Remko cmf / cmt – REMKO CMF-80 v.2 User Manual
Page 6
REMKO CMF / CMT
A heat pump is a device which
makes use of a working medium
to absorb ambient heat under low
temperatures and transports this
heat to a place where it can be
of use for heating purposes. Heat
pumps work according to the same
principles as a refrigerator. The dif-
ference is that the "waste product"
of the refrigerator, the heat, is the
goal in this case.
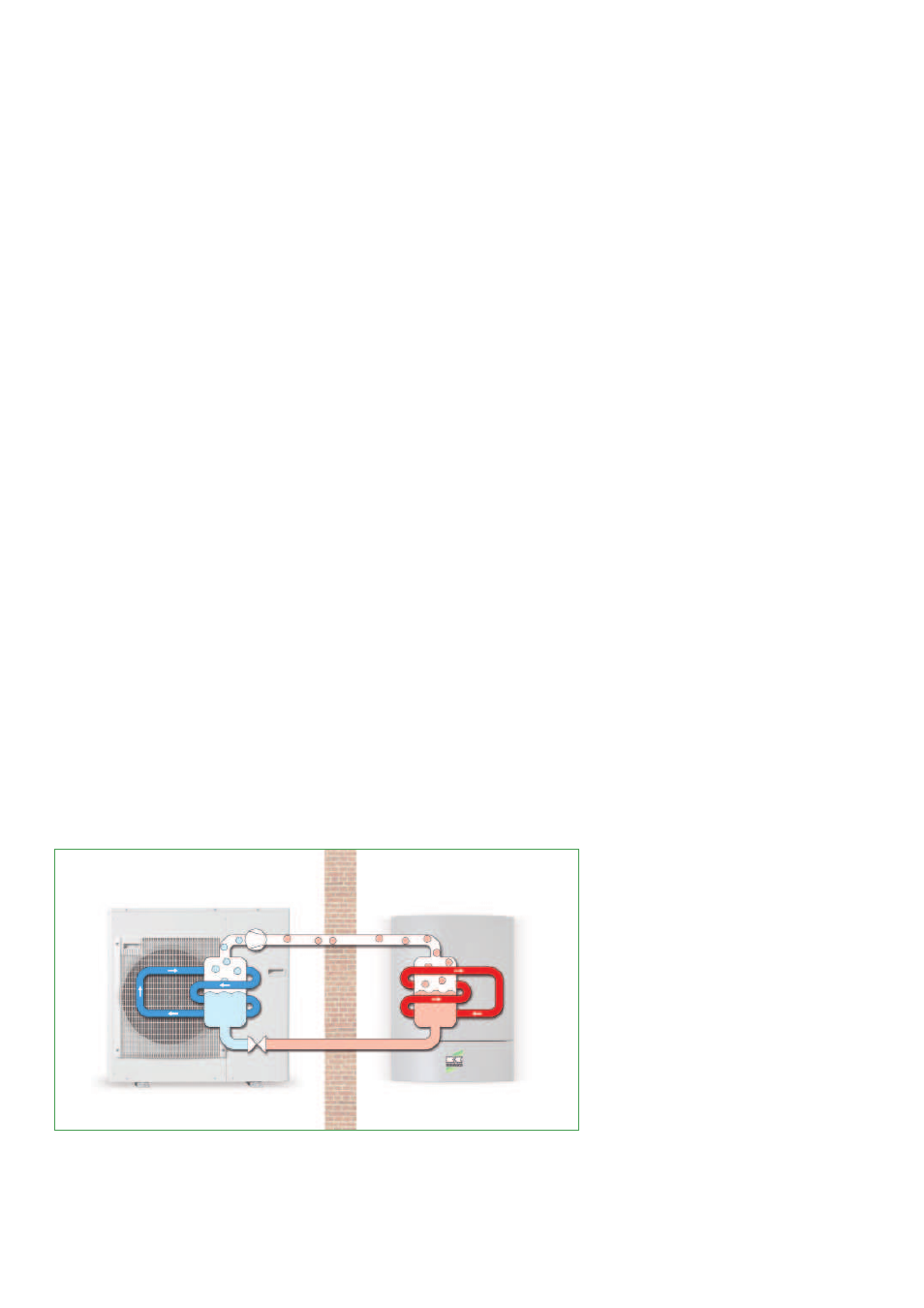
The main components of the
refrigeration circuit consist of an
evaporator, compressor, liquefier
and expansion valve.
Finned evaporators serve to evapo-
rate the refrigerant at low pressure
even at low heat source tem-
peratures, thereby absorbing the
ambient energy. In the compres-
sor, the refrigerant is compressed
to a higher pressure by means of
applying electrical energy, thereby
increasing it up the correct tem-
perature level.Afterwards the hot
refrigerant gas reaches the liquefier,
a plate heat exchanger.
Here the hot gas condenses and
releases its heat to the heating
system.The liquefied refrigerant is
Heat pump modes
Heat pumps can work in various
operating modes.
Monovalent The heat pump is the
sole heating appliance in the build-
ing all year round.This mode is par-
ticularly suitable for heating plants
with low supply water temperatures
and is primarily used in combina-
tion with brine/water and water/
water heat pumps.
Single energy sourceThe heating
system does not require a second-
ary heating boiler. The heat pump
covers a large proportion of the re-
quired heating power. Occasionally,
when it is extremely cold outside,
an electrical booster heating system
switches on in order to support the
heat pump as required.
Bivalent parallel modeThe heat
pump provides the entire heating
energy down to a predetermined
outdoor temperature. If the out-
door temperature falls below this
value, a secondary heating appli-
ance switches on in order to sup-
port the heat pump.
This may take the form of alterna-
tive operation with oil or gas-fired
heating or regenerative operation
utilising solar energy or wood fuel
heating.
This mode is possible for all heating
systems.
then decompressed and cooled in a
flow regulator, the expansion valve.
Subsequently, the refrigerant flows
back into the evaporator and the
circuit is completed.
A heat pump manager is used in or-
der to control the process, which in
addition to all safety functions also
provides fully automatic operation.
The water circuit for the CMF Series
indoor units includes a circulation
pump, a plate heat exchanger,
dirt trap, safety valve, manometer,
filling and drain valve, automatic
deaerator and flow monitor.The
CMT Series is additionally equipped
with a diaphragm expansion vessel,
a three-way switching valve and a
storage tank.
Wall and fl oor-mounted units, con-
densation pans, condensate trough
heating, 3-way switching valves,
overfl ow valves and additional
sensors are available as accessories.
Evaporation
Liquefaction
Condensing
Decompression
Functional diagram heating
inverter heat pump
Heat pump outdoor unit
Outdoor area
Heat pump indoor unit
Indoor area
6
