B distributed cumulative pmd measurement theory – EXFO FTB-5600 Distributed PMD Analyzer User Manual
Page 119
Distributed PMD Analyzer
113
B Distributed Cumulative PMD
Measurement Theory
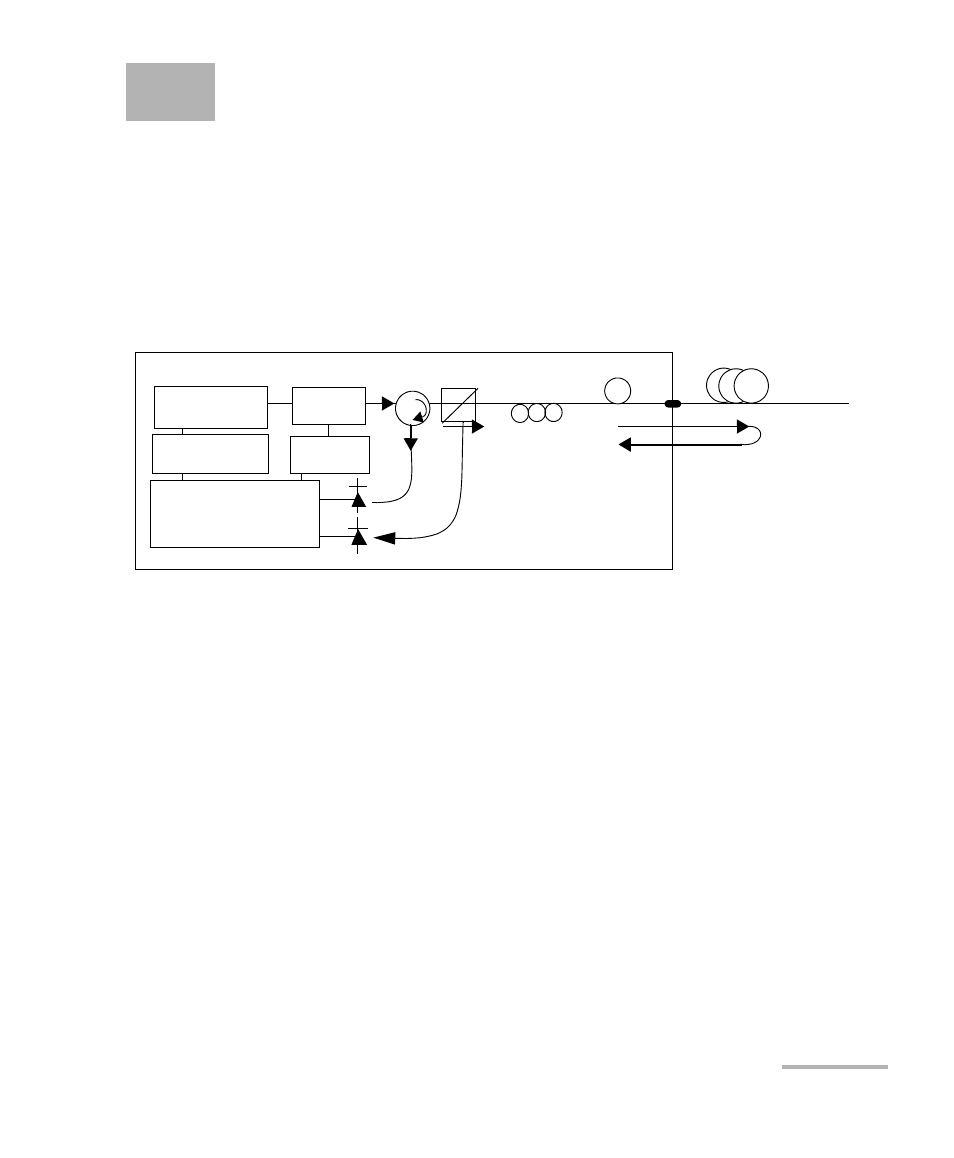
The FTB-5600 is a Distributed PMD Analyzer that uses a random-scrambling
tunable-polarization-sensitive OTDR (RS-POTDR) to measure the
cumulative PMD as a function of the distance along a single-mode optical
fiber. In this way, bad high-PMD fiber sections can be identified and
quantified. The basic FTB-5600 design is illustrated schematically in the
figure below.
The output from a tunable laser is modulated and amplified by a
semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) to produce standard OTDR light
pulses having a narrow spectral width of ∼4 GHz (FWHM). The OTDR
pulses are routed by a circulator (C) and a polarization beam splitter (PBS),
serving as a polarization analyzer, before passing through an
input-and-output state-of-polarization (I/O-SOP) scrambler.
The I/O-SOP randomly selects both the SOP of light, which is input into the
FUT and the SOP of the Rayleigh backscattered light. The Rayleigh
backscattered light from the FUT travels back through the I/O-SOP
scrambler, is split into two orthogonal-polarization portions by the PBS, and
these portions are then measured by photodetectors 1 and 2 (that is, PD1
and PD2). This detection is time-gated, as with any conventional OTDR,
allowing the P-OTDR raw data to be acquired.
LF
C
PBS
PD1
PD2
Scrambler
SOA
Pulses
Data
Acquisition
Rayleigh
Backscattering
IO-SOP
k
Tunable
laser
FUT
ν
k
1
2
---d
ν
±
