Operational examples – BendixKing KFC 500 User Manual
Page 37
Operational Examples
64
65
June 15, 1999
006-18081-0000
006-18081-0000
June 15, 1999
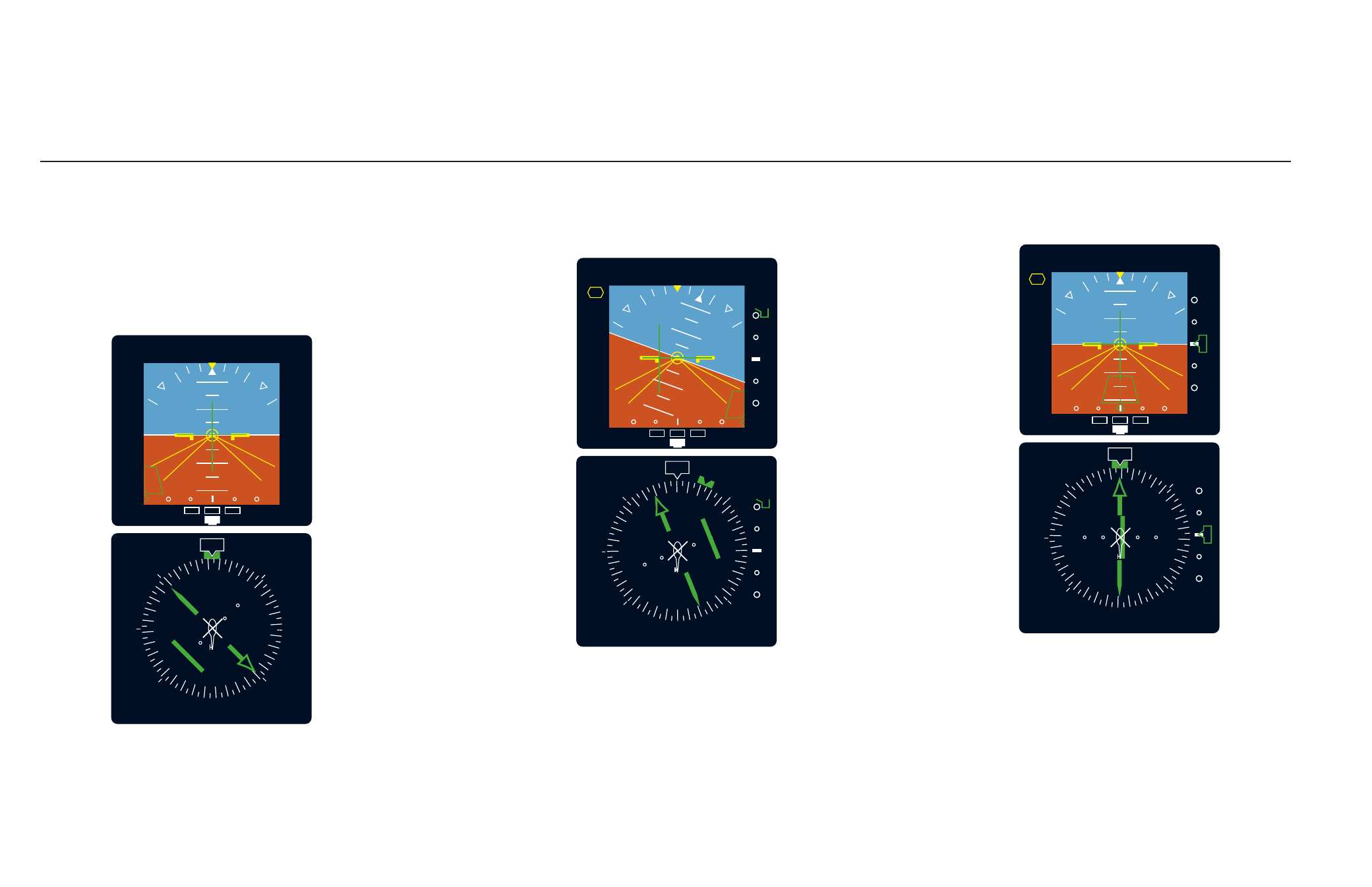
4.
At the point specified to begin the procedure turn inbound, select 103°
with the heading bug for a 180° turn toward the localizer front course. The dei-
vation bar shows pictorially the course you are to intercept. Depress the APR
push button to arm the approach mode. Automatic capture will occur to direct
the aircraft on the localizer inbound.
During the procedure turn outbound, the deviation bar shows pictorially that
the aircraft is flying away from the localizer centerline at a 45° angle.
Note: When activating approach arm, it is important that the aircraft be rela-
tively close to and not making any turns away from the localizer. Side lobes or
false signals are often present from the localizer transmitter. These false sig-
nals may cause the autopilot to approach couple prior to reaching the actual
localizer signal.
6.
Throughout the approach procedure, the airspeed must be controlled by
the pilot via the collective.
283
HDG
283
058
L
O
C
1
1 2 . 6
NM
117.95
CRS
H
AP
HDG
ALT
RA
DH
2500
200
3000 FT
LOC
20
20
20
20
10
10
10
10
N
33
30
W
24
21
S
15
12
E
6
3
103
HDG
080
058
L
O
C
1
1 2 . 6
NM
117.95
CRS
H
AP
LOC
ALT
GS
RA
DH
2500
200
LOC
MM
N
33
30
W
24
21
S
15
12
E
6
3
20
20
20
20
10
10
10
10
S
S
3000 FT
058
HDG
058
058
L
O
C
1
1 2 . 6
NM
117.95
CRS
H
AP
LOC
GS
RA
DH
1500
200
LOC
20
20
20
20
10
10
10
10
N
33
30
W
24
21
S
15
12
E
6
3
MM
G
S
G
S
5.
The autopilot is following the flight director commands which maintain
localizer centerline tracking. Once approach coupled (APR in green, glides-
lope is automatically armed (GS in white). The point of glideslope capture is
based on the glideslope deviation and the rate of closure to the beam. Both
pitch and roll are commanded by the flight director to maintain glideslope and
localizer track.
Note: The KFC 500 Autopilot/ Flight Director will only maintain one pitch
mode at a time (pitch attitude hold, altitude hold, vertical speed hold, indi-
cated airspeed hold, glideslope, or go around). As an example, if the AFCS is
coupled to the glideslope then the pilot must manually maintain airspeed with
the collective.
