Compaq 3000 User Manual
Page 45
RAID Array 3000 Controller Shelf
2–12
EK–SMCPQ–UG. C01
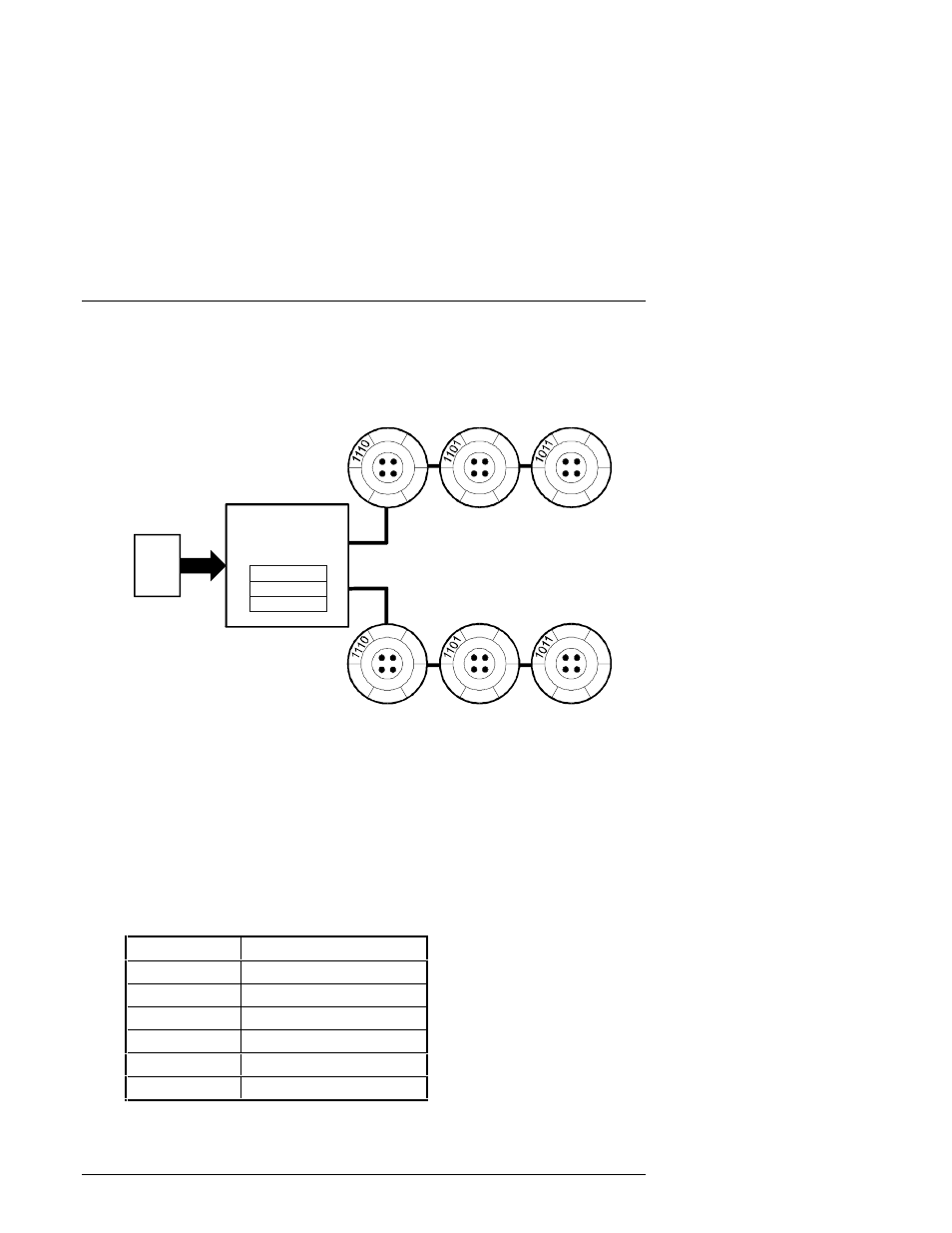
Figure 2–7 Diagram of RAID 0+1 Write
1110
1101
1011
Host Data
Controller divides
the data into
chunksized units
1110
1101
1011
Striped data written
to half the drives
Striped data mirrored
to the remaining drives
SHR-1056
In the event of a drive failure, a RAID 0+1 array will enter degraded mode and
continue to operate by substituting the failed drive with its mirror.
When the controller creates a RAID 0+1 set, it first sorts the drives by channel
number and SCSI ID. Then it stripes the data across every other drive and forms
a mirrored pair with the first two drives, another mirrored pair with the second
two drives, and so on. Table 2–4 describes how the controller uses the drives in a
RAID 0+1 set.
Table 2–4 RAID 0+1 Example
Drives Selected
Function
Channel 1, ID 0
First member of stripe set.
Channel 1, ID 1
Mirror of channel 1, ID 0
Channel 1, ID 2
Second member of stripe set
Channel 2, ID 0
Mirror of channel 1, ID 2
Channel 2, ID 1
Third member of stripe set
Channel 2, ID 2
Mirror of channel 2, ID 1
