Current share board - optional feature – Vicor PFC MicroS Power Factor Corrected AC-DC Switcher User Manual
Page 19
03-000049 rev A
Vicor 800-735-6200 Westcor Division 408-522-5280 Applications Engineering 800-927-9474 Pg. 19
PFC MicroS Design Guide
"
Current sharing" also known as Load
Sharing, is the ability to divide the out-
put current evenly across all active
power supplies. This greatly reduces
stresses on each power supply and
allows them to run cooler, resulting in
higher reliability. Standard "current
sharing" techniques typically utilize
shunt resistors or Hall Effect devices to
measure the current from each power
supply. Power shunt resistors continual-
ly dissipate power and require cooling
especially when dealing with high output
currents of >100Amps. Hall Effect
devices measure magnetic fields generat-
ed by current flowing through a conduc-
tor and, although they dissipate no
power, they tend to be large and expen-
sive.
First developed by Westcor Engineering
for paralleling MegaPAC supplies, the
Box-to-Box Current Share Board or CSB
allows two or more Vicor power supplies
to current share by utilizing the inherent
voltage drop produced in the negative
output return cable. This eliminates the
need for additional shunt resistors or
expensive Hall Effect devices and pro-
vides a simple 5 wire connection method
to achieve a +/-1mV accuracy between
the Negative Output power rails. This
accuracy translates to a 1% current shar-
ing if there is a total of 100mV conduc-
tional voltage drop in the negative return
path.
Constructed as a current source to drive
the Trim pin of a Vicor module, the
design uses an accurate comparator cir-
cuit to monitor the power returns. In
addition, the circuit is unidirectional and
can only trim an output voltage up. The
benefit is that only the supply that is sup-
porting less current is adjusted up. This
action balances the currents to the load
by matching the output voltages of the
supplies. In the case of one supply fail-
ing, the circuit will attempt to trim the
failed supply only. This will leave the
remaining functional supply alone to
provide power to the load at its nominal
voltage. Thus the circuit also offers sim-
ple redundancy. In addition, because
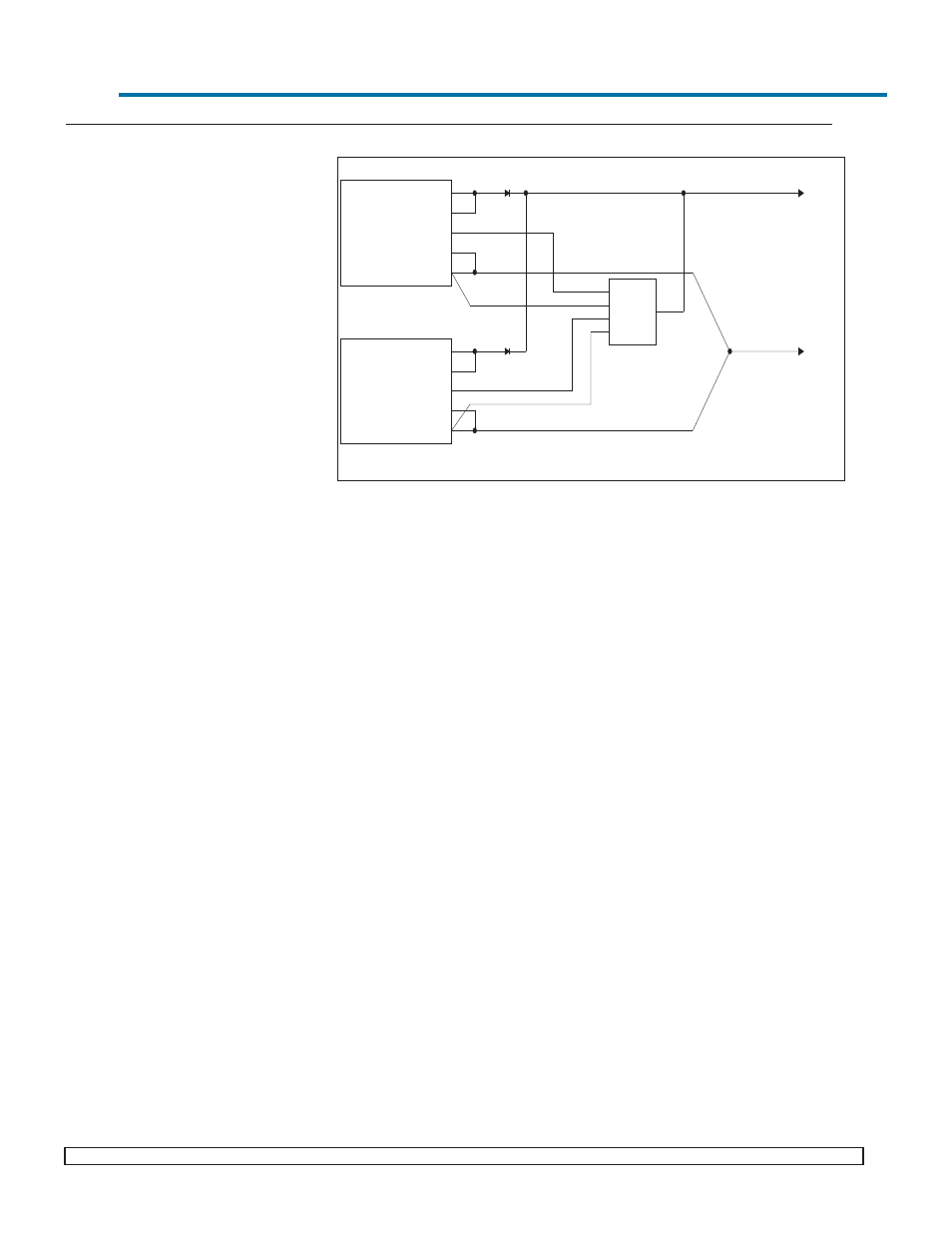
Figure 1. CSB Interconnect Example
Supply # 1
5V @ 120A
+OUT
+S
-OUT
-S
TRIM
Supply # 2
5V@120A
+OUT
+S
-OUT
-S
TRIM
T1
-V1
T2
-V2
Power
+VOUT
-VOUT
D*
D*
CSB02
Black
White
Brown
Yellow
Red
CSB functions as a current source, the Trim outputs (T1 and T2) of the CSB can be
placed in parallel to create a summing node. This allows current sharing between
more than two supplies by paralleling the T2 output of one CSB circuit with the T1
output of the next CSB.
Please note: The CSB is not intended for use in Hotswap Applications.
Requirements:
1. For proper operation, the power supplies being paralleled should be enabled at the
same time.
2. -Out conductors must be of equal length and wire gauge. Separate -Out conduc-
tors must be used from each supply to the load, or the use of a "Y" connection to a
common point must be used as shown in figure 1. Each leg of the "Y" must have a
minimum of a few millivolts of drop in order for proper operation. 50mV to 100mV
of drop will provide from 5% to 1% accuracy.
3. -V1 and -V2 for all Box-to-Box circuits must be connected directly at the nega-
tive output power studs or terminals to achieve accurate current sharing.
4. D* can be added if redundancy is needed. If redundancy is not required, D* can
be replaced with direct wire connections.
5. When using D*, the Power input should be connected on the cathode side of the
paralleling diodes as shown above.
6. Terminate Sense Leads either locally or remotely as shown in figure 1.
7. For paralleling more than 2 supplies consult factory for assistance.
CURRENT SHARE BOARD - Optional Feature
