Ro system troubleshooting – Watts PWR2511 User Manual
Page 6
6
G. Troubleshooting
RO Membrane Troubleshooting Guide
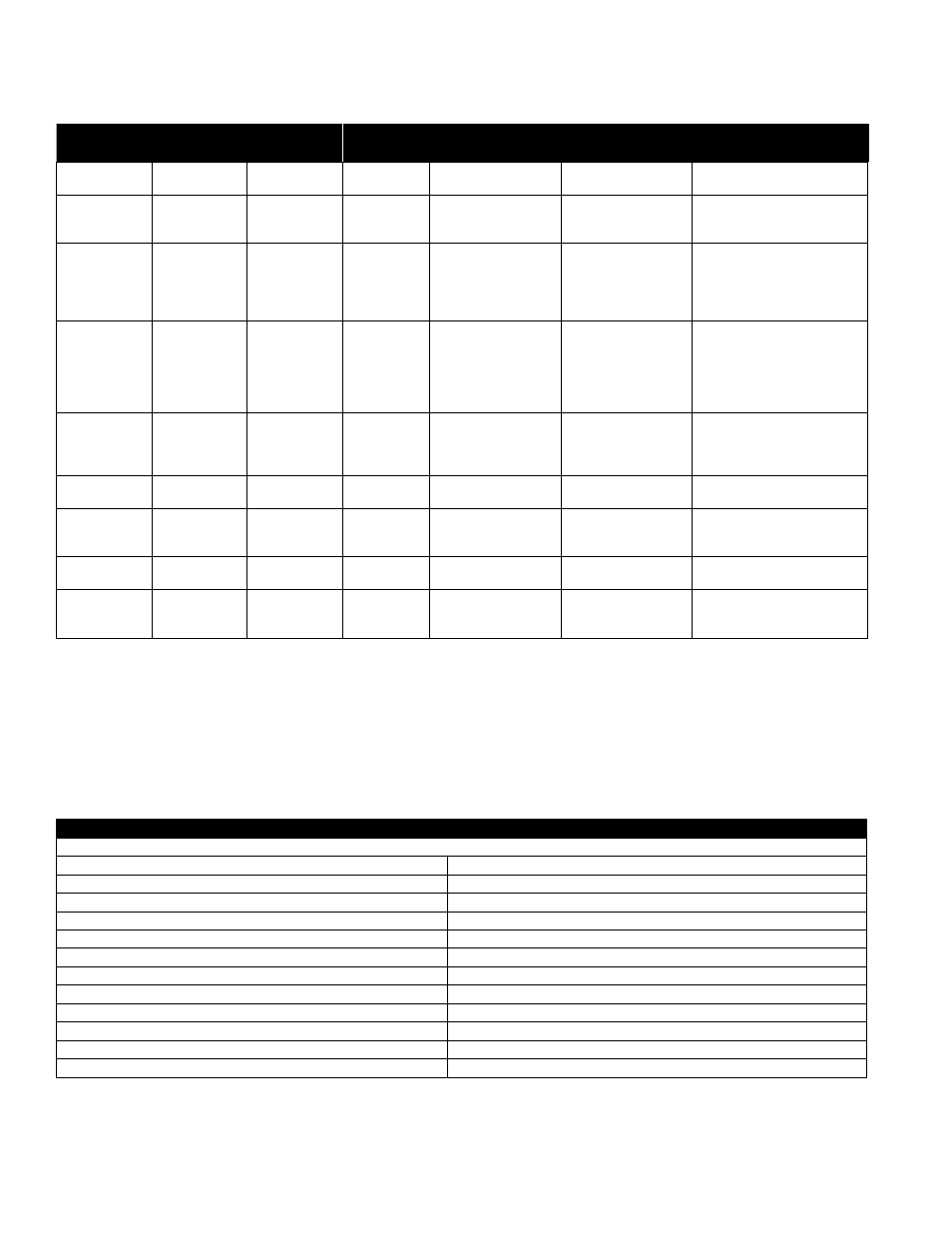
sYmPtoms
salt PassaGe
PeRmeate FloW
PRessuRe DRoP
locatioN
Possible causes
veRiFicatioN
coRRective actioN
Normal to increased Decreased
Normal to increased Predominantly
first stage
Metal oxide
Analysis of metal ions in
cleaning solution.
Improved pretreatment to remove met-
als. Cleaning with acid cleaners.
Normal to increased Decreased
Normal to increased Predominantly
first stage
Colloidal fouling
SDI measurement of feed/
X-ray diffraction analysis of
cleaning sol. residue.
Optimize pretreatment system for
colloid removal. Clean with high pH,
anionic detergent formulation.
Increased
Decreased
Increased
Predominantly
last stage
Scaling (CaSO
4
, CaSO
3
,
BaSO
4
, SiO
2
)
Analysis of metal ions in
cleaning sol. Check LSI of
reject. Calculate maximum
solubility for CaSO
4
, BaSO
4
,
SiO
2
in reject analysis.
Increase acid addition and scale
inhibitor for CaSO
3
and CaSO
4
. Reduce
recovery. Clean with an acid formula-
tion for CaCO
3
, CaSO
4
and BaSO
4
.
Normal to moderate
increase
Decreased
Normal to moderate
increase
Can occur in any
stage
Biological fouling
Bacteria count in permeate
and reject. Slime in pipes
and vessels.
Shock dosage of sodium bisulfite.
Continuous feed of low conc. bisulfite
at reduced pH. Peracetic acid steriliza-
tion. Clean with alkaline anionic sur-
factant. Chlorine dosage upstream with
dechlorination. Replace cartridge filters.
Decreased or mod-
erately increased
Decreased
Normal
All stages
Organic fouling
Destructive testing, e.g. IR
reflection analysis.
Optimization of pretreatment system
(e.g. coagulation process.) Resin/
activated carbon treatment. Clean with
high pH detergent.
Increased
Increased
Decreased
Most severe in
the first stage
Chlorine oxidant attack
Chlorine analysis of feed.
Destructive element test.
Check chlorine feed equipment and
dechlorination equipment.
Increased
Increased
Decreased
Most severe in
the first stage
Abrasion of membrane by
crystalline material
Microscopic solids analysis
of feed. Destructive ele-
ment test.
Improved pretreatment. Check all filters
for media leakage.
Increased
Normal to increased Decreased
At random
O-ring leaks, End or side
seal glue leaks.
Probe test. Vacuum test.
Colloidal material passage.
Replace O-rings. Repair or replace
elements.
Increased
Normal to low
Decreased
All stages
Conversion too high.
Check flows and pressures
against design guidelines
Reduce conversion rate. Calibrate
sensors. Increase analysis and data
collection.
RO System Troubleshooting
PRoblem
coRRective actioN
General
high Product Water tDs
Membrane frozen, high temp, or backpressure.
Replace membrane.
Membrane attack by chlorine Carbon pre-filter may be exhausted.
Replace filter and membrane.
Product seal on end cap. Determine if seal or O-ring is bad.
Replace as needed.
No Product Water or Not enough Product Water
Feed water shut off.
Turn on feed water.
Low feed pressure. Feed pressure must be at least 20psi.
Consider booster pump.
Pre-filter cartridge clogged.
Replace pre-filter cartridge.
Membrane fouled.
Determine and correct cause; replace or clean membrane.
Product check valve stuck.
Clean or replace check valve.
Low pump discharge pressure
Adjust reject valve or replace pump
Low feed water temperature
Increase membrane feed pressure or heat the feed water.
