1 pharmacopoeia and thermodynamic melting points – BUCHI Melting Point M-565 User Manual
Page 17
4 Description of function
17
Melting Point M-565 Operation Manual, Version D
4 .1 .1
Pharmacopoeia and thermodynamic melting points
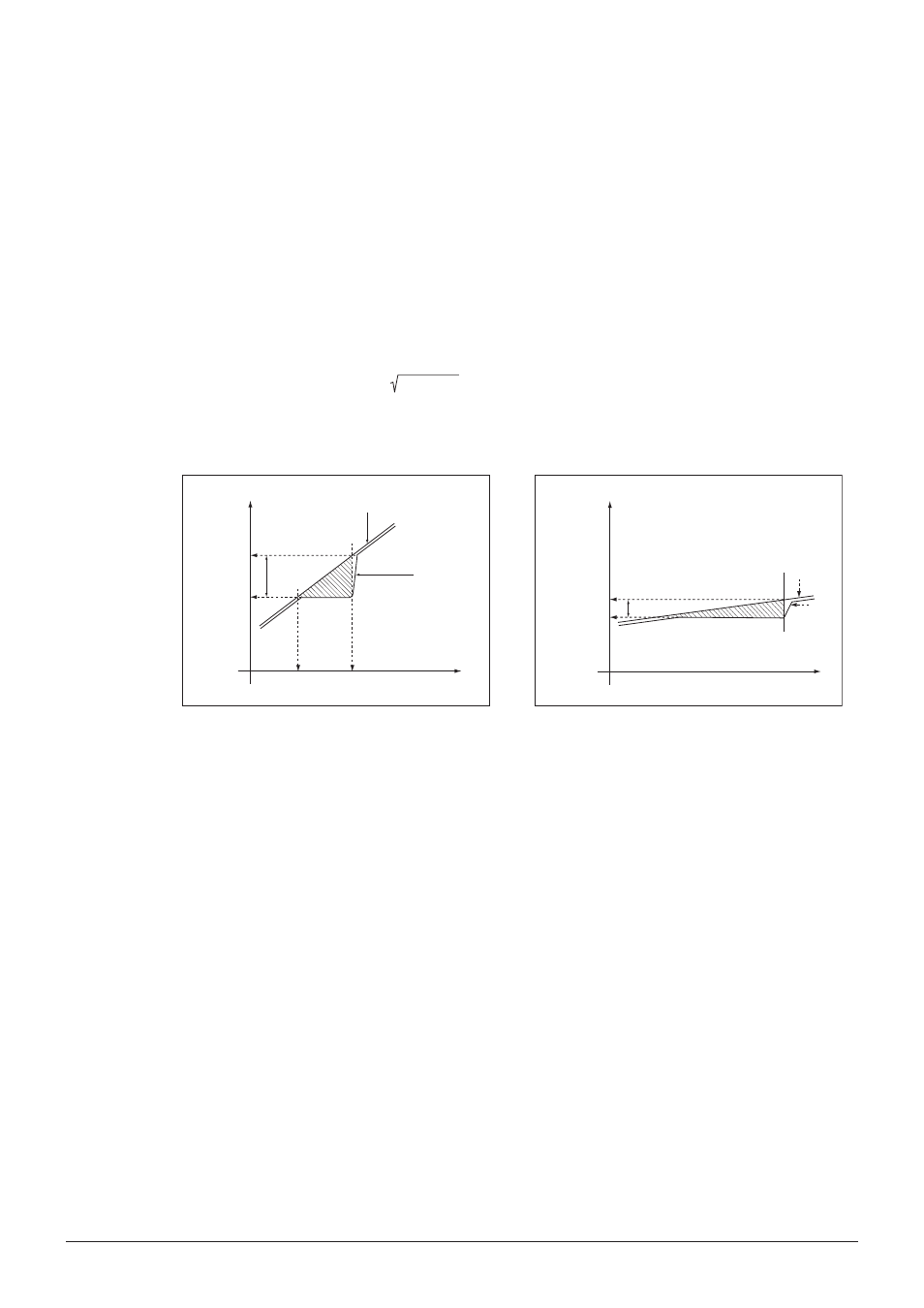
The melting process of a substance does not take place instantaneously - it requires a finite amount
of time. The melting process begins at the point where the first particles of the substance turn into the
liquid state (thermodynamic melting point). The end of the melt is reached when the last solid particles
have gone over into the liquid phase (pharmacopoeia melting point).
During the entire melting process of a pure compound, the temperature of the pure substance remains
constant while heat is constantly transferred from the heating block to the sample.
For pure substances the thermodynamic melting point can be approached by multiplying the ther-
modynamic correction factor by the square root of the gradient and subtracting the result from the
pharmacopoeia melting point.
temperature
Steep gradient
Flat gradient
thermodynamic
correction
all molten:
moment of
detection
oven
temperature
oven
temperature
sample
temperature
sample
temperature
thermodynamic
correction
temperature
at moment of
detection
melting
temperature
melting
temperature
temperature
at moment of
detection
time
time
temperature
melting start
Fig. 4.2:
The amount of thermodynamic correction depends on the gradient selected: The smaller the
gradient, the less the correction required.
mp
[thermodyn.]
=
mp
[pharma.]
–(
k × gradient)
k = thermodynamic factor
