Trouble shooting chart-motor – Sears 113.2945 User Manual
Page 19
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
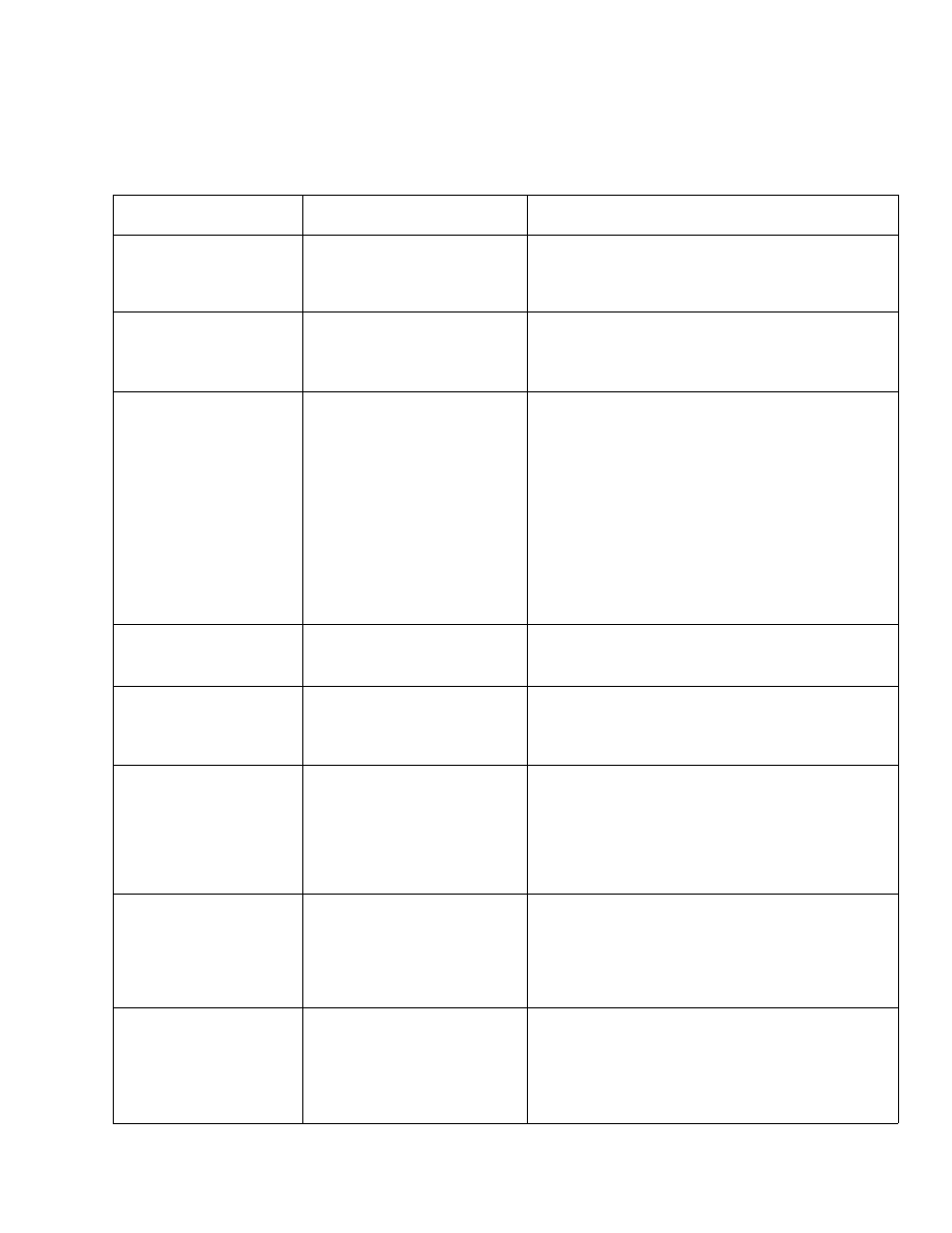
TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART-MOTOR
NOTE: Motors used on wood-working tools
are particularly susceptible to the accumula
tion of sawdust and wood chips and should
be blown out or “vacuumed" frequently
to prevent interference with normal motor
ventilation.
TROUBLE
PROBABLE CAUSE
REMEDY
Motor will not run.
1. Protector open; circuit
broken.
2. Low voltage.
1. Reset protector by pushing in on red button, located
on top of motor junction box (indicated by audible
click).
2. Check power line for proper voltage.
Motor will not run and
fuses "BLOW."
1. Short circuit in line cord or
plug.
2. Short circuit in motor terminal
box or loose connections.
1. Inspect line cord and plug for damaged insulation
and shorted wires.
2. Inspect all terminals in motor terminal box for loose
or shorted terminals.
Motor
fails
to
develop
full power. (Power output
of motor decreases rapidly
with decrease in voltage
at motor terminals.) For
example: a reduction of
10% in voltage causes a
reduction of 19% in
maximum power output of
which the motor is capable,
while a reduction of 20%
in voltage causes a reduc
tion of 36% in maximum
power output.
1. Power line overloaded with
lights, appliances and other
motors.
2. Undersize wires or circuit too
long.
3. General overloading of power
company's facilities. (In many
sections of the country, demand
for electrical power exceeds
the capacity of existing gen
erating and distribution
systems.)
4. Incorrect fuses in power line.
1. Reduce line load.
2. Increase wire sizes, or reduce length of wiring.
3. Request a voltage check from the power company.
4. Install correct fuses.
Motor starts slowly or fails
to come up to full speed.
1. Low voltage — will not trip
relay.
2. Starting relay not operating.
1. Correct low voltage condition.
2. Replace relay.
Motor overheats.
1. Motor overloaded.
2. Improper cooling. (Air circula
tion restricted through motor
due to sawdust, etc.)
1. Correct overload condition.
2. Clean out sawdust to provide normal air circulation
through motor.
Starting relay in motor
will not operate.
1. Burned relay contacts (due to
extended hold-in periods
caused by low line voltage,
etc.)
2. Open relay coil.
3. Loose or broken connections
in motor terminal box.
1. Replace relay and check line voltage.
2. Replace relay.
3. Check and repair wiring.
Motor stalls resulting in
blown fuses or tripped
circuit breakers .
1. Starting relay not operating.
2. Voltage too low to permit
motor to reach operating
speed.
3. Fuses or circuit breakers do
not have sufficient capacity.
1. Replace relay.
2. Correct the low line voltage condition.
3. Replace fuses or circuit breakers with proper capacity
units.
Frequent opening of fuses
or circuit breakers.
1. Motor overloaded.
2. Fuses or circuit breakers do
not have sufficient capacity.
3.
Starting relay not operating
(motor does not reach normal
speed.)
1. Reduce motor load.
2. Replace fuses or circuit breakers.
3. Replace relay.
19
