Metrohm NIRS XDS Process Analyzer – MicroBundle User Manual
Page 62
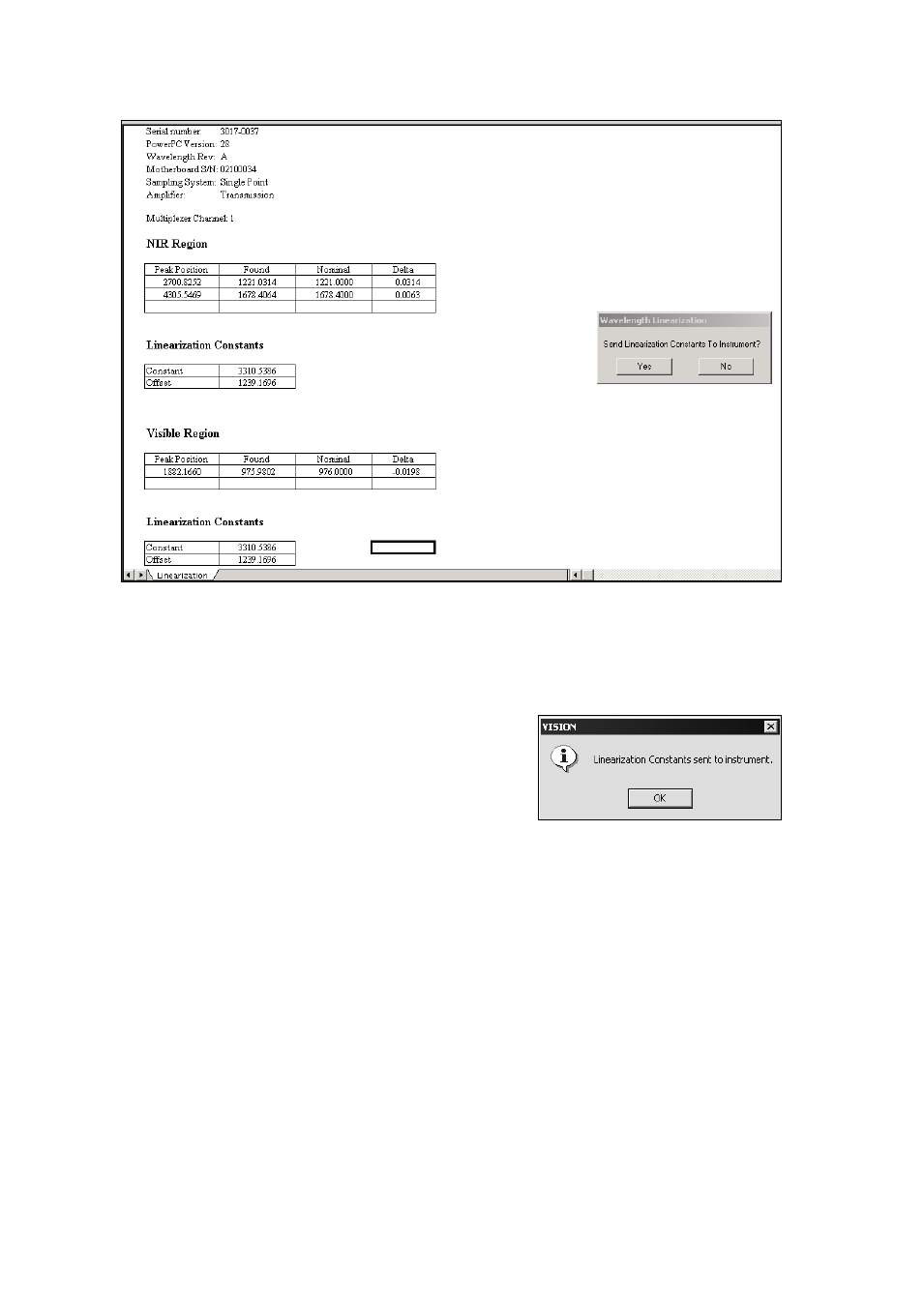
60
▪▪▪▪▪▪▪
The results screen shown above is typical. Peak positions for the reference materials are located using
a peak-finding algorithm. These “found” peaks are compared to the nominals. Differences should be
no more than 0.4nm for any peak. Click “Yes” to send the linearization to the instrument.
This is done twice, one for each direction of the grating motion.
After the linearization is successfully sent to the instrument,
this message confirms the transfer.
Click “OK” to proceed.
10.2.2
Reference Standardization, Interactance Reflectance
Reference Standardization is a method to provide a virtual 100% reflectance reference at each data
point, to serve as a true spectroscopic reference with no character attributable to the physical
reference that is used. This will minimize spectroscopic differences between the sample fiber lengths.
Reference Standardization is important to achieve a high-quality spectrum on each instrument
channel, and to enhance transferability between instruments.
A photometric standard of known reflectivity (as measured on an absolute reflectance scale) is
scanned on the instrument. The instrument standard is scanned. The differences of the instrument
standard from 100% reflectivity are mapped, and a photometric correction is generated. This
correction is then applied to every spectrum taken on the sample channel, to make each spectrum
appear as if taken with a reference of 100% reflectance. This assures that bright samples do not
saturate the instrument, or produce negative absorbance values.
Vision software stores the Reference Standardization file, which is downloaded to the instrument,
and is applied as a correction to each spectrum.
