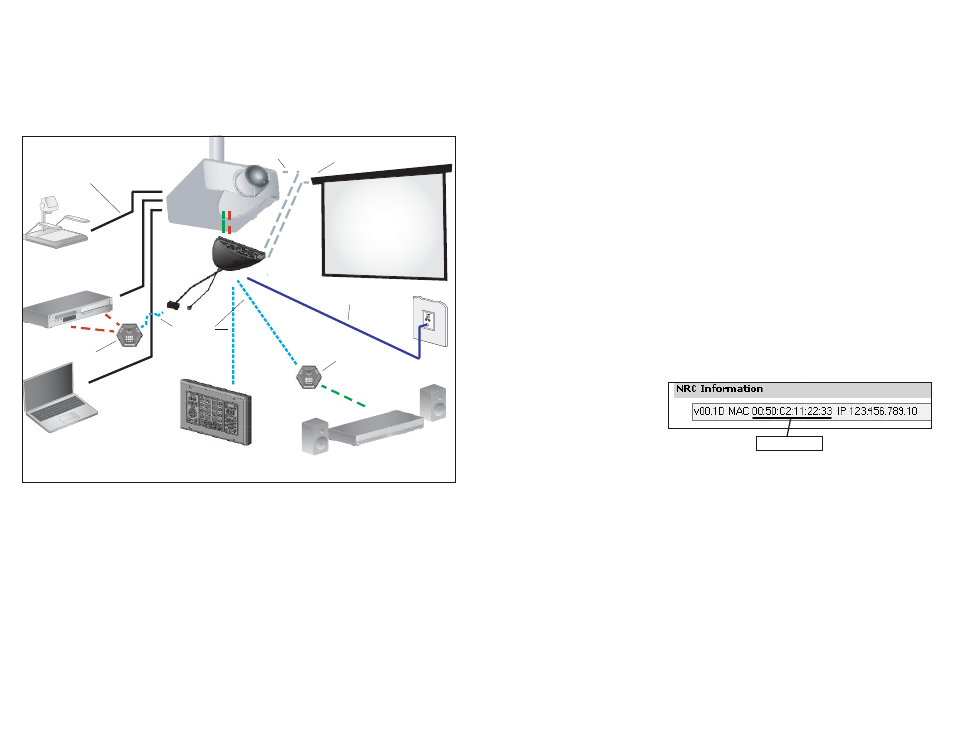
System 3:
NRC and Modular Panel combined to control a projector, with the relays on the NRC used for a
screen. It “listens” for contact closure on one of its sense ports, which triggers a theft warn-
ing email. An IR Puck controls a DVD player and a VCR. One RS-232/IR Puck controls an am-
plifier-receiver.
In this example, the NRC is the control center for several devices connected as a single system. As
shown in the image above, the NRC is mounted at the projector, controlling it with a combination of
RS-232 and IR. It controls a screen with low-voltage relays, and it is connected to a Modular Panel for
in-room control of the system. It is also connected to a network, so Web-based control is possible.
In this example, the NRC also sends commands to two Control Pucks. The first Puck has four IR
ports, two of which are used to control the DVD and VCR. The second Puck has one RS-232 port and
controls the amplifier with RS-232. One of the NRC sense ports is wired to a security loop such that if
the loop is broken, it will trigger the NRC to send an alert email to security staff.
IR Puck
(controls
combo unit
)
RS-232 Puck
(controls amp)
SP Bus
MAC address
5
Video
Network
Sense Port
(wired to security loop)
Control Relay
(screen control)
4
