Measurement Computing USB-1208FS-Plus User Manual
Page 18
USB-1208FS-Plus User's Guide
Functional Details
18
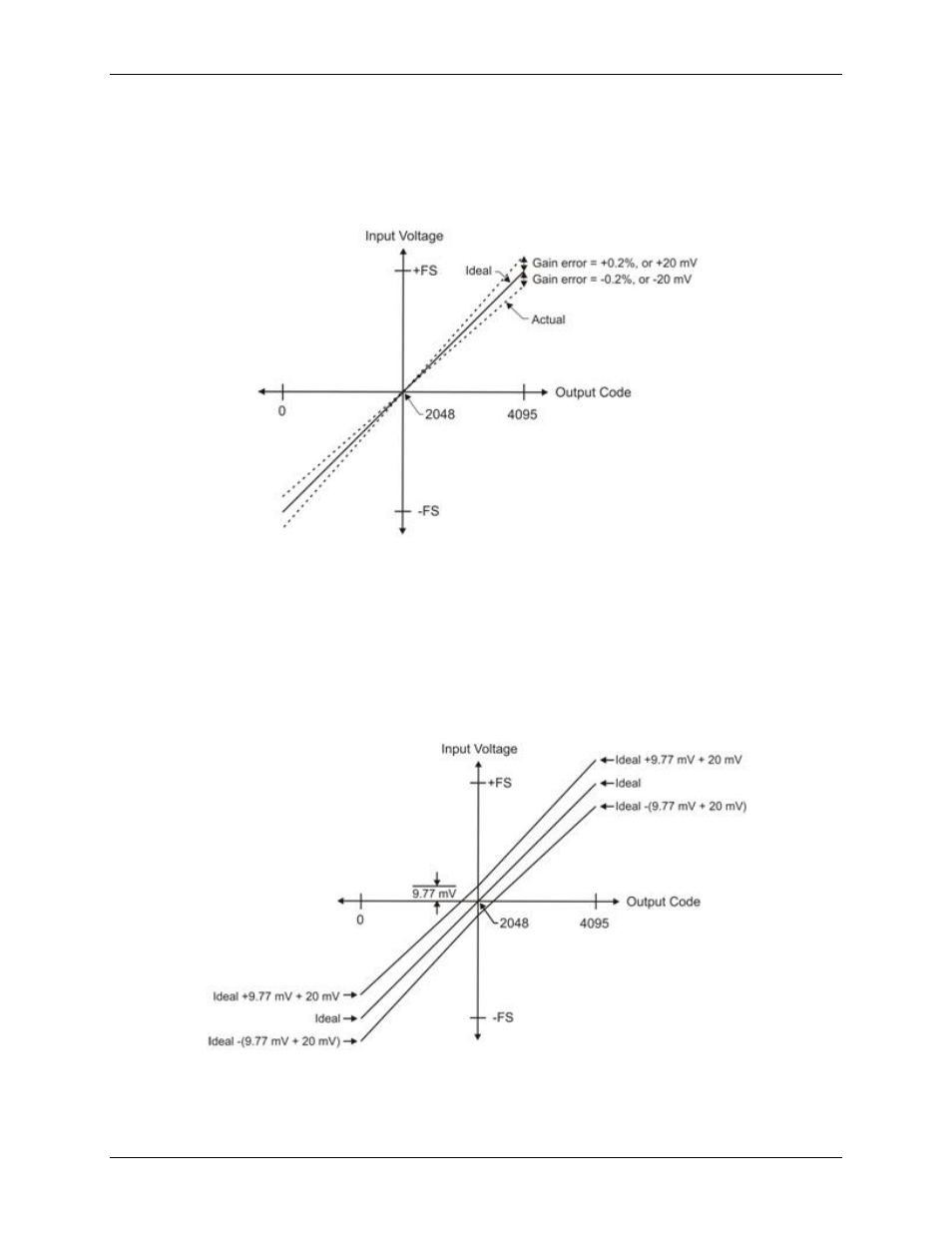
Gain error is a change in the slope of the transfer function from the ideal, and is typically expressed as a
percentage of full-scale.
Figure 13 shows the transfer function with gain error. Gain error is easily converted to voltage by multiplying
the full-scale (
FS
) input by the error.
The accuracy plots in Figure 13 are drawn for clarity and are not drawn to scale.
Figure 13. ADC Transfer function with gain error
For example, the USB-1208FS-Plus exhibits a typical calibrated gain error of ±0.2% on all ranges. For the
±10 V range, this would yield 10 V × ±0.002 = ±20 mV. This means that at full scale, and neglecting the effect
of offset, the measurement would be within 20 mV of the actual value. Note that gain error is expressed as a
ratio. Values near ±FS are more affected from an absolute voltage standpoint than are values near mid-scale,
which see little or no voltage error.
Combining these two error sources in Figure 14, we have a plot of the error band for the ±10 V range. This is a
graphical version of the typical accuracy specification of the product.
The accuracy plots in Figure 14 are drawn for clarity and are not drawn to scale.
Figure 14. Error band plot
