Pyrgeometer physical properties, Spectral range – Kipp&Zonen CGR 4 Pyrgeometers User Manual
Page 19
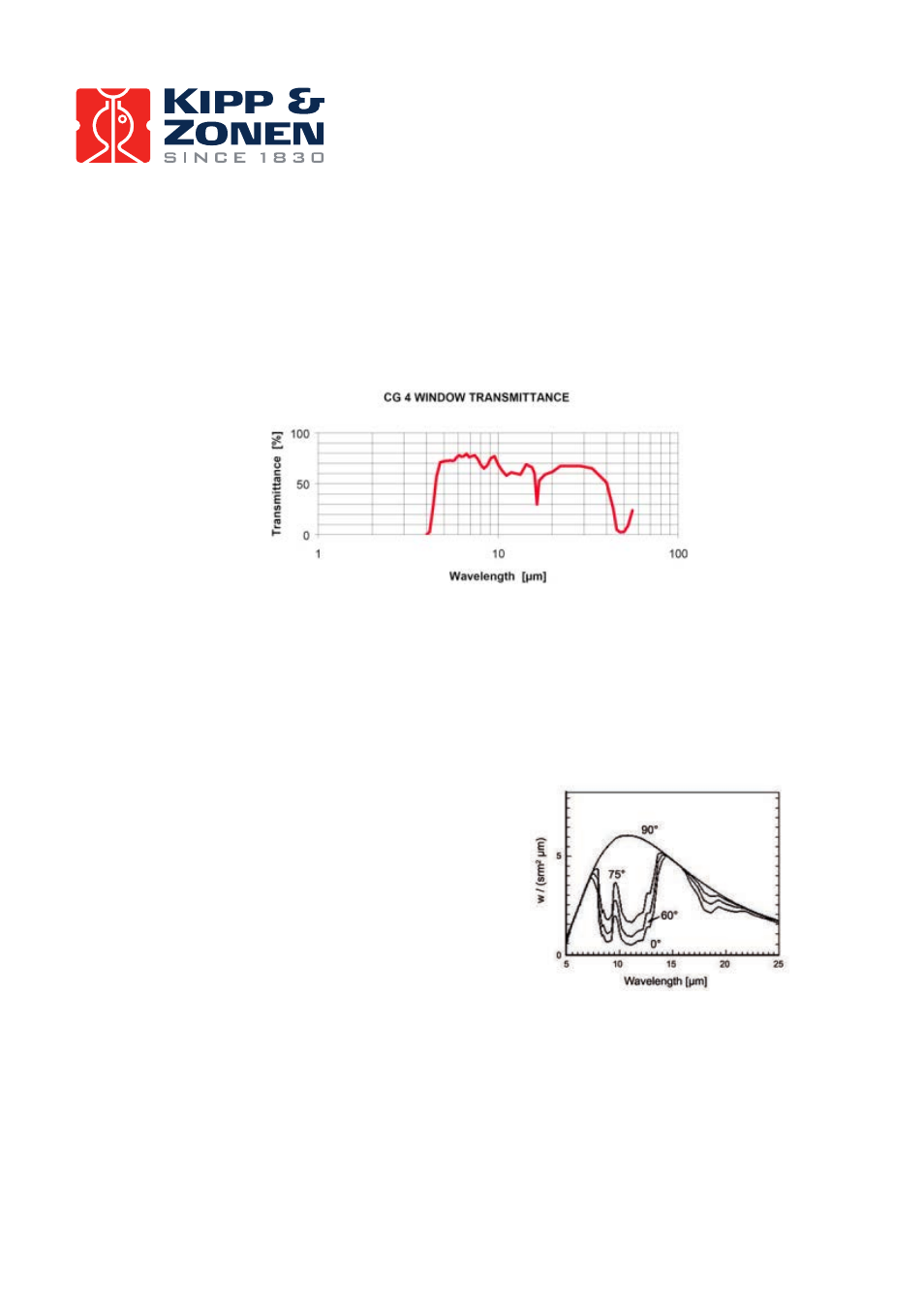
4. Pyrgeometer physical properties
4.1. Spectral range
The spectral properties of the pyrgeometer are mainly determined by the filter characteristics of the silicon
window and the coatings. The application is primarily to measure long-wave downward atmospheric
radiation. The spectral range is from 4.5 to 42 µm, where most of this radiation is present.
Figure 11:
Pyrgeometer spectral window properties
The atmosphere is transparent to long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface in certain wavelength
intervals, particularly within a spectral range of approximately 8 to 14 µm. This is called the ‘atmospheric
window’. Within this spectral range the Earth is able to maintain an equilibrium temperature by losing a
certain quantity of heat gained each day from the sun.
The sun radiates approximately as a blackbody at an equivalent temperature of 5770K. Almost 99% of its
emitted energy is contained in wavelengths less than 4µm, called short-wave radiation. The equivalent
radiant temperature of the Earth’s surface is about 275K. More than 99% of this energy is emitted at
wavelengths greater than 3 µm and is called long-wave, thermal, or infrared radiation.
Downward long-wave radiation is a result of atmospheric
re-emission. Re-emission is the reversible effect of
absorption of long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth
and by chemical elements such as water (H₂O), Oxygen
(O₂), Ozone (O₃), Carbon dioxide (CO₂), etc. These
elements are the main emitters of long-wave radiation in
the atmosphere. The remaining unabsorbed portion of the
Earth’s radiation escapes into outer space. Under clear skies
an object can be cooled below ambient air temperature by
radiative heat loss to the sky.
Observing the earth from outer space, a blackbody is seen
in a range of 8 to 14 µm with a temperature of 14°C and
outside this wavelength range a blackbody of -60°C.
Under clear sky conditions in a reverse direction, outer Figure 12: Atmospheric radiation
space can be observed in the same spectral range.
Page 19
CGR 4 Manual
