Repetitive pulse loading – Rockwell Automation 1606-XLS960E-3 Power Supply Reference Manual User Manual
Page 21
All parameters are specified at 24V, 40A, 3x400Vac, 25°C ambient and after a 5 minutes run-in time, unless noted otherwise.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1606-RM005A-EN-P - February 2014
21
Bulletin 1606 Switched Mode Power Supplies
25. Application Notes
25.1. Repetitive Pulse Loading
Typically, a load current is not constant and varies over time. This power supply is designed to support loads with a
higher short-term power demand (=BonusPower). The short-term duration is hardware controlled by an output
power manager and is available on a repeated basis. If the BonusPower load lasts longer than the hardware
controller allows it, the output voltage will dip and the next BonusPower is available after the BonusPower recovery
time (see Section 6) has elapsed.
To avoid this, the following rules must be met:
a)
The power demand of the pulse must be below 150% of the nominal output power.
b)
The duration of the pulse power must be shorter than the allowed BonusPower time (see output section).
c)
The average (R.M.S.) output current must be below the specified continuous output current.
If the R.M.S. current is higher, the unit will respond with a thermal shut-down after a period of time. Use the
maximum duty cycle curve (Fig. 25-2) to check if the average output current is below the nominal current.
d)
The duty cycle must be below 0.75.
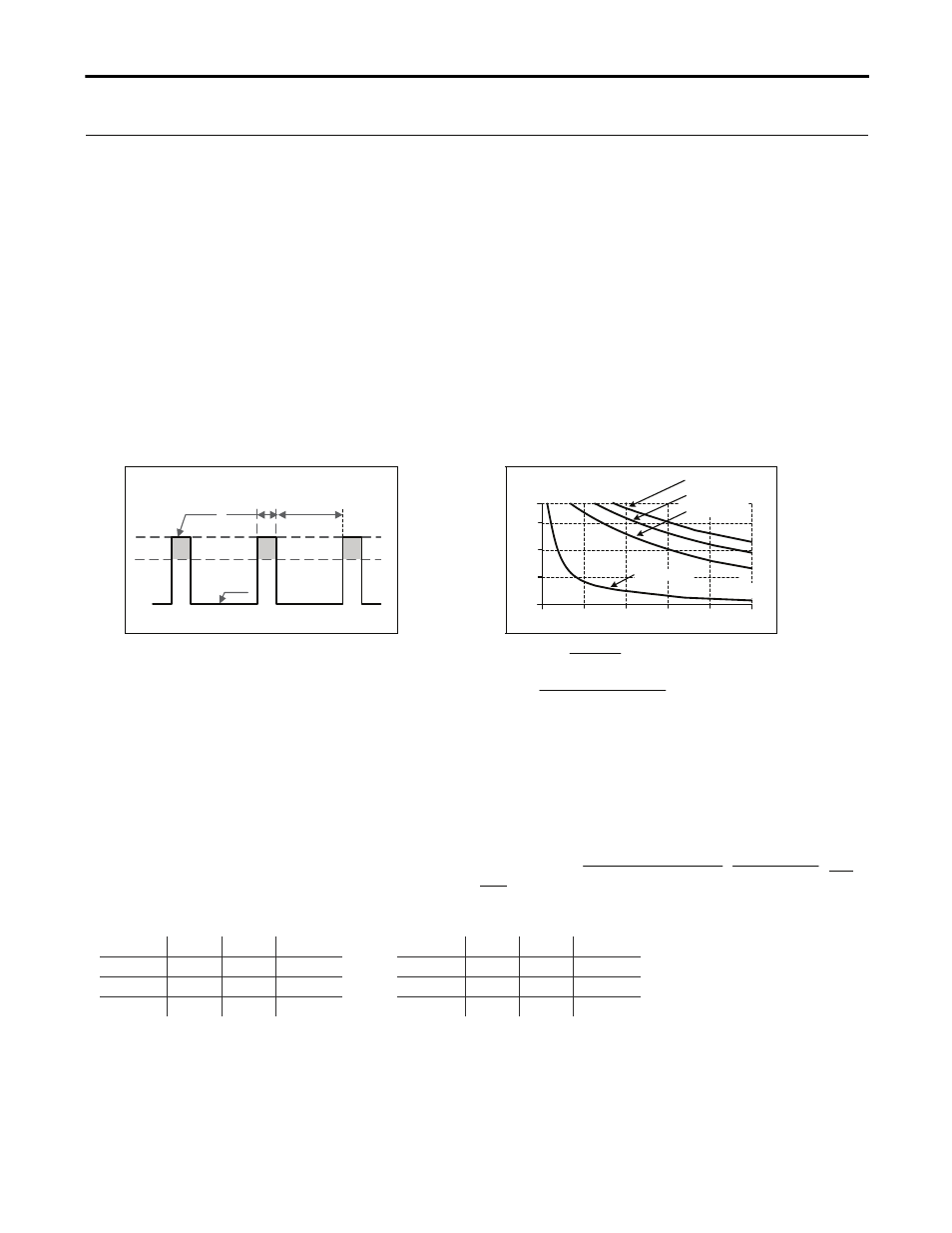
Fig. 25-1 Repetitive pulse loads, definitions
Fig. 25-2 Max. duty cycle curve
100%
P
PEAK
T
PEAK
P
0
T
0
max.
150%
150%
100
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.75
Duty Cycle
110
120
130
140
P
PEAK
P
0
= 10%
P
0
= 50%
P
0
= 75%
P
0
= 100%
P
0
Base load (W)
P
PEAK
Pulse load (above 100%)
T
0
Duration between pulses (s)
T
PEAK
Pulse duration (s)
D
uty
C
ycle
T
0
=
T
peak
-
(D
uty
C
ycle
x T
peak
)
T
peak +
T
0
T
peak
D
uty
C
ycle
=
Example:
A load is powered continuously with 480W (= 50% of the rated output load). From time to time a peak
power of 1440W (= 150% of the rated output load) is needed for 1 second.
The question is: How often can this pulse be supplied without overloading the power supply?
- Make a vertical line at P
PEAK
= 150% and a horizontal line where the vertical line crosses the P
0
= 50%
curve. Read the max. duty cycle from the duty cycle-axis (= 0.37)
- Calculate the required pause (base load) length T
0
:
- Result: The required pause length = 1.7s
- Max. repetition rate = pulse +pause length = 2.7s
More examples for pulse load compatibility:
P
PEAK
P
0
T
PEAK
T
0
P
PEAK
P
0
T
PEAK
T
0
1440W 960W 1s
>25s
1440W 480W 0.1s >0.16s
1440W 0W 1s
>1.3s
1440W 480W 1s
>1.6s
1200W 480W 1s
>
0.75s
1440W 480W 3s
>4.9s
D
uty
C
ycle
T
0
=
T
peak
-
(D
uty
C
ycle
x T
peak
)
0.37
1s
-
(0.37 x 1s)
=
= 1.7s
