Bio-Rad Profinity IMAC Resins User Manual
Page 8
4
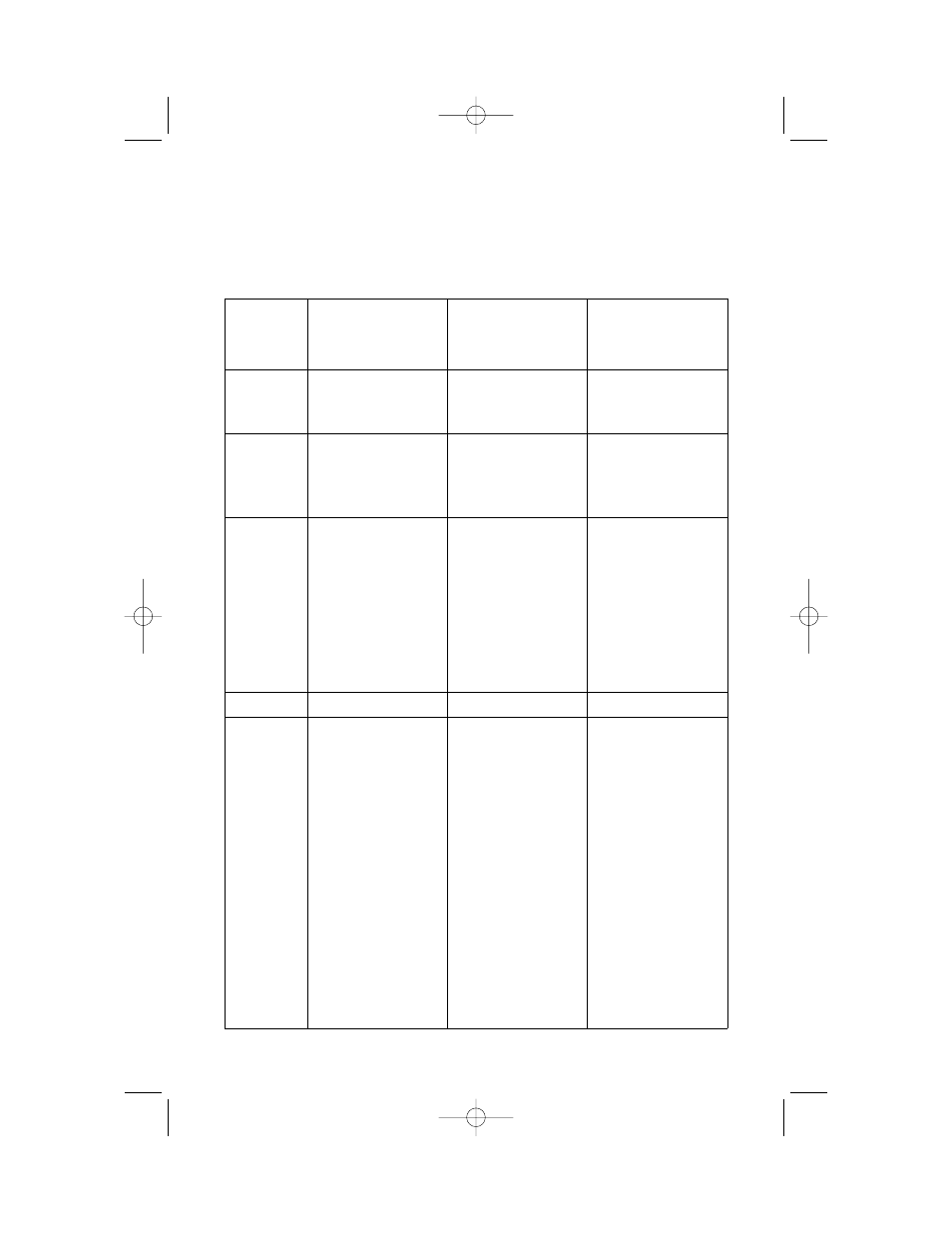
Reagent
Reagent
Comments
Stability
Group
Buffer reagents
Tris, HEPES, MOPS
Sodium or potassium phosphate
Used with proteins more stable
in nonphosphate buffers
≤50 mM secondary and tertiary
amines
50 mM sodium or potassium
phosphate are recommended as
starting buffers
Chelating
reagents
EDTA, EGTA
Strips nickel ions from the resin
≤0.1 mM successfully used to
remove trace metal contaminants
(>1 mM causes significant
reduction in binding capacity
Sulfhydryl
reagents
β-Mercaptoethanol
DTT, TCEP
Reduces random disulfide bonds;
preventing protein aggregation
during purification
Transition metals at the center of
IMAC resin (Ni
2+
) are susceptible
to reduction
≤30 mM
≤5 mM DTT and 10 mM TCEP
Detergents
Nonionic detergents (Triton,
Tween, NP-40)
Cationic detergents (CTAB)
Zwitterionic detergents (CHAPS,
CHAPSO)
Anionic detergents (SDS,
Sarkosyl)
Removes background proteins
and nucleic acids
Improves solubility of
membrane/lipid associating
proteins or proteins with
hydrophobic domains
Solubilizes membrane proteins
Selectively solubilizes membrane
proteins; in higher concentrations
anionic functionalities might cause
stripping of metal ion
≤5%
≤1% but care must be taken to
avoid protein precipitation
≤5%
≤1% may be used; solubility of
Sarkosyl in 50 mM potassium
phosphate/300 mM NaCl is better
than solubility of SDS
Denaturants
Guanidine HCl (GuHCl)
Urea
Solubilizes proteins
≤6 M
≤8 M
Other additives
NaCl
MgCl
2
CaCl
2
Glycerol
Ethanol
Imidazole
Citrate
Deters nonspecific protein binding
due to ionic interactions
Essential component for
purification of Ca
2+
binding
proteins
Essential metal cofactor for
nucleases
Included to prevent hydrophobic
interactions between proteins
Included to prevent hydrophobic
interactions between proteins
Competes for binding sites with
His-tagged residues by
interaction with the metal residues
Carboxylic side chains could
potentially serve as chelation site
for Ni
2+
, causing metal leakage
≤2 M (at least 300 mM NaCl
should be included in buffers)
≤100 mM (HEPES or Tris buffers
should be used to prevent
precipitation)
≤10 mM (HEPES or Tris buffers
should be used to prevent
precipitation)
≤20%
≤20%
May be used in low
concentrations in the wash buffer
(<25 mM) to limit binding of
undesired proteins; for elution,
≤500 mM may be used
≤80 mM
Table 2. Chemical Compatibilities for Profinity IMAC Resins
Chemical Compatibilities
The chemical characteristics of Profinity IMAC resin are detailed in Table 2.
10001677B.qxd 1/28/2005 12:42 PM Page 7
